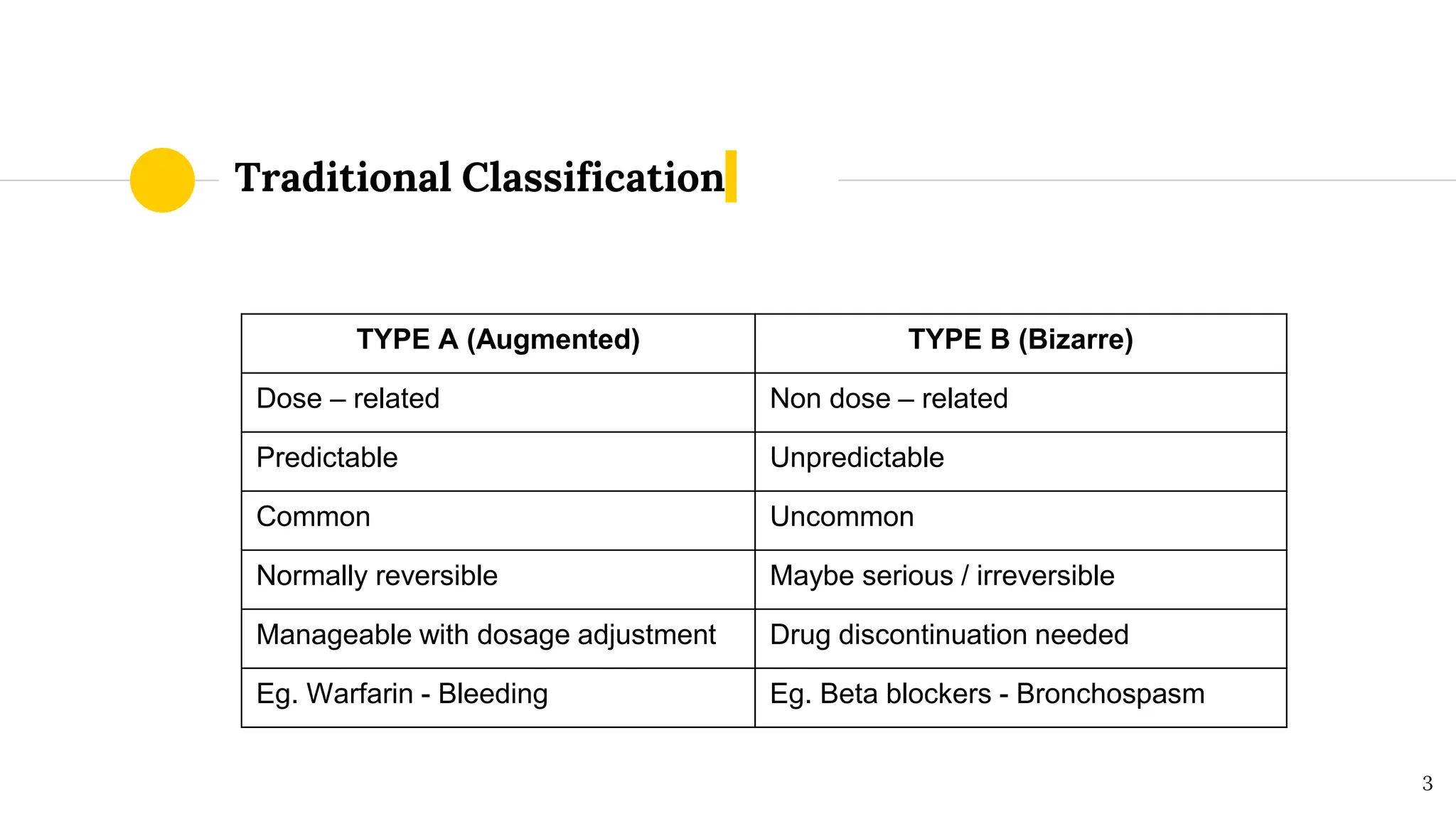
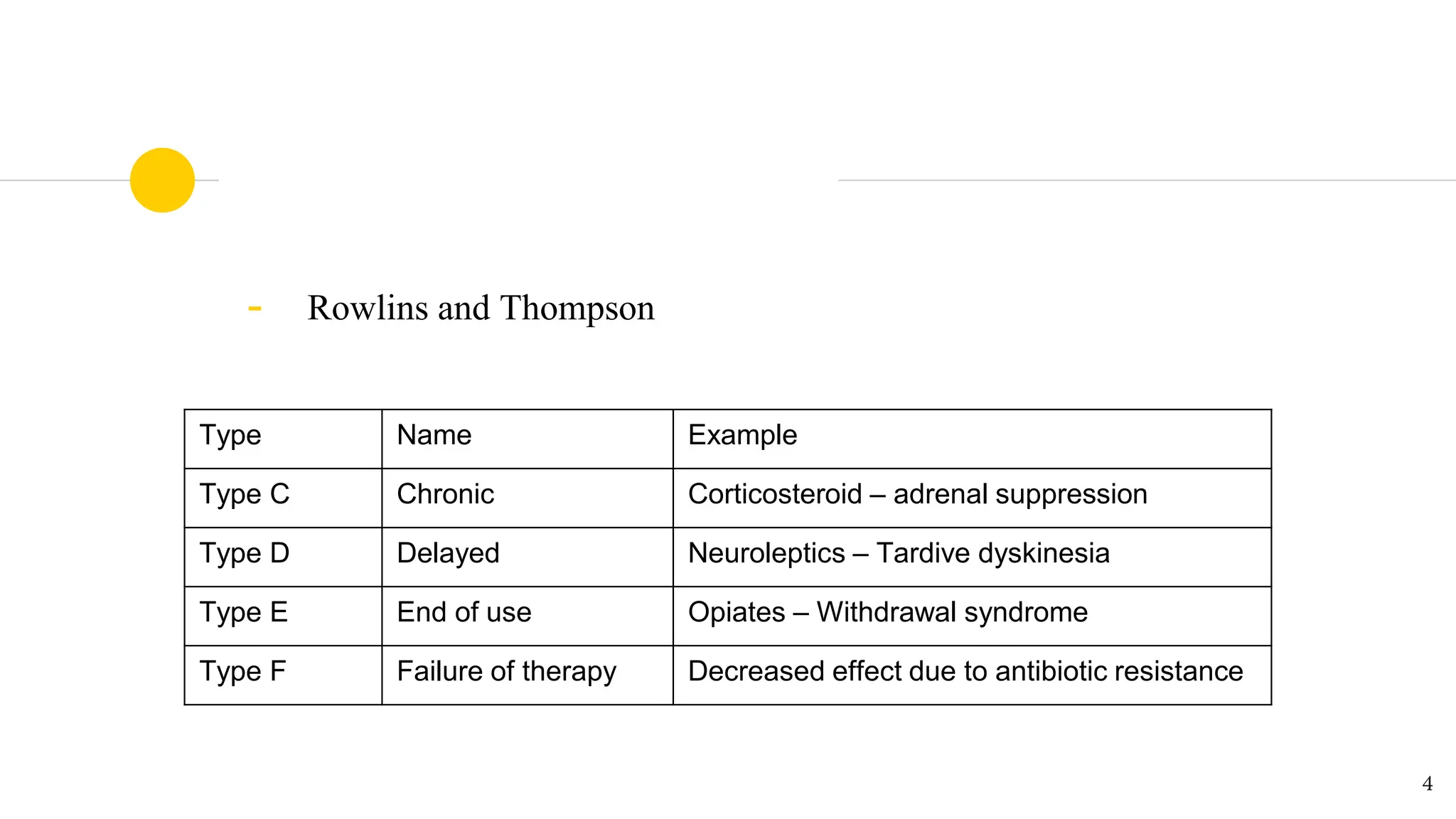
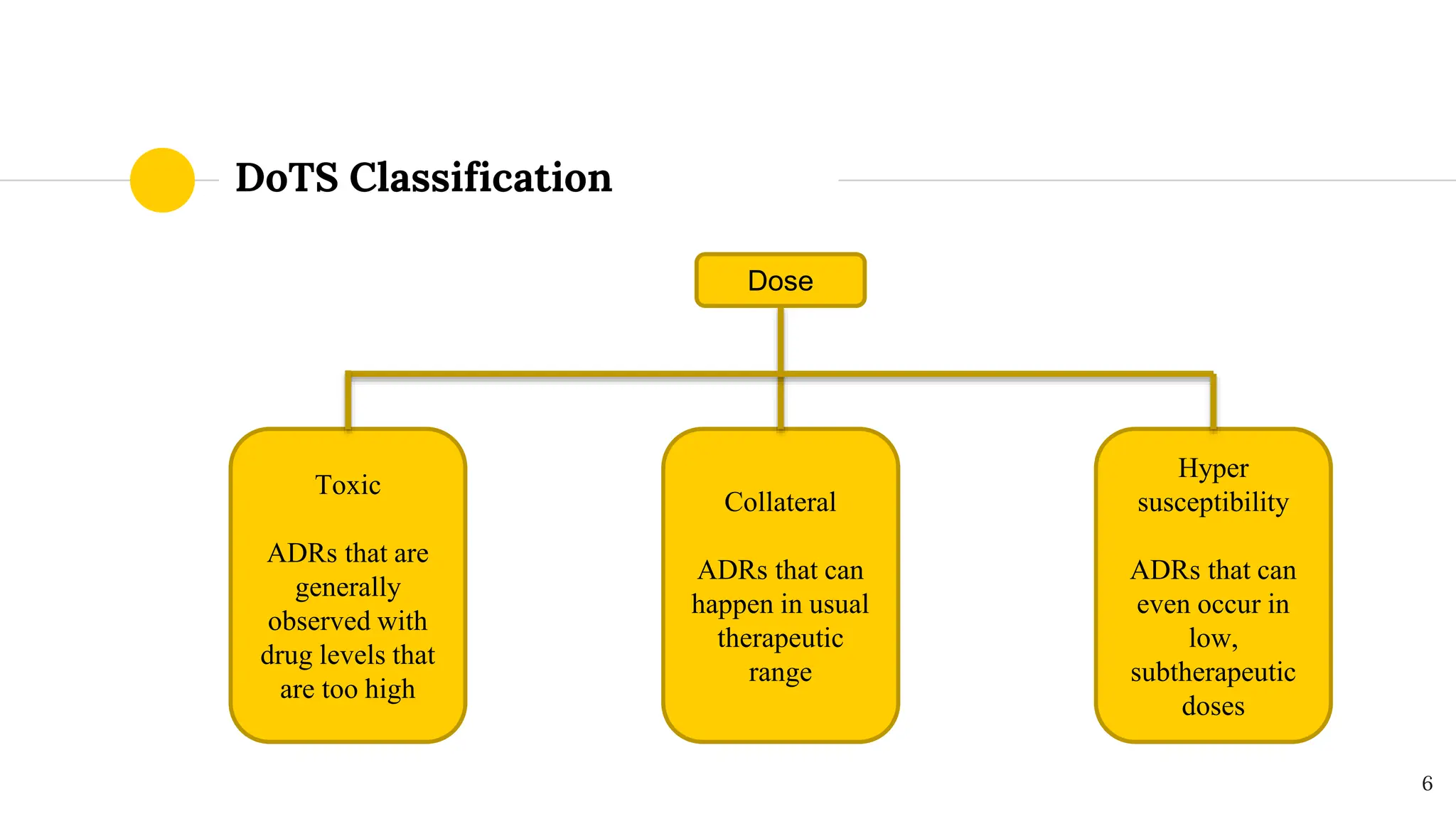
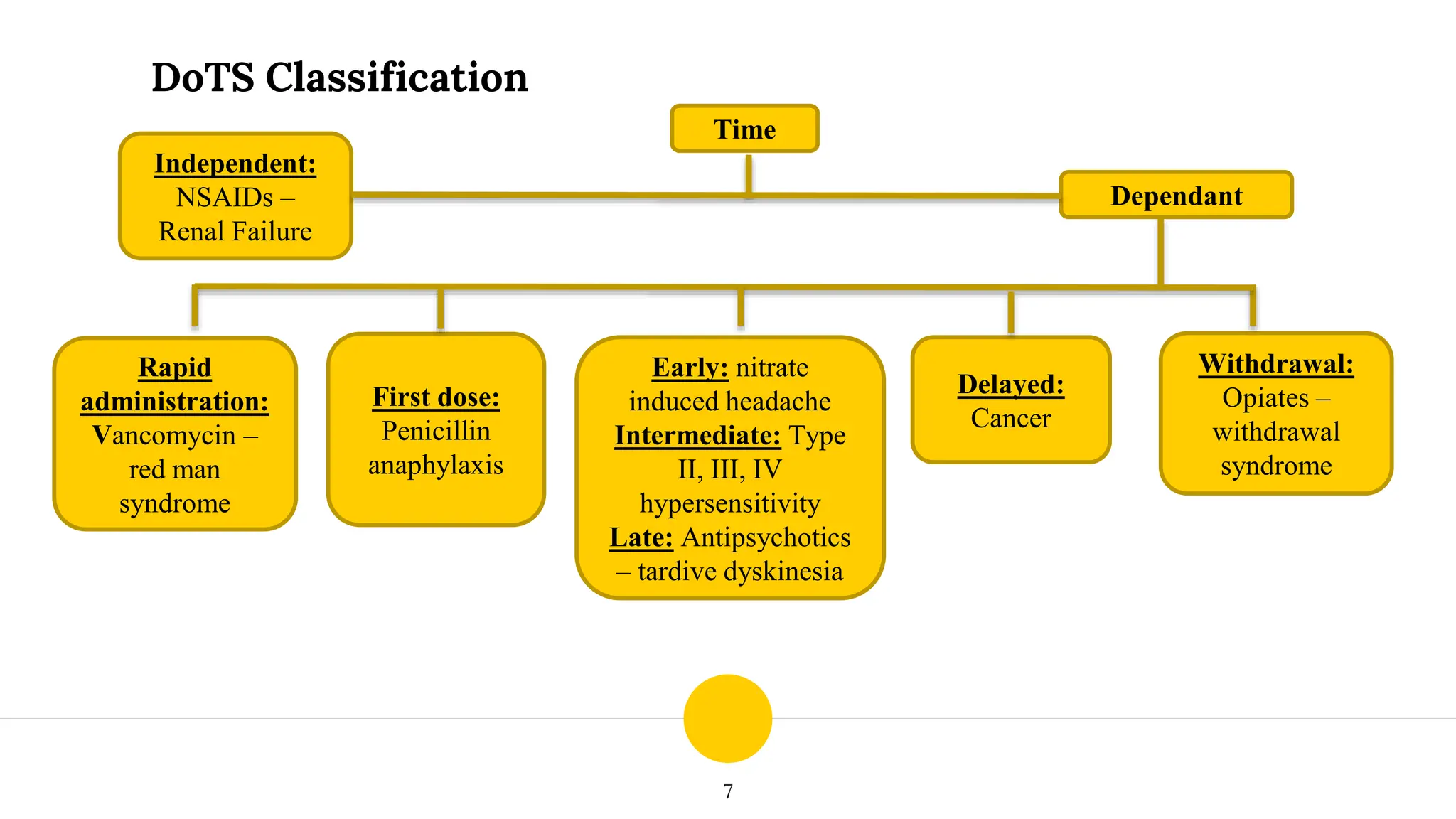
This document discusses different classifications of adverse drug reactions (ADRs). The traditional classification divides ADRs into type A reactions, which are dose-dependent and predictable, and type B reactions, which are not dose-dependent and are unpredictable. Later classifications include type C-E reactions by Rowlins and Thompson based on chronicity, delay of onset, and end of drug use. The DoTS classification by Aronson and Ferner in 2000 categorizes ADRs based on dose, time course, and patient susceptibility. It provides examples of ADRs like corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis and penicillin anaphylaxis. The DoTS classification is gaining acceptance as it better accounts for ADRs