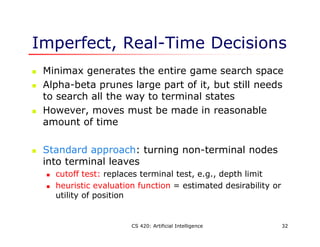
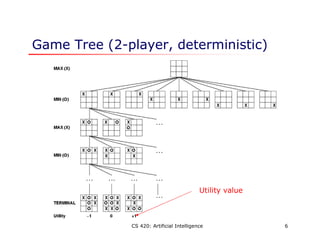
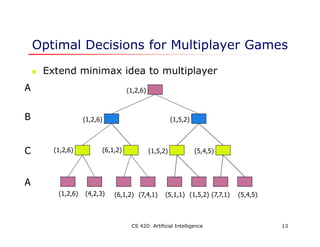
This document discusses adversarial search problems where agents have conflicting goals, such as in games. It introduces the concept of minimax search which finds the optimal strategy for a game by considering all possible moves by both players. The algorithm works by assigning numeric values to terminal states and recursively backing up values through the game tree. Alpha-beta pruning is also described, which improves on minimax by pruning branches that cannot influence the final decision. Evaluation functions are used to estimate the value of non-terminal states when the full search space cannot be explored within time limits.













![CS 420: Artificial Intelligence 16
α-β Pruning Example
[-∞, 3]
[-∞,+∞]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adversarialsearch-210211023315/85/Adversarial-search-16-320.jpg)
![CS 420: Artificial Intelligence 17
α-β Pruning Example
[-∞,+∞]
[-∞, 3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adversarialsearch-210211023315/85/Adversarial-search-17-320.jpg)
![CS 420: Artificial Intelligence 18
α-β Pruning Example
[3, 3]
[3,+∞]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adversarialsearch-210211023315/85/Adversarial-search-18-320.jpg)
![CS 420: Artificial Intelligence 19
α-β Pruning Example
[3, 3]
[3,+∞]
[-∞, 2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adversarialsearch-210211023315/85/Adversarial-search-19-320.jpg)
![CS 420: Artificial Intelligence 20
α-β Pruning Example
[3, 3]
[3, 14]
[-∞, 2] [-∞, 14]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adversarialsearch-210211023315/85/Adversarial-search-20-320.jpg)
![CS 420: Artificial Intelligence 21
α-β Pruning Example
[3, 3]
[3, 5]
[-∞, 2] [-∞, 5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adversarialsearch-210211023315/85/Adversarial-search-21-320.jpg)
![CS 420: Artificial Intelligence 22
α-β Pruning Example
[3, 3]
[3, 3]
[-∞, 2] [2, 2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adversarialsearch-210211023315/85/Adversarial-search-22-320.jpg)








![CS 420: Artificial Intelligence 31
Dealing with Repeated States
In games, repeated states occur frequently
because of transpositions --
different permutations of the move sequence end up in
the same position
e.g., [a1, b1, a2, b2] vs. [a1, b2, a2, b1]
It’s worthwhile to store the evaluation of this
position in a hash table the first time it is
encountered
similar to the “explored set” in graph-search
Tradeoff:
Transposition table can be too big
Which to keep and which to discard](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adversarialsearch-210211023315/85/Adversarial-search-31-320.jpg)