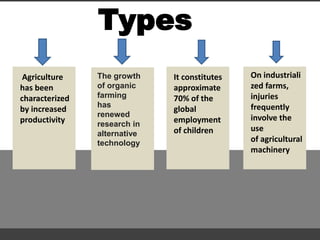
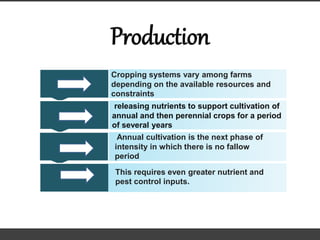
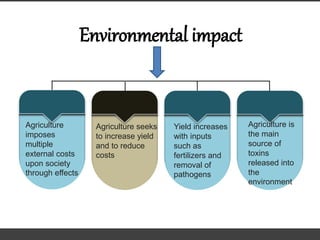
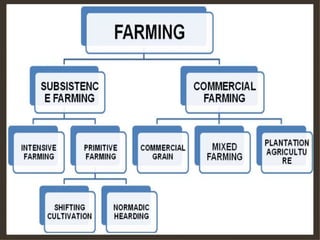
Agriculture involves the cultivation of crops and rearing of livestock. There are different types of agriculture like subsistence farming which satisfies local needs and shifting cultivation which clears small areas of forest land. Agriculture production varies depending on available resources, with annual cultivation involving no fallow periods requiring greater nutrient and pest control inputs. Agriculture impacts the environment through effects like increased yields from fertilizer use but also being a main source of environmental toxins.