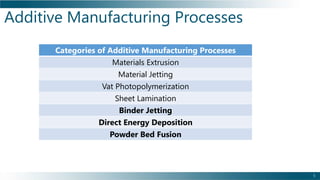
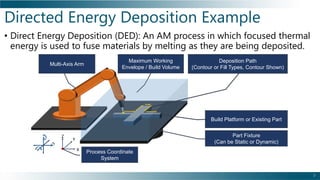
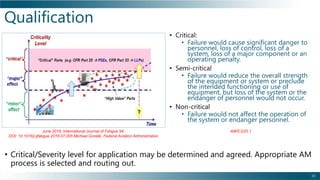
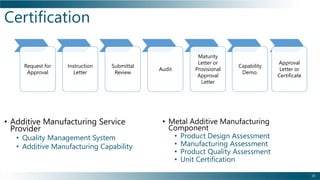
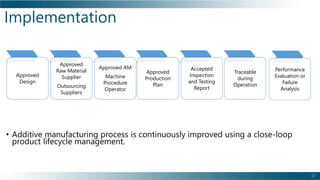
This document outlines the background, benefits, and processes of additive manufacturing (AM), contrasting it with traditional manufacturing. It details qualification and certification methods, categorizes various AM techniques, and emphasizes the advantages such as design freedom, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to produce complex shapes. The document also discusses challenges and provides information on implementation and continuous improvement in AM practices.