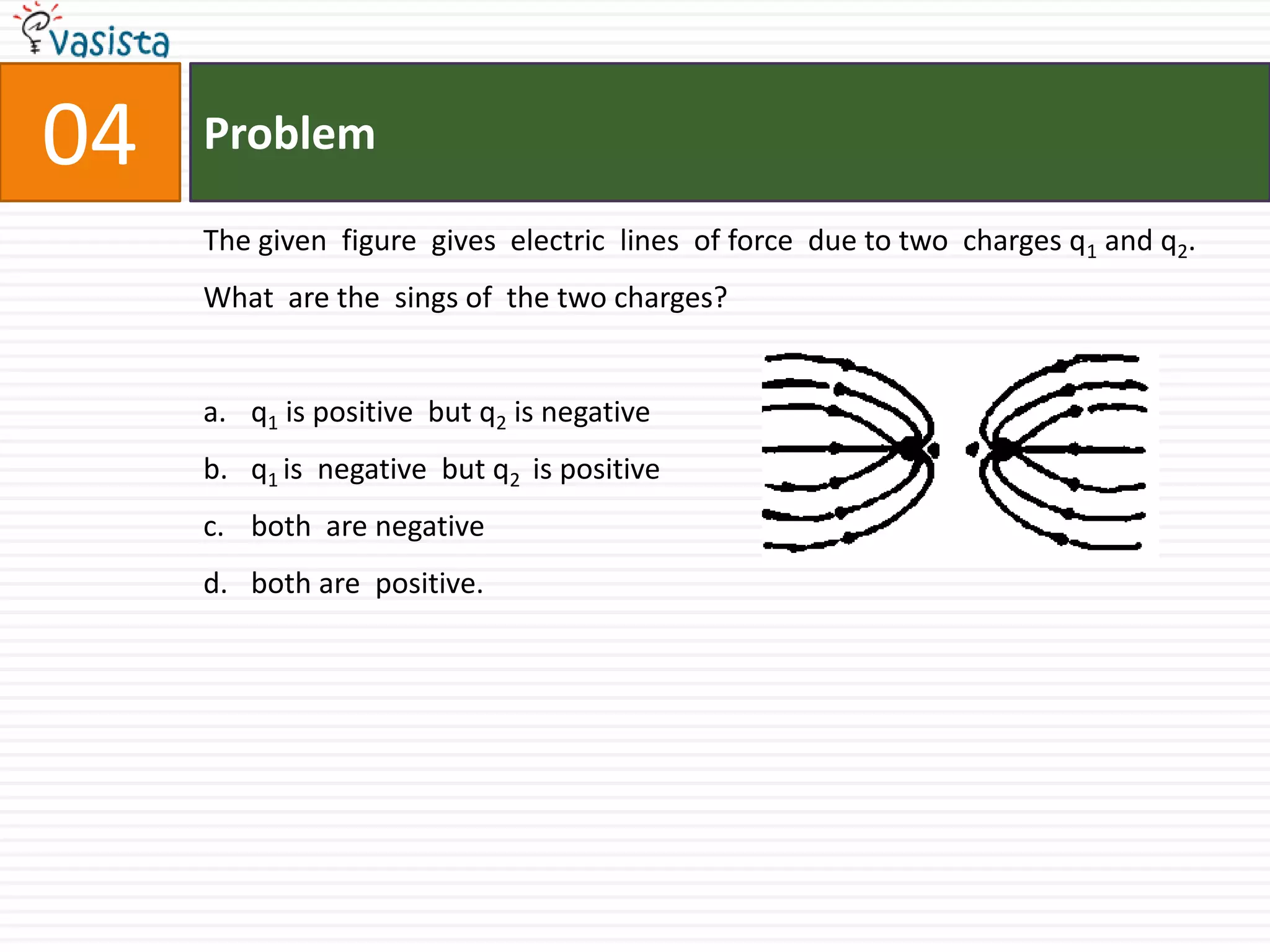
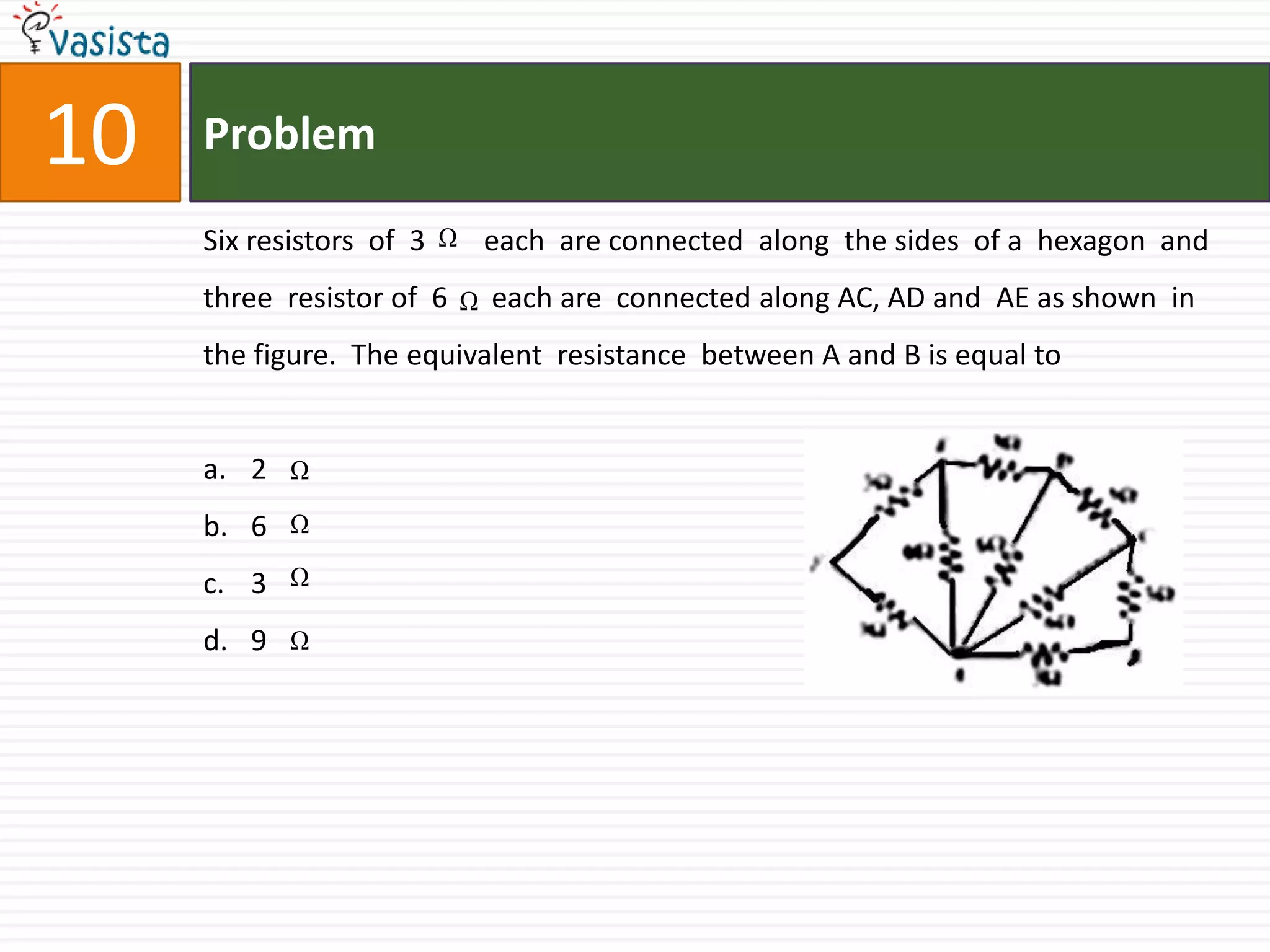
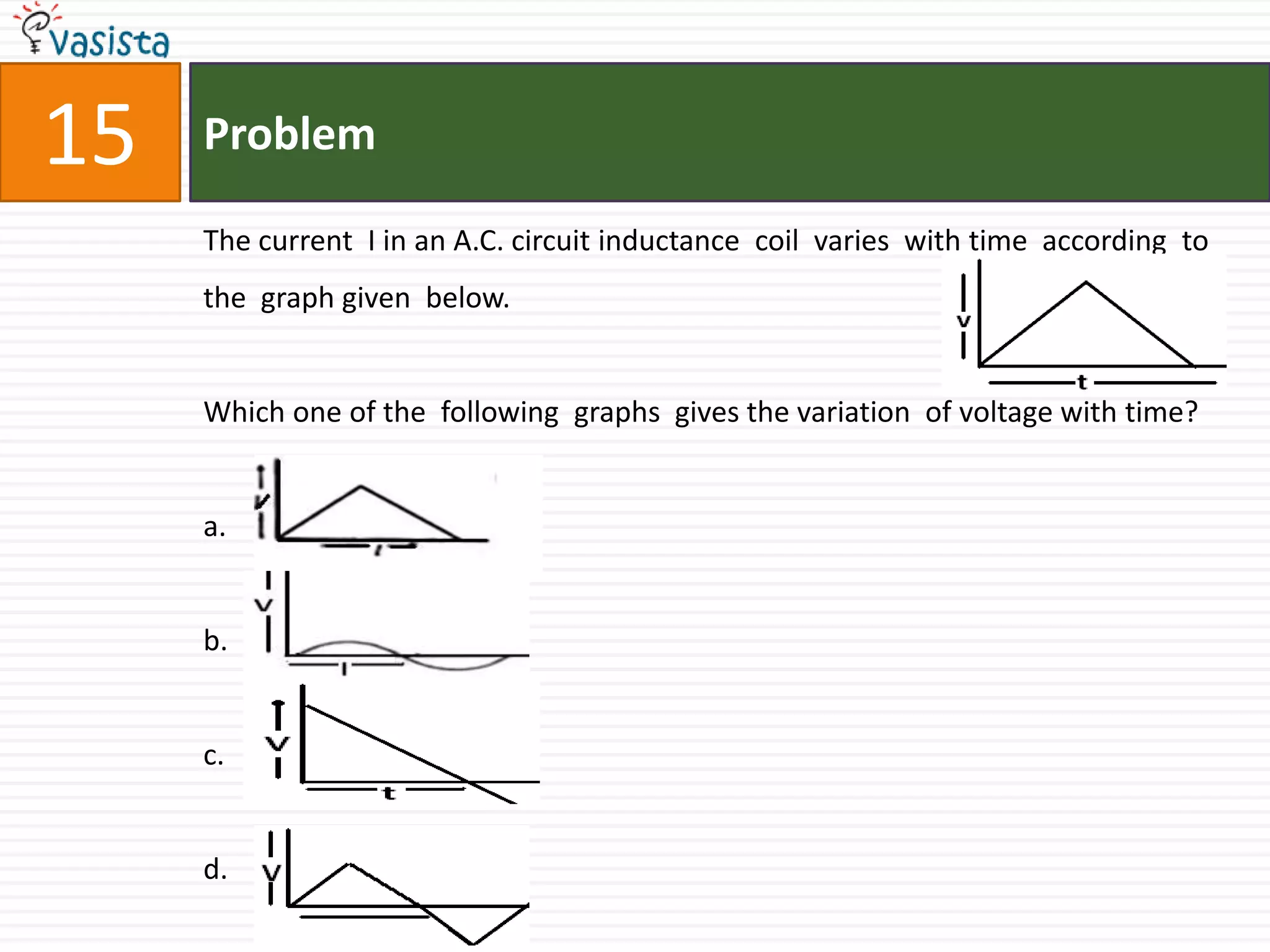
This document contains an unsolved physics exam from 1994 consisting of 44 multiple choice questions testing concepts in mechanics, electricity and magnetism, waves, optics and modern physics. The questions cover topics such as electric potential, work done by electric fields, simple harmonic motion, electromagnetic waves, reflection and refraction of light, quantum physics, and more.