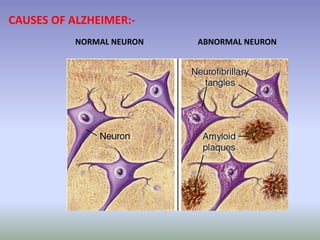
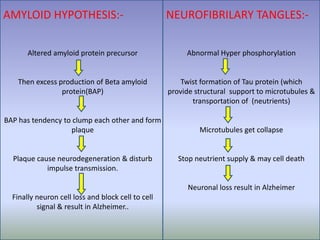
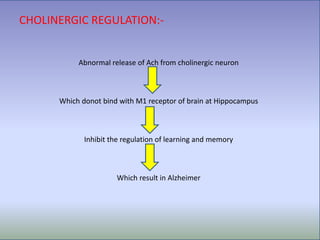
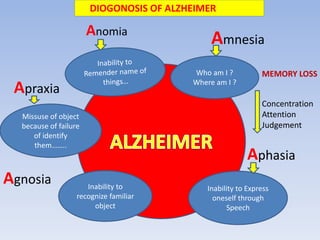
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive brain disorder that destroys memory and mental functions. It is the most common cause of dementia. The disease is caused by the buildup of beta amyloid plaques and tau protein tangles in the brain, which interfere with cell-to-cell communication and lead to the loss of connections between neurons. This neuronal loss results in the symptoms of Alzheimer's such as memory loss, problems with thinking and reasoning, and behavioral changes. Current drug treatments for Alzheimer's aim to boost acetylcholine levels or block NMDA receptors to help mitigate cognitive decline.