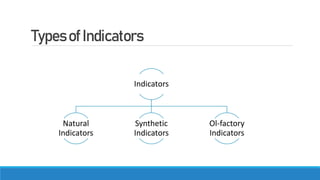
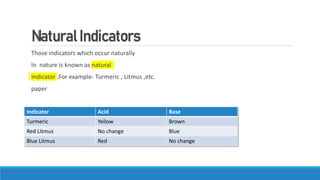
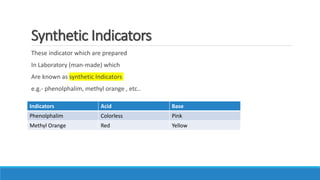
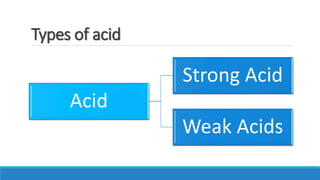
This document summarizes key information about acids, bases, indicators, and salts. It discusses how indicators change color in acids and bases. It describes natural indicators like litmus and synthetic indicators like phenolphthalein. It defines acids as substances that release H+ ions in water and describes strong acids like HCl that fully dissociate and weak acids like acetic acid that partially dissociate. It also discusses the properties and reactions of bases as well as the neutralization reaction between acids and bases that forms salts and water. Common salts formed are also summarized like NaCl, NaOH, and NaHCO3. The uses of indicators, acids, bases, and various salts in everyday life and applications are highlighted.
















![Bleaching Powder
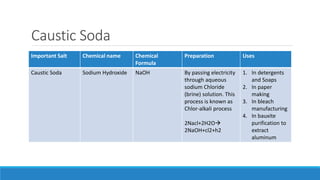
Important
Salts
Chemical Name Chemical
Formula
preparation Uses
Bleaching
Powder
Calcium
Oxychloride
CaOCl2 By passing chlorine gas over
dry slaked lime[Ca(OH2)]
Ca(Oh)2 +Cl2 CaOCl2
+H2O
I. For bleaching cotton
and linen for
bleaching wood pulp
in paper factories
and for bleaching
washed clothes in
laundry textile.
II. For disinfecting
drinking water](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbasesalt-230926153600-e9f579ad/85/ACID-BASE-SALT-pptx-22-320.jpg)

