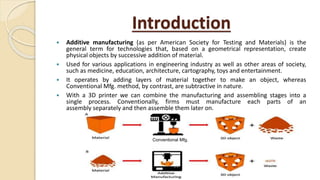
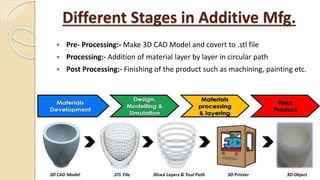
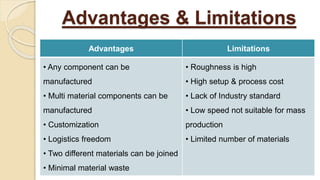
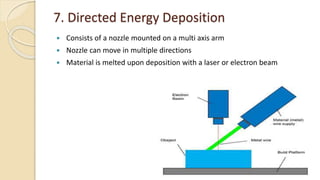
Additive manufacturing (AM) operates by adding layers of material together to make an object, unlike conventional manufacturing which subtracts material. AM allows for combining manufacturing and assembly into a single process. The main AM techniques are vat photopolymerization, material jetting, binder jetting, material extrusion, powder bed fusion, sheet lamination, and directed energy deposition. AM provides advantages like customization and reduced waste but also has limitations like roughness and cost. Current research focuses on areas like smart components and additive manufacturing of dissimilar materials.