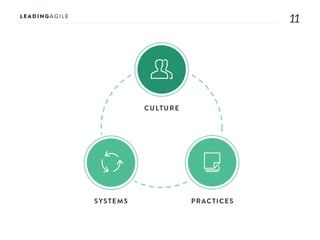
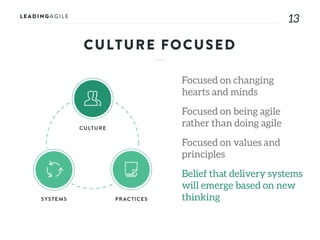
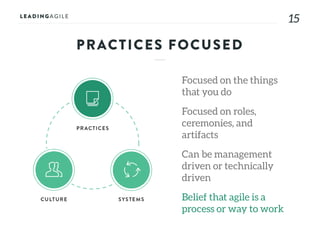
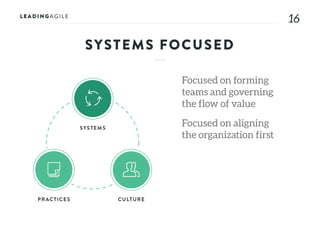
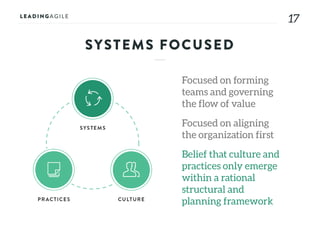
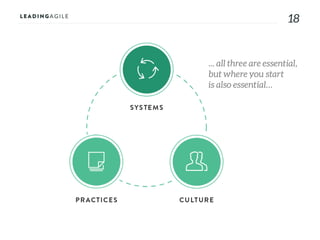
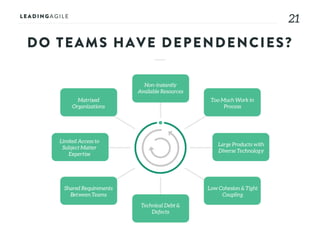
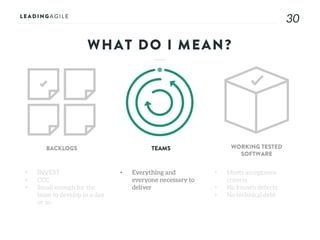
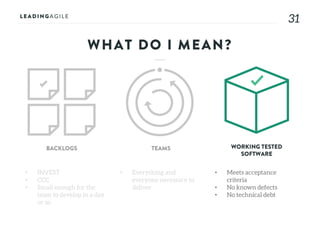
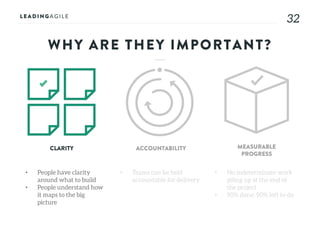
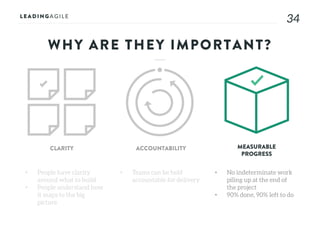
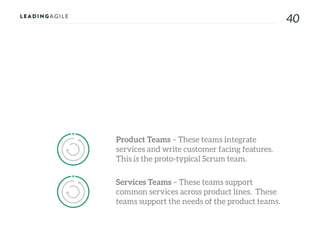
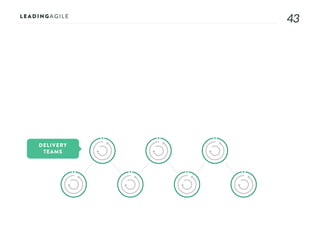
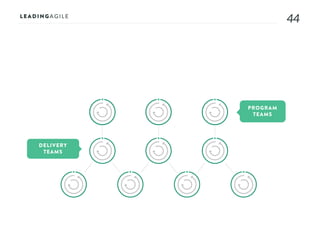
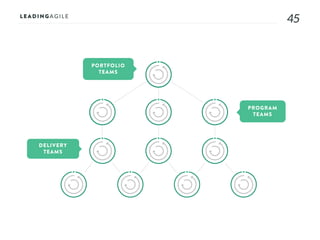
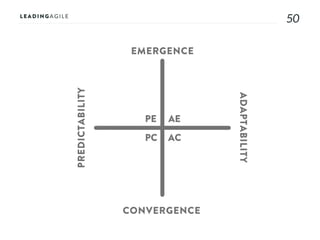
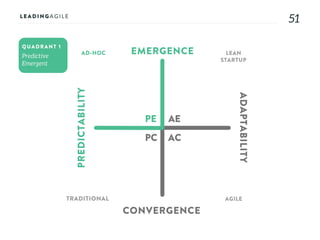
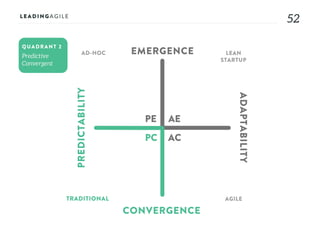
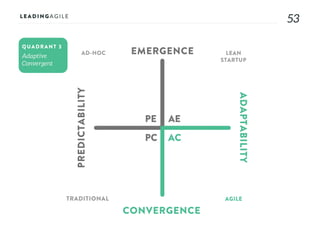
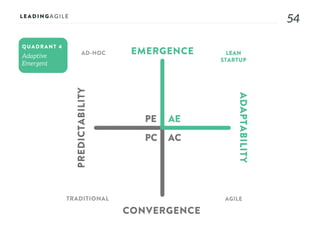
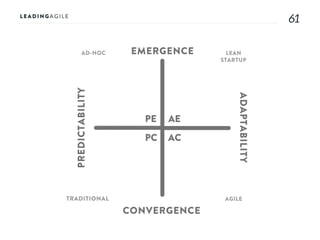
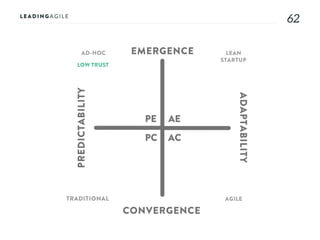
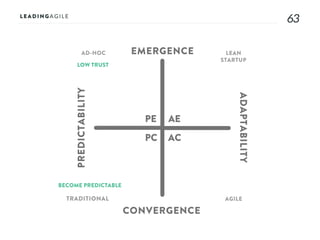
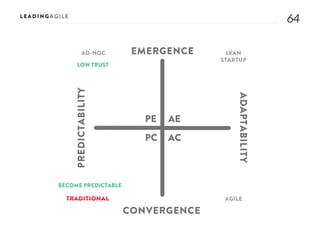
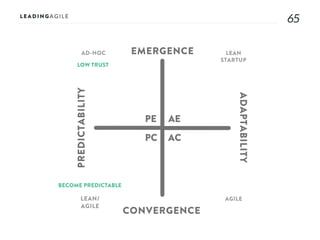
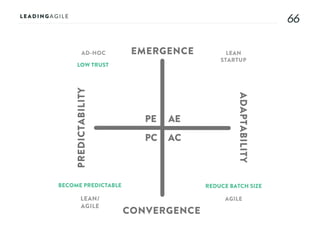
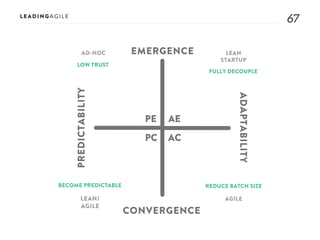
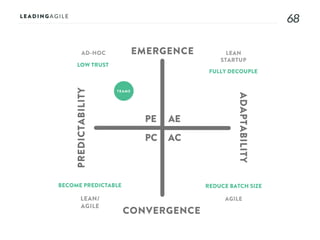
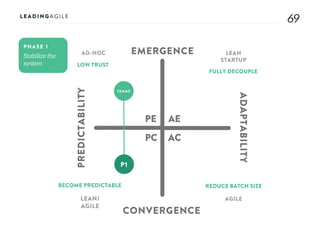
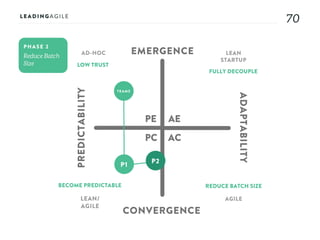
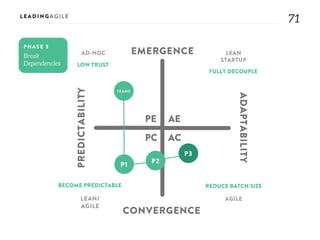
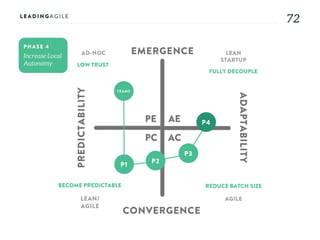
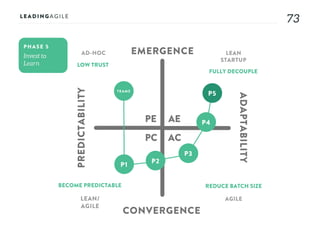
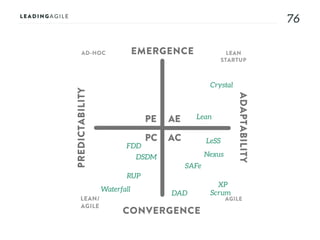
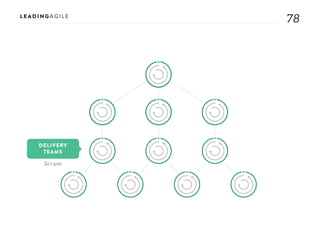
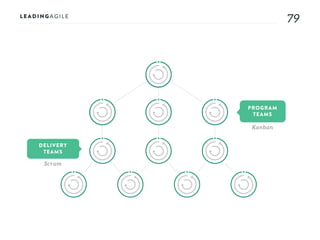
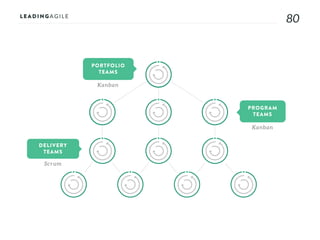
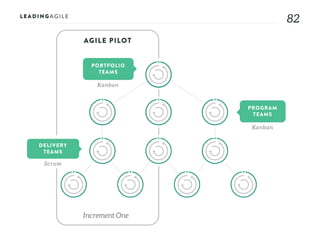
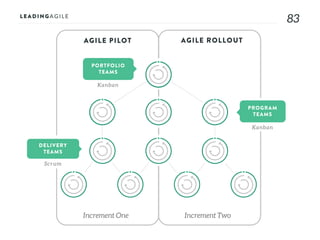
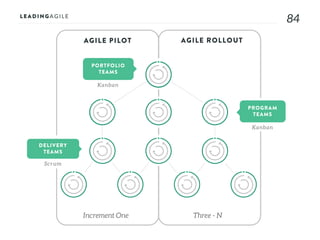
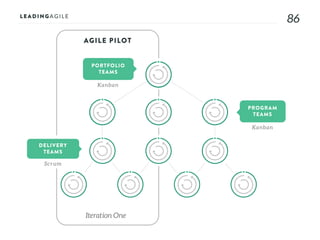
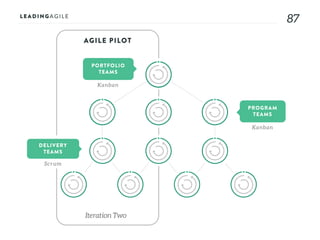
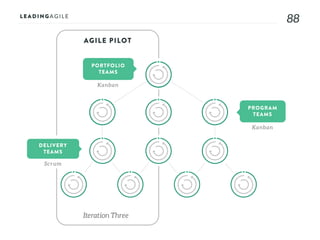
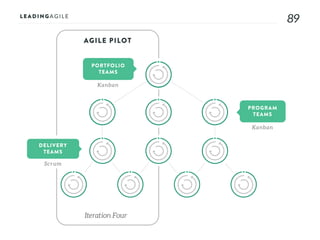
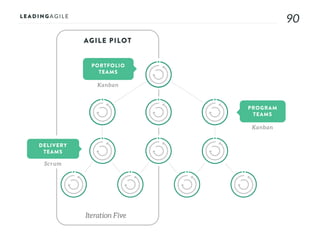
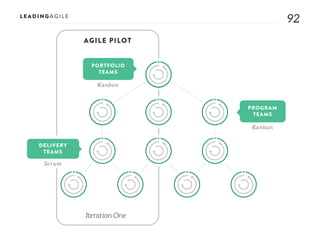
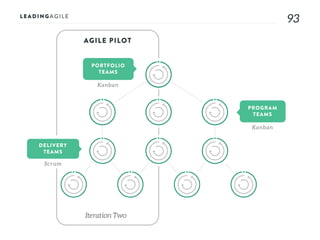
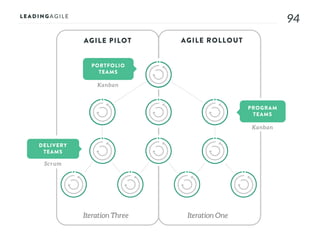
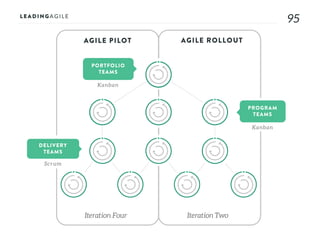
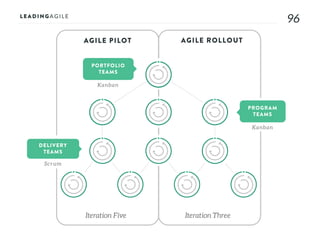
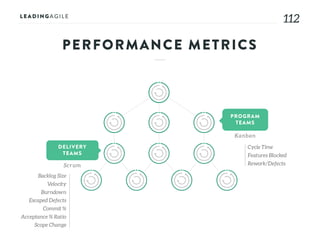
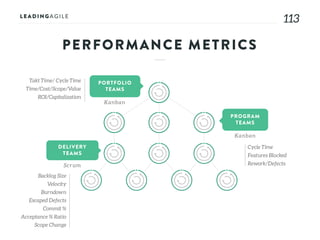
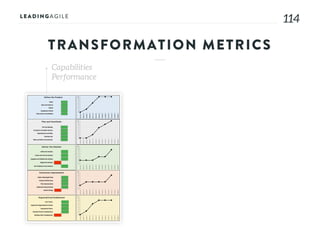
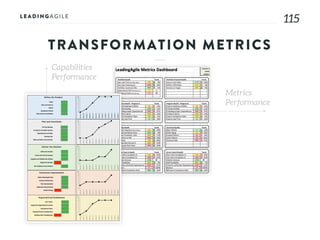
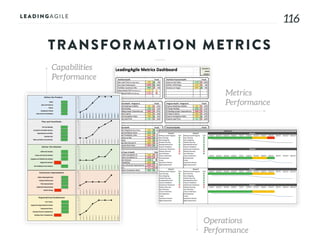
The document outlines key aspects of agile transformation, focusing on the importance of deciding the scope, approach, and how to manage change and measure progress. It emphasizes goals such as improving predictability, accelerating time to market, enhancing innovation, and maintaining product quality. Additionally, it addresses the need for organization structure, team formation, and ongoing assessment to ensure the successful adoption of agile practices.