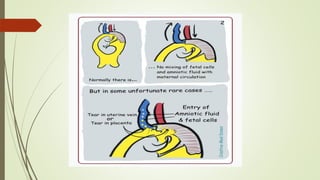
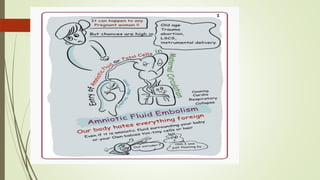
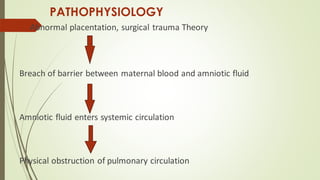
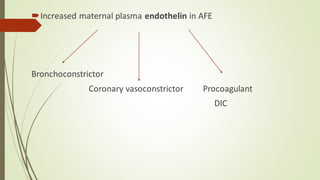
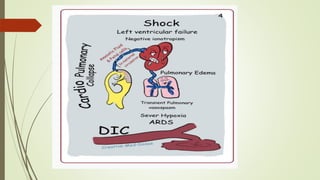
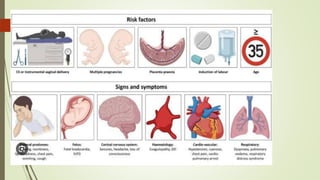
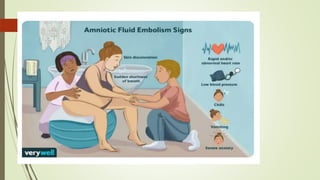
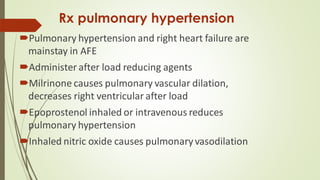
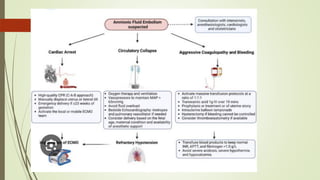
Amniotic fluid embolism (AFE) is a critical obstetric emergency and the second leading cause of peripartum maternal death, characterized by sudden respiratory collapse and disseminated intravascular coagulation. It occurs when amniotic fluid enters the maternal bloodstream, with risk factors including maternal age, multiparity, and fetal complications. Management focuses on early recognition, oxygenation, hemodynamic stability, and correcting coagulopathy, with potential interventions including fluid resuscitation, vasopressors, and in severe cases, ECMO.