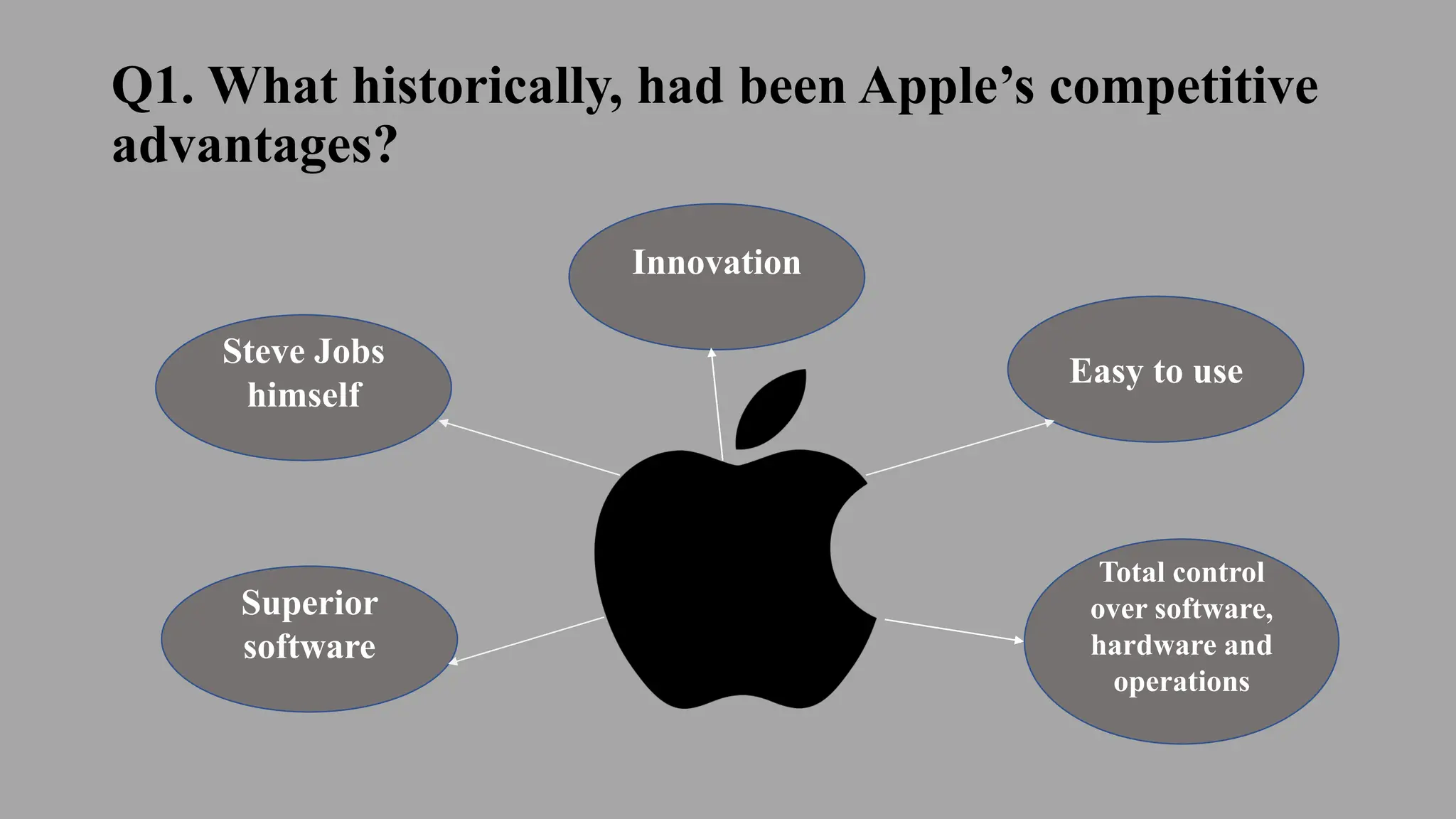
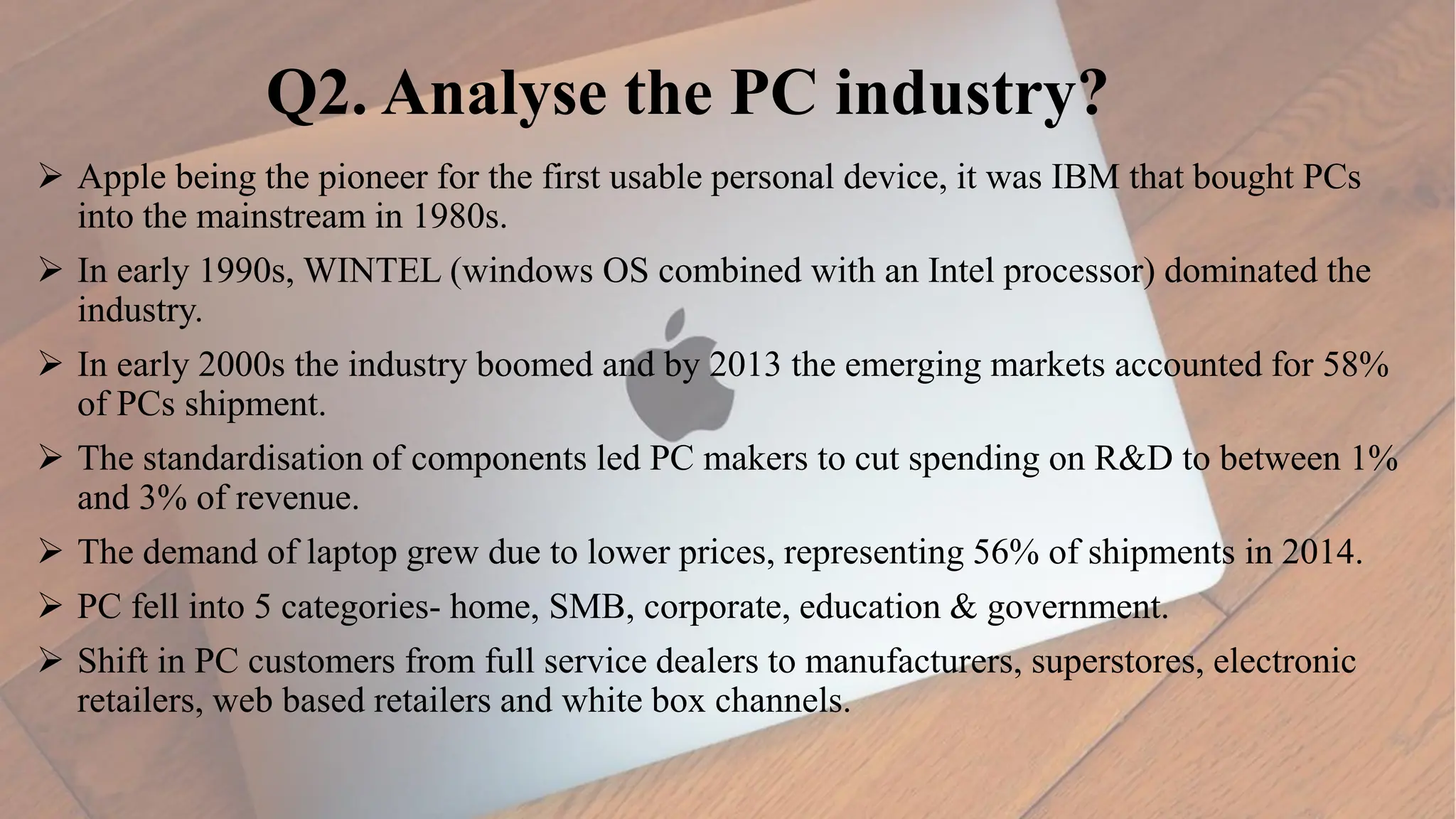
Apple Inc. was established in 1976 and is a multinational technology company headquartered in Cupertino, California. It designs, develops, and sells consumer electronics, computer software, and online services. Some of Apple's major products include the iPhone, iPad, Mac computers, Apple Watch, AirPods, and services like the App Store, Apple Music, and iCloud. The document discusses Apple's history, products, strategies, and competitive position.