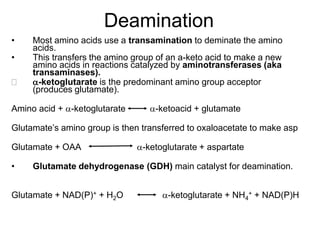
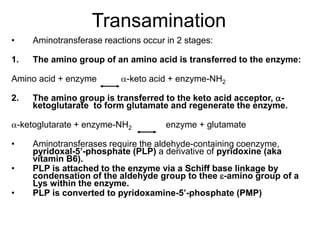
The document outlines the metabolism of amino acids, highlighting their roles as energy metabolites and precursors for various nitrogen-containing compounds. It describes the processes of deamination and transamination, detailing enzyme involvement and the conversion of amino acids to metabolic intermediates. Additional information includes the urea cycle and the metabolic breakdown of amino acids into TCA cycle intermediates for energy production or gluconeogenesis.






































![Regulation of the urea cycle
• Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I is allosterically
activated by N-acetylglutamate.
• N-acetylglutamate is synthesized from glutamate and acetyl-
CoA by N-acetylglutamate synthase, it is hydrolyzed by a
specific hydrolase.
• Rate of urea production is dependent on [N-acetylglutamate].
• When aa breakdown rates increase, excess nitrogen must be
excreted. This results in increase in Glu through
transamination reactions.
• Excess Glu causes an increase in N-acetylglutamate which
stimulates CPS I causing increases in urea cycle.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aminoacidsmetabolism-240425122727-8e4ed34a/85/Amino-acids-metabolism-ppt-41-320.jpg)
