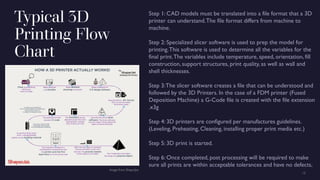
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, has been evolving for decades. Early 3D printers were expensive and produced low quality products, limiting growth. Patent expirations led to cheaper consumer 3D printers. While quality is still improving, additive manufacturing is being used more in fields like medicine, engineering, and space travel. There are several types of 3D printing processes that work in different ways, such as material jetting, powder bed fusion, and material extrusion. Additive manufacturing allows for complex designs and less waste but also has slower speeds and higher costs than traditional manufacturing.