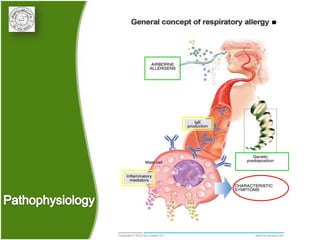
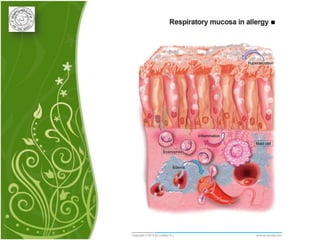
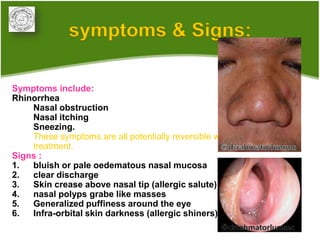
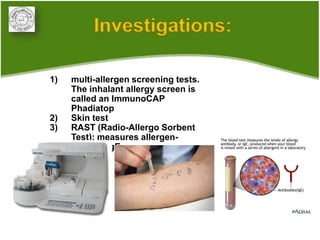
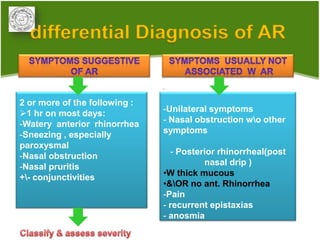
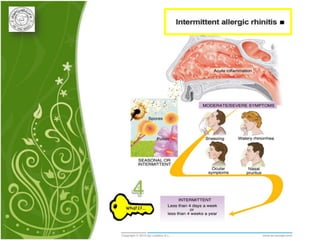
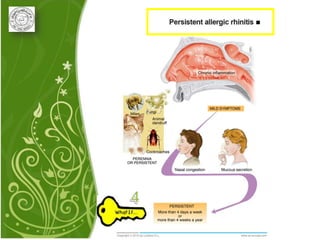
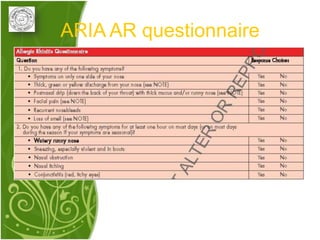
1. Allergic rhinitis (AR) is a major chronic respiratory disease affecting 10-20% of the population globally. It is characterized by symptoms of sneezing, rhinorrhea, nasal obstruction and pruritis induced by an IgE-mediated response to allergens.
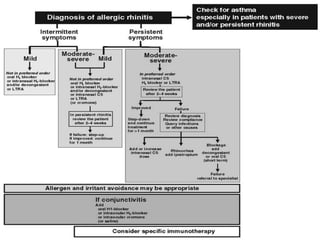
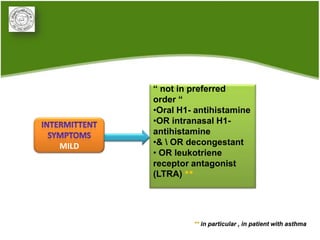
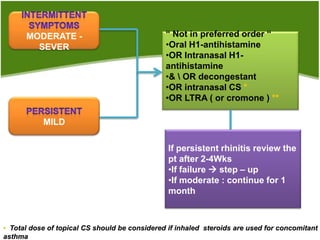
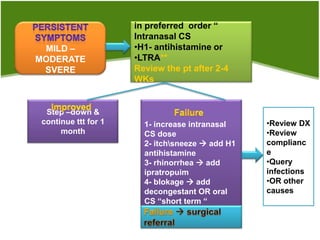
2. Management of AR involves environmental control measures, pharmacotherapy including oral or intranasal antihistamines, intranasal corticosteroids, leukotriene receptor antagonists and immunotherapy. The treatment approach is stepped up based on disease severity.
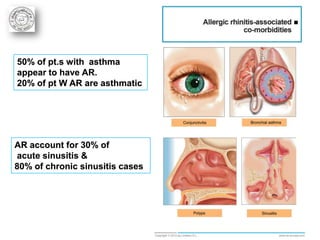
3. AR is associated with comorbidities like asthma, conjunctivitis and sinusitis. It is important to evaluate patients with persistent AR for asthma