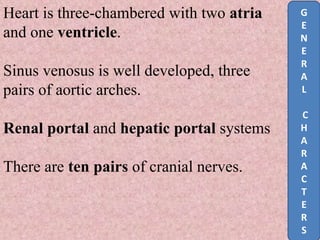
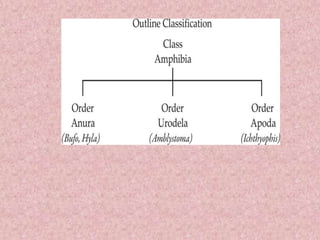
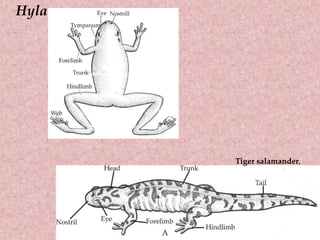
Amphibians like frogs, toads, newts, and salamanders are characterized as having two pairs of limbs, lungs for aerial respiration in addition to aquatic respiration through their skin, a three-chambered heart, and indirect development where young possess gills before metamorphosing into adults. They have smooth, glandular skin without scales except in caecilians, and pentadactyl limbs without claws. Amphibians exhibit traits that fall between fully aquatic and terrestrial vertebrates.