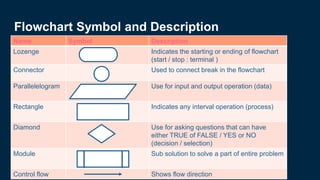
This document discusses algorithms and sorting. It begins by defining an algorithm as a precise set of instructions for solving a problem or completing a task. Algorithms can be expressed as flowcharts or pseudocode. Sorting is introduced as arranging elements in an array in a relevant order like ascending or descending. Selection sort is provided as an example sorting algorithm. It works by iterating through the array, finding the minimum value, and swapping it into the sorted position. The example shows selection sort sorting an array of numbers in ascending order over three iterations.











![Sorting
● Sorting means arranging the elements of an array so that they are placed in
some relevant order which may be either ascending or descending.
● Can be used as a first step for searching the data.
● That is, if A is an array, then the elements of A are arranged in a sorted order
(ascending order) in such a way that A[0] < A[1] < A[2] < … < A[N].
● The practical considerations for different sorting techniques would be:
○ Number of sort key comparisons that will be performed.
○ Number of times the records in the list will be moved.
○ Best, average and worst case performance.
○ Stability of the sorting algorithm where stability means that equivalent
elements or records retain their relative positions even after sorting is](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithmbyamt-230626070016-fc9d2776/85/Algorithm-By-AMT-pptx-13-320.jpg)





![Selection Sort
● Iteration-1
The array is scanned starting from the first to the last element and the element that has the
smallest value is selected. The smallest value is 1 at location 3. The address of element that
has the smallest value is noted and the selected value is interchanged with the first element
i.e.
A[1] and A[3] are swapped
4 19 1 3
1 19 4 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithmbyamt-230626070016-fc9d2776/85/Algorithm-By-AMT-pptx-19-320.jpg)
![Selection Sort
● Iteration-2
The array is scanned starting from the second to the last element and the element that has
the smallest value is selected. The smallest value is 3 at location 4. The address of element
that has the smallest value is noted. The selected value is interchanged with the second
element i.e.
A[2] and A[4] are swapped
1 19 4 3
1 3 4 19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithmbyamt-230626070016-fc9d2776/85/Algorithm-By-AMT-pptx-20-320.jpg)
![Selection Sort
● Iteration-3
The array is scanned starting from the third to the last element and the element that has the
smallest value is selected. The smallest value is 4 at location 3. The address of element that
has the smallest value is noted. The selected value is interchanged with the third element
i.e.
A[3] and A[3] are swapped
1 3 4 19
1 3 4 19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithmbyamt-230626070016-fc9d2776/85/Algorithm-By-AMT-pptx-21-320.jpg)


