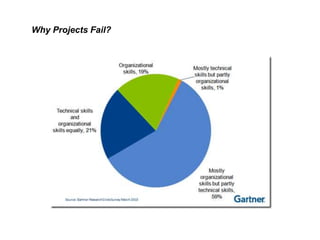
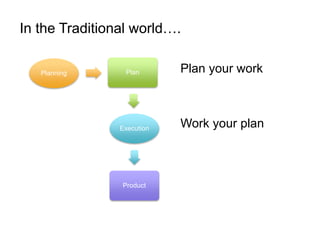
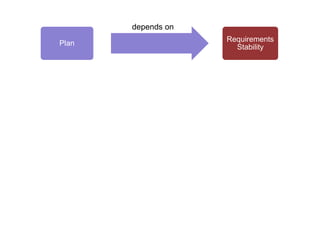
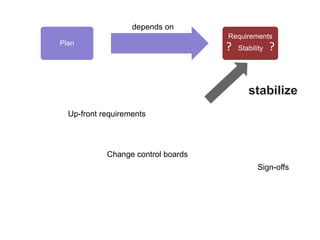
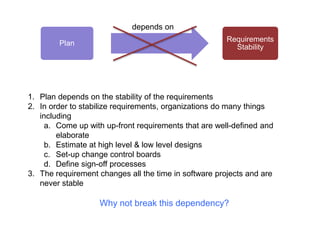
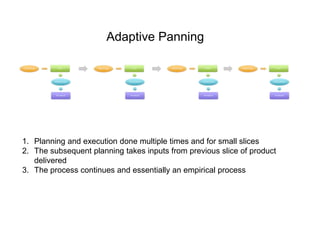
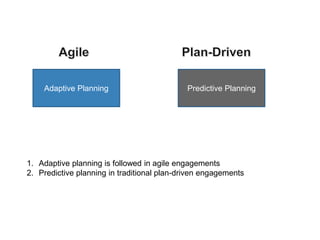
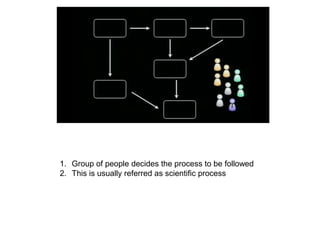
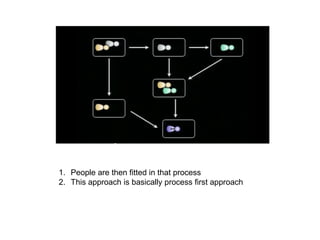
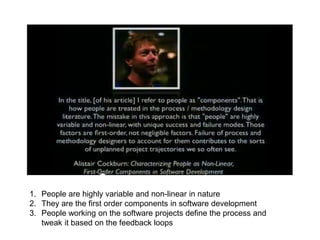
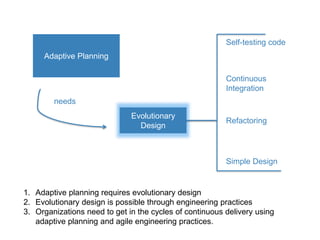
Adaptive planning involves planning and execution occurring multiple times for small slices of the product. Each subsequent planning takes input from the previously delivered slice, making it an empirical process. This allows the breaking of dependency between plans and requirement stability seen in predictive planning. Adaptive planning puts people first by having them define and tweak the process based on feedback, making it evolutionary, whereas predictive planning is process first.