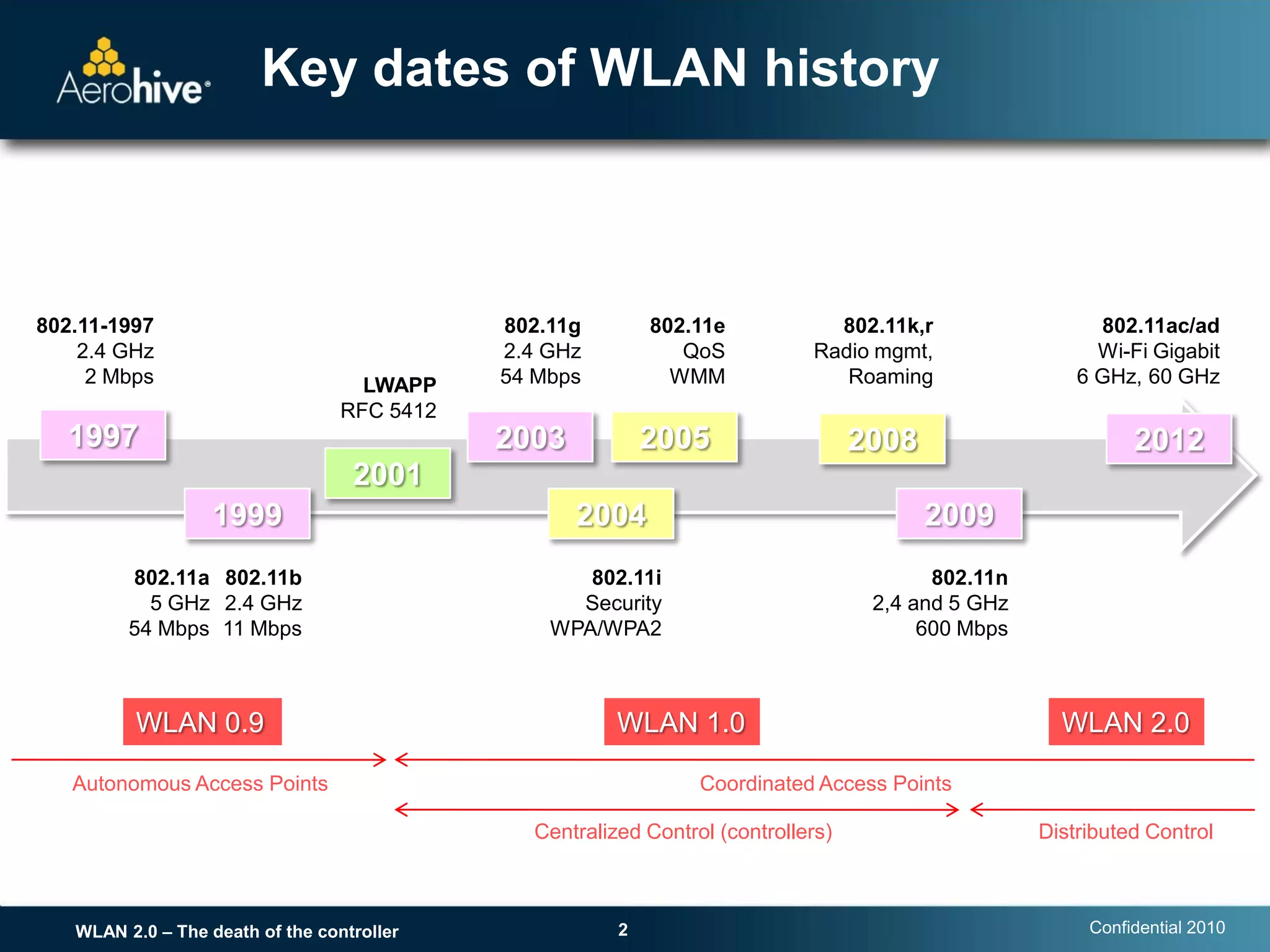
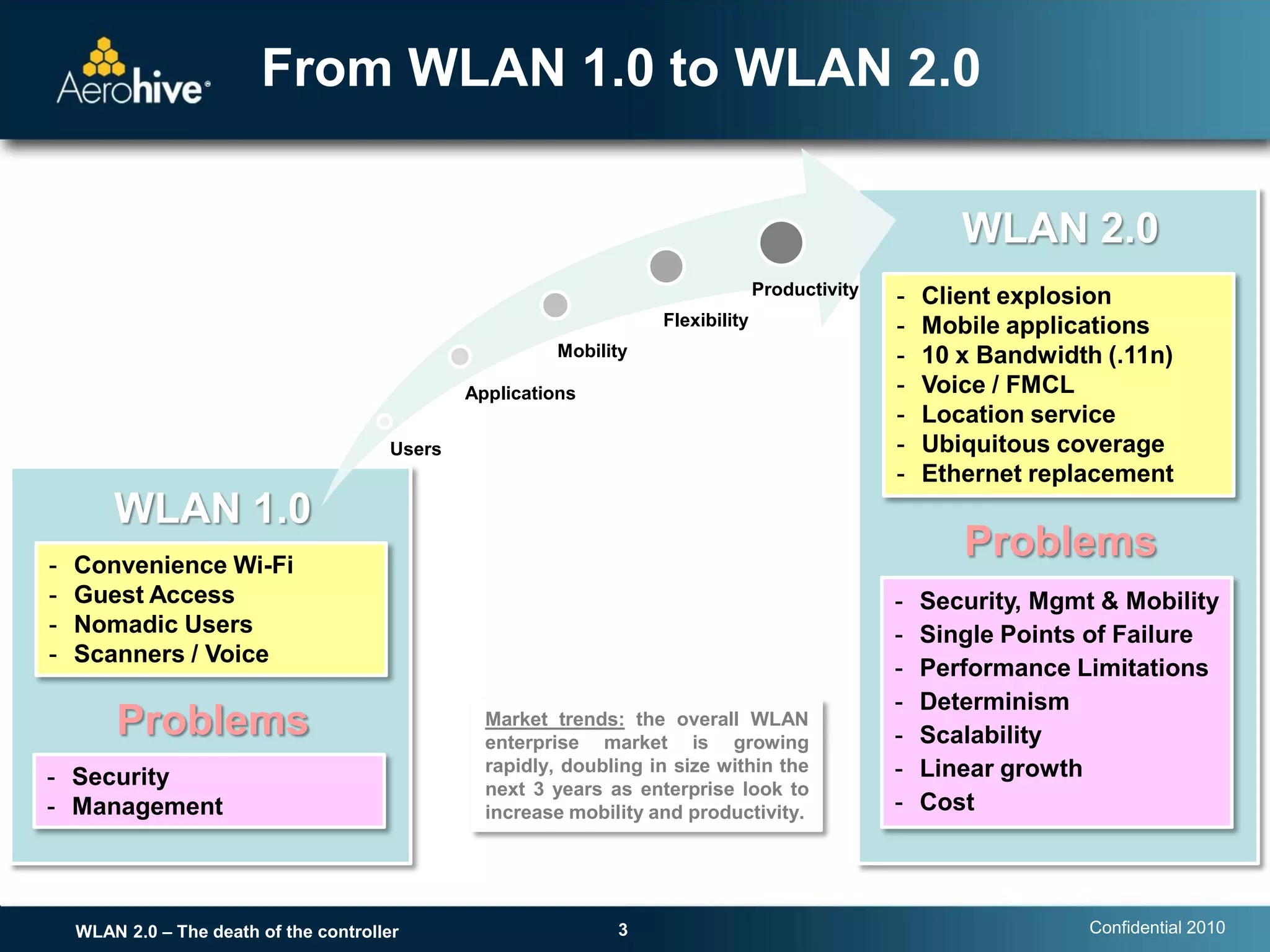
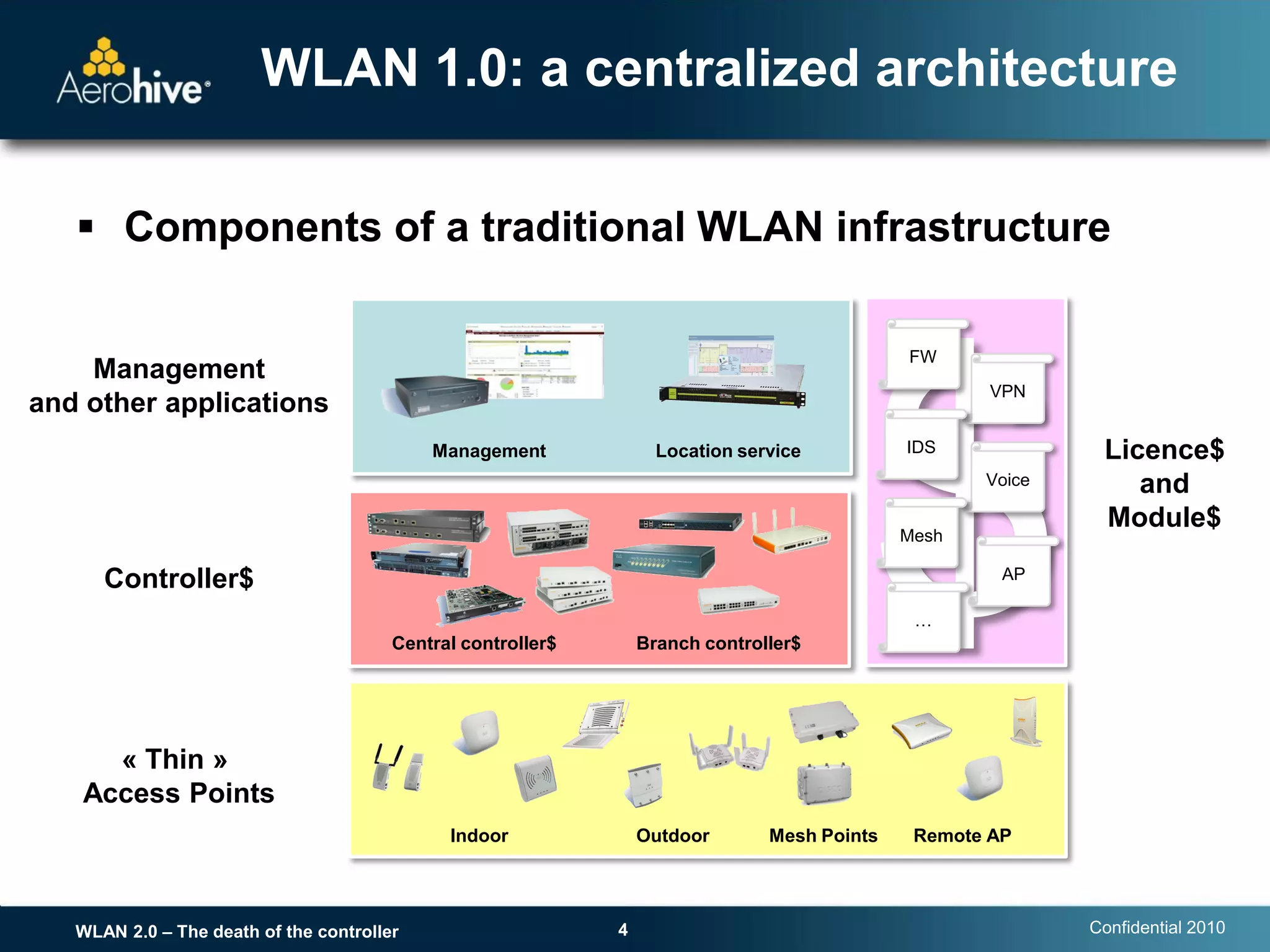
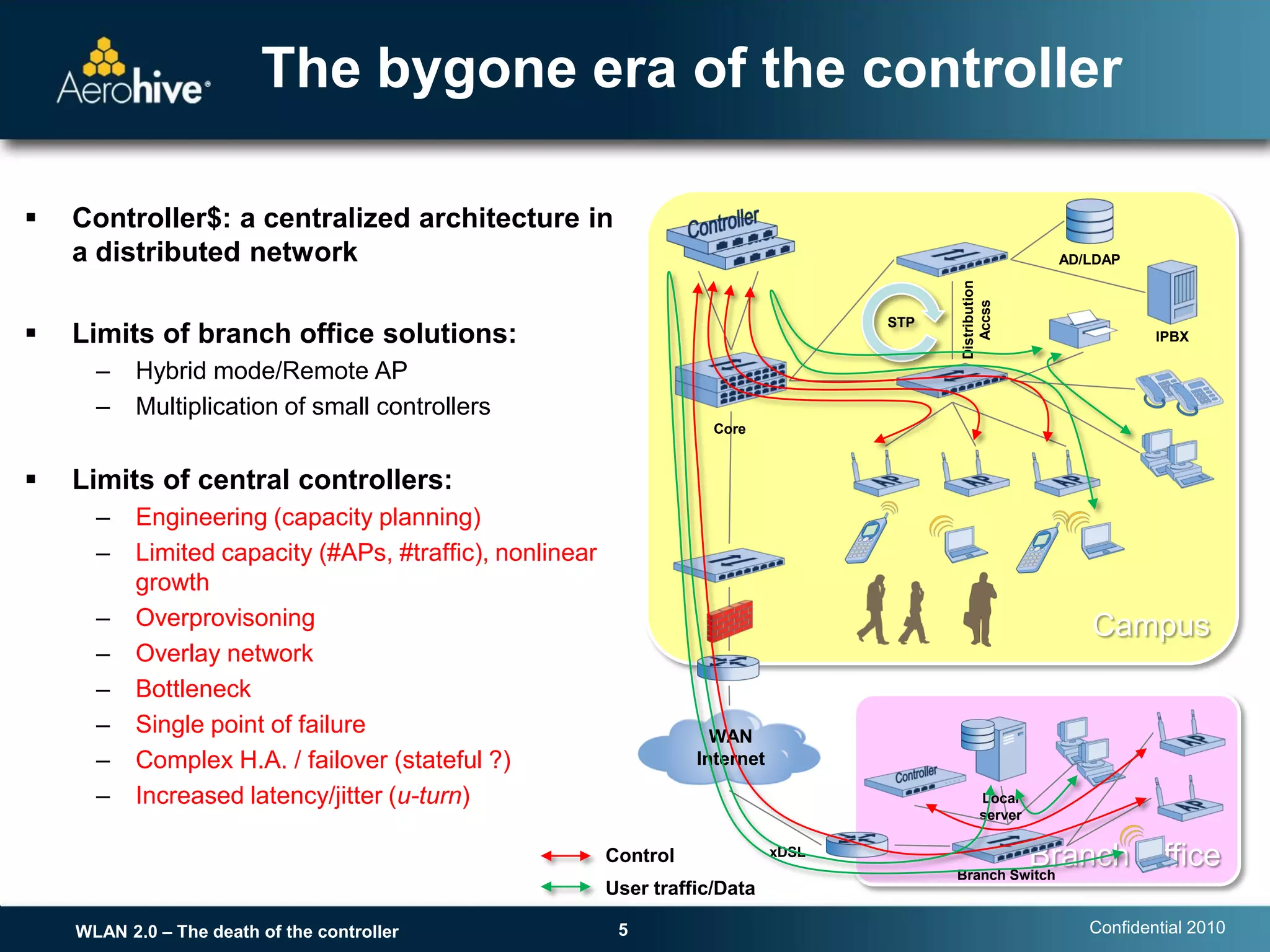
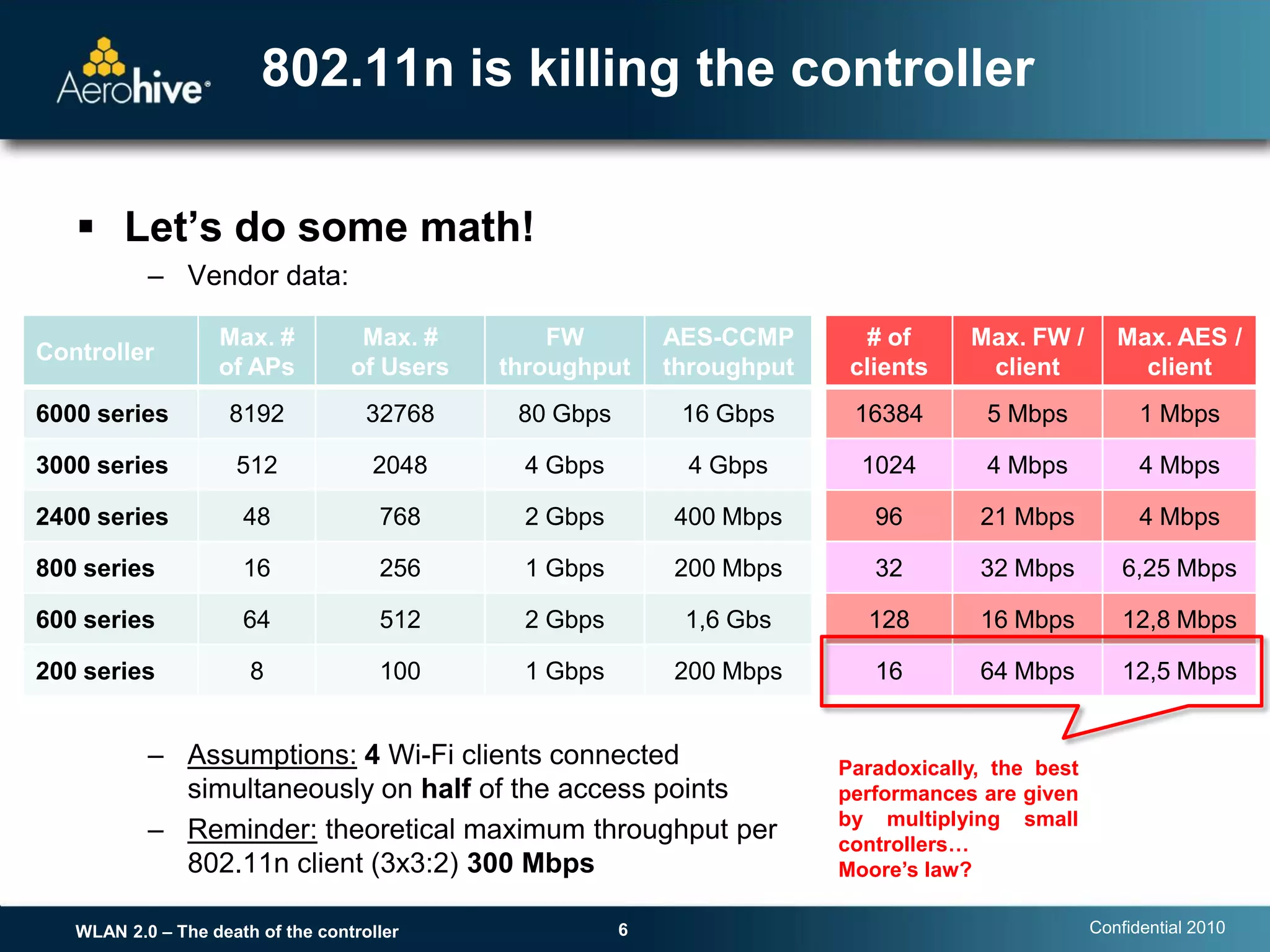
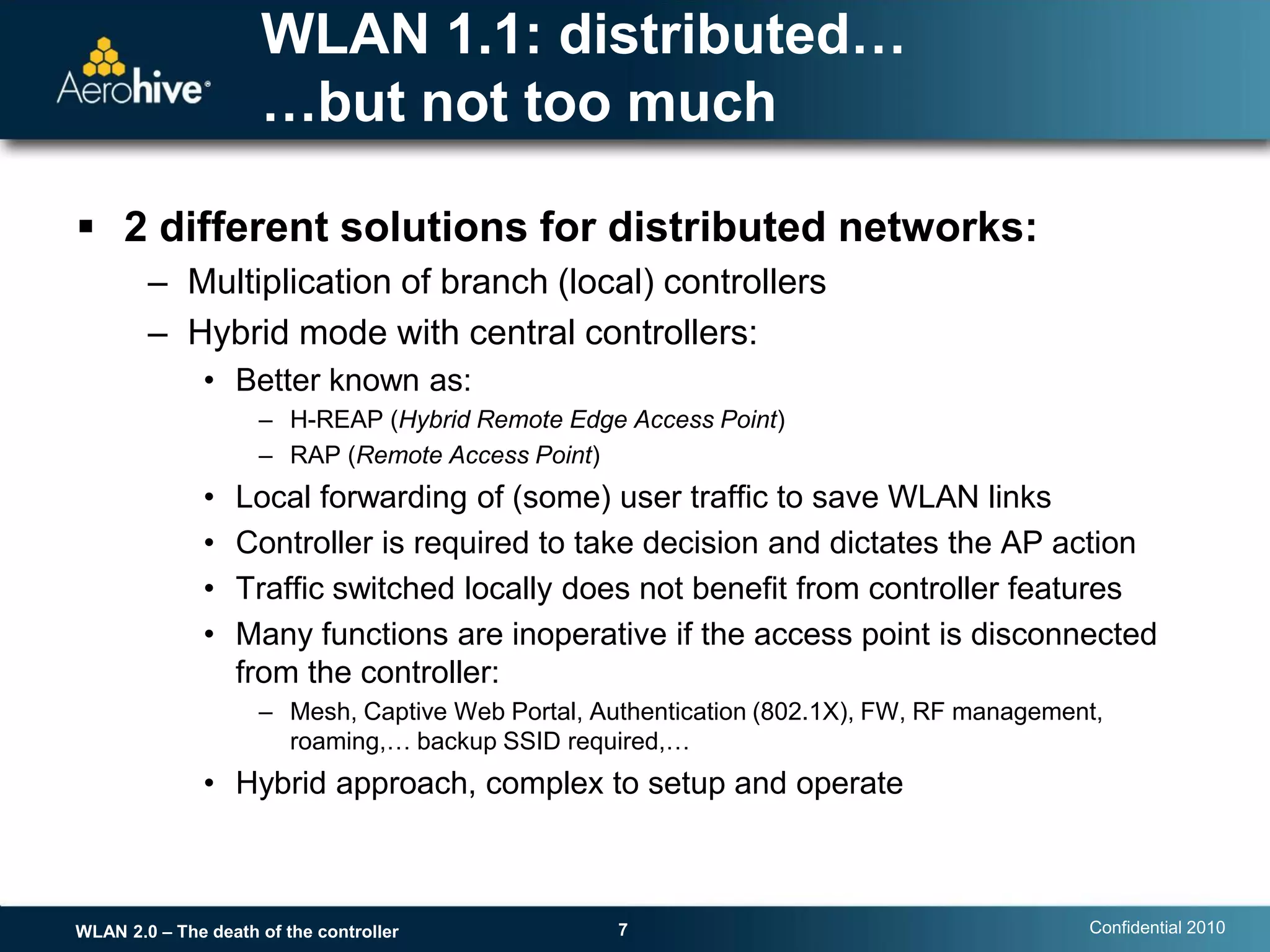
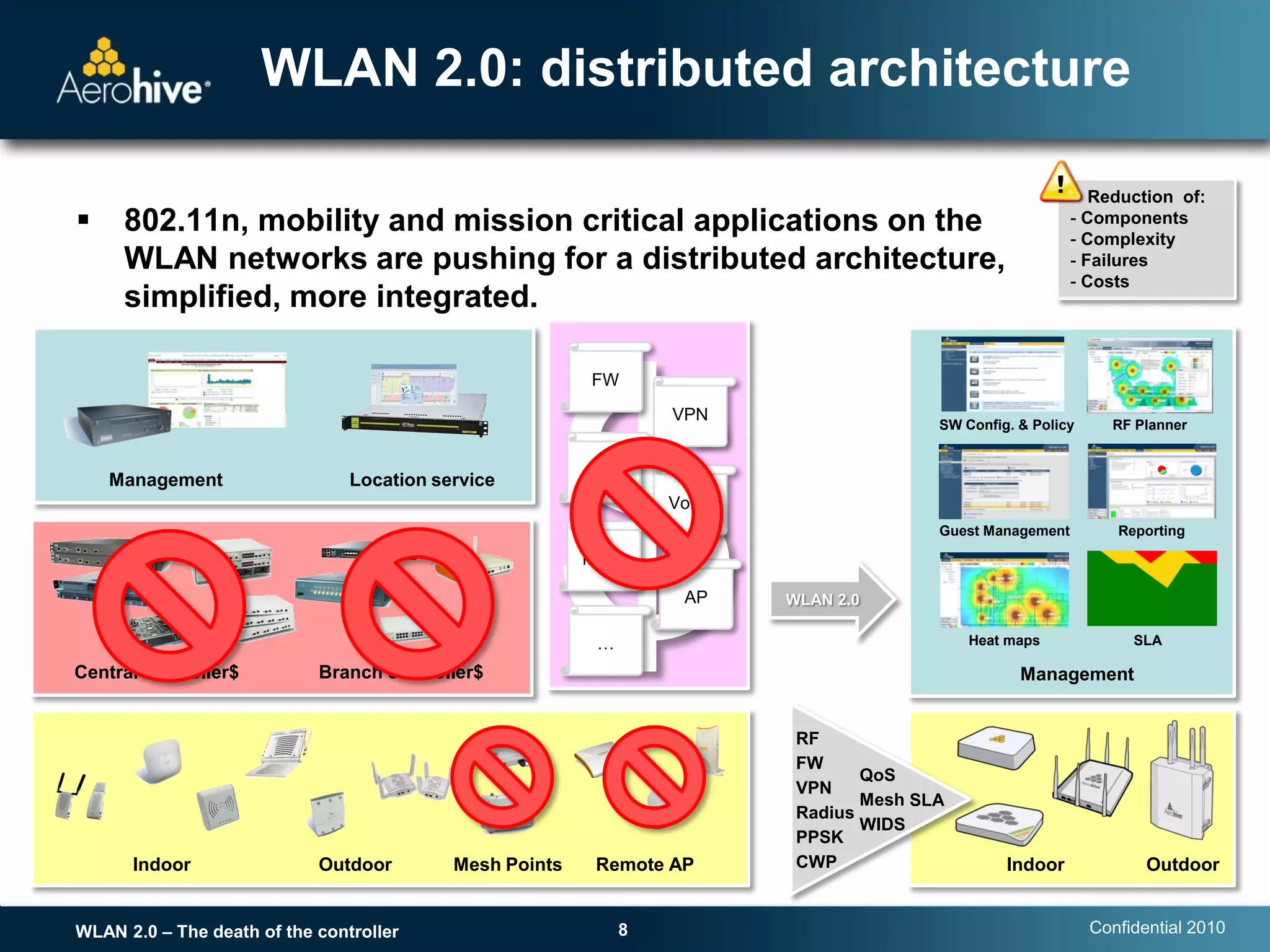
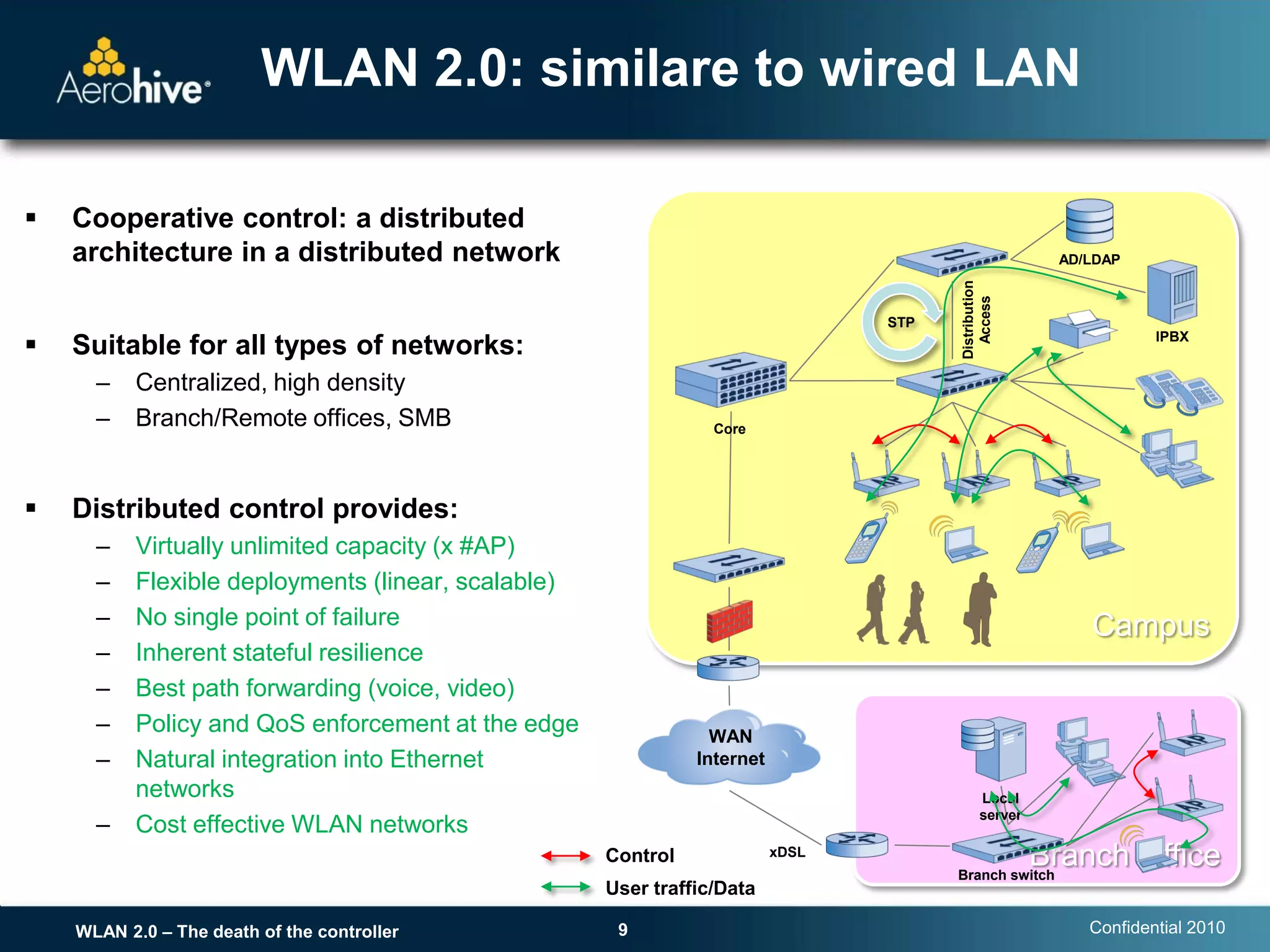
The document discusses the transition from centralized wireless LAN (WLAN) architectures (WLAN 1.0) that rely on controllers to distributed architectures (WLAN 2.0) without controllers. It argues that the rise of high-bandwidth 802.11n networks, increased user mobility, and real-time applications are making centralized control inefficient and a single point of failure. WLAN 2.0 adopts a distributed cooperative control model similar to wired Ethernet with autonomous access points that provide scalability, redundancy and better performance without controllers.