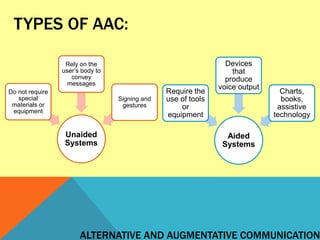
Alternative and augmentative communication (AAC) refers to methods of communication other than speech that can help people who have difficulty communicating verbally. AAC benefits a wide range of individuals, from beginning communicators to more advanced users who generate their own messages. There are two main types of AAC: unaided systems that do not require equipment and rely on the body, such as signing and gestures, and aided systems that use tools or devices to produce messages, including communication boards, assistive technology, and voice output devices. AAC can benefit anyone with a disability affecting communication, as well as their family members. Determining eligibility for AAC involves considering an individual's cognitive and physical abilities, important vocabulary, motivation to use AAC