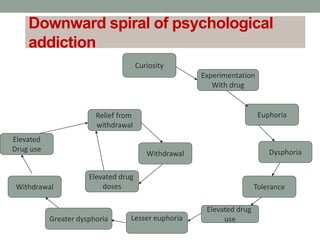
Addiction is characterized as a progressive disease caused by long-term substance abuse. It is defined by compulsive drug use, tolerance, and withdrawal symptoms. While detox removes drugs from the body, addiction is not cured but managed over time. The addiction process typically involves experimental, social, instrumental, habitual, and compulsive stages where an individual's life revolves around substance use. Physical, behavioral, and social dependencies can develop, driving an obsessive cycle of increased use and dysphoria. Though initially used for pleasure, drugs eventually provide only temporary relief from discomfort of non-use.