Embed presentation
Download to read offline






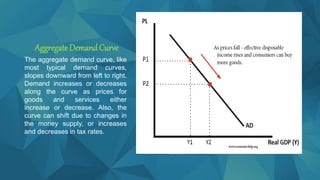


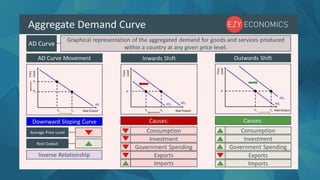

Aggregate demand refers to the total demand for final goods and services in an economy at a given overall price level and time. It is represented by the sum of consumption (C), investment (I), government spending (G), and net exports (X-M). The aggregate demand curve slopes downward, as demand increases when prices decrease. Factors that can cause shifts in aggregate demand include changes in the money supply, tax rates, government policies, consumer and business confidence, and economic conditions in other countries.










