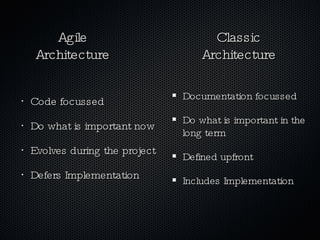
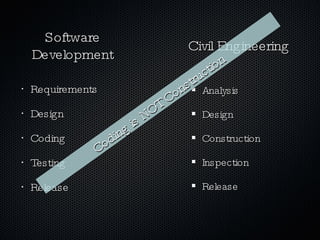
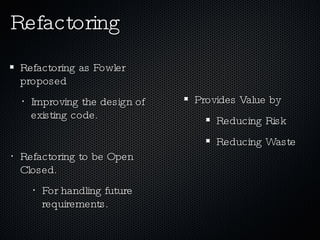
Agile software architecture aims to deliver value fast by evolving the architecture during the project based on what is important now, rather than defining it upfront. This reduces risk and waste by allowing decisions to be made based on actual knowledge gained during development. The architecture should be the simplest solution to support current functionality and evolve economically through changes without making the software worse. Principles like separation of concerns, refactoring, and tests that drive design help enable evolving the architecture in a controlled way.