This document defines and discusses acid-base disorders. It begins by defining terms like acidosis, alkalosis, and the normal ranges for pH, PCO2, and HCO3-. It then discusses the bicarbonate-carbonic acid buffer system and how acid-base disorders are classified based on initial chemical changes and compensatory responses. Etiologies of different acid-base disturbances are provided along with examples. Guidelines for interpreting arterial blood gases are outlined in a step-wise manner. Several case examples of acid-base disorders are then presented.


![Definitions cont’d
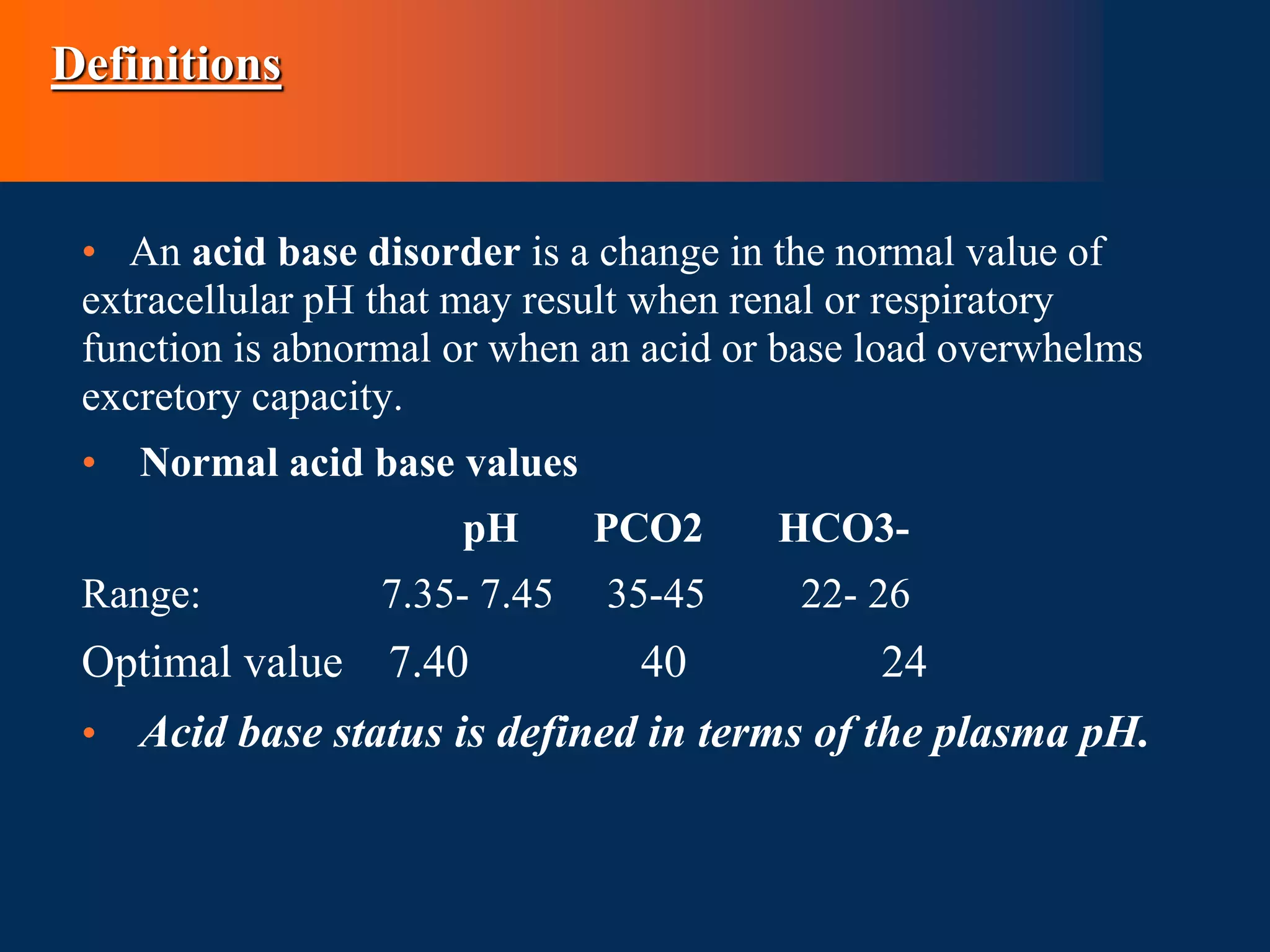
Acidemia - decrease in the blood pH below normal range (i.e.PH
<7.35)
• Alkalemia - Elevation in blood pH above the normal range of
(i.e. pH >7.45)
• Clinical disturbances of acid base metabolism classically are
defined in terms of the HCO3- /CO2 buffer system.
• Acidosis – process that increases [H+] by increasing PCO2 or
by reducing [HCO3-]
Alkalosis – process that reduces [H+] by reducing PCO2 or by
increasing [HCO3-]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbasedisorders2-230829081008-977190ff/75/ACID-BASE-DISORDERS-2-pptx-4-2048.jpg)







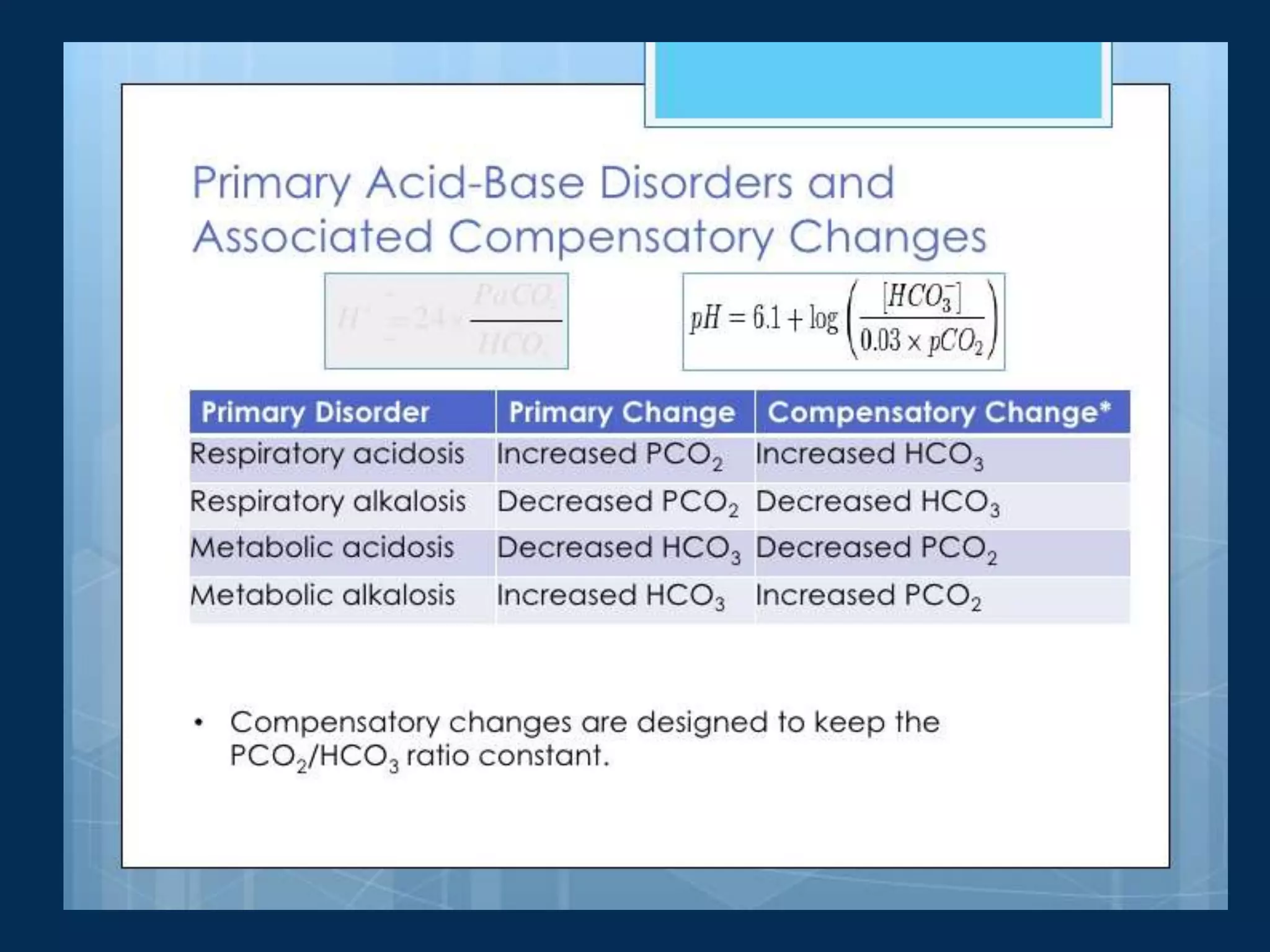
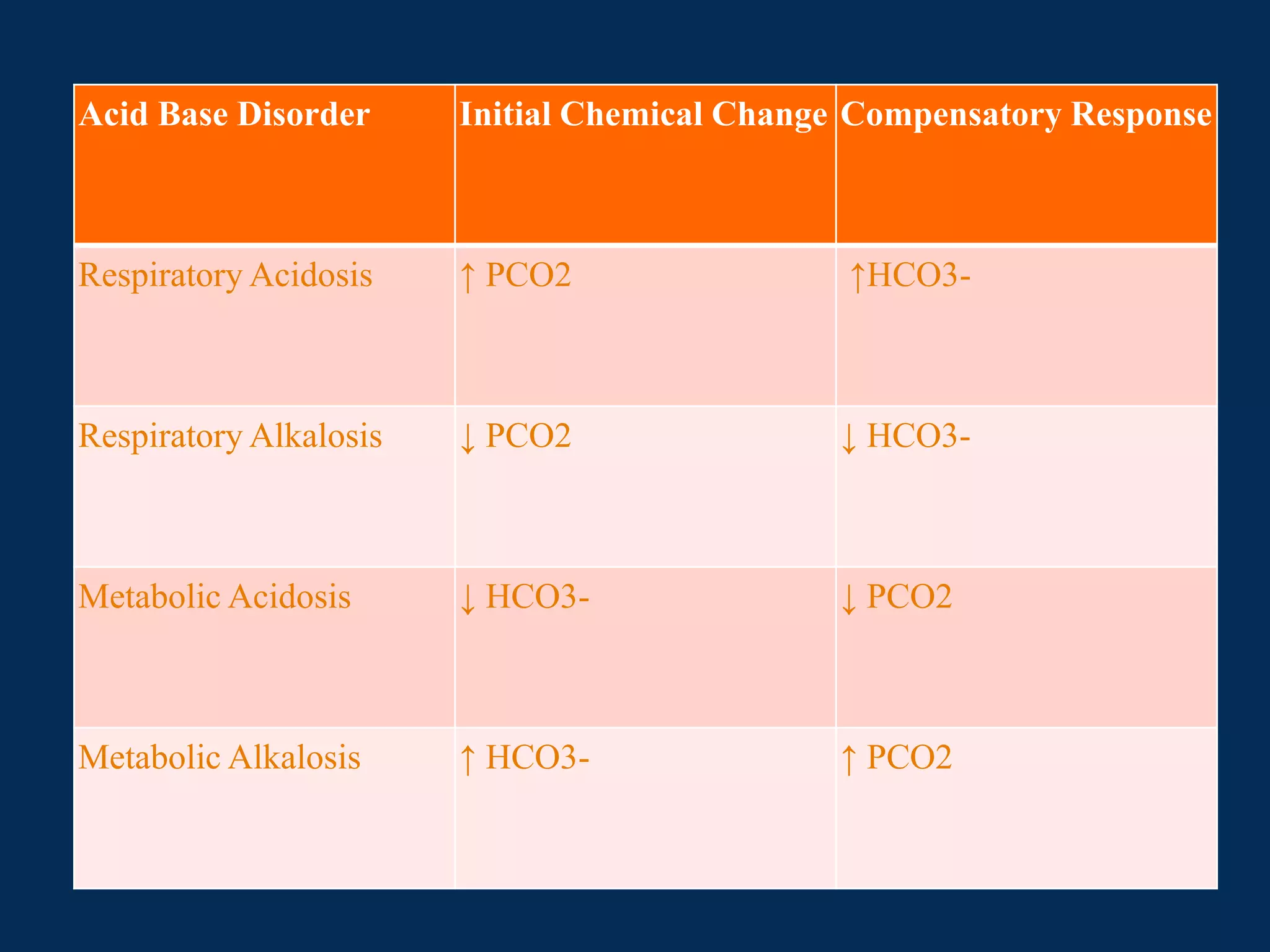
![Below is table summarizing compensatory
responses and their mechanisms
Primary
disorder
Initial chemical
change
Compensatory
response
Compensatory
Mechanism
Expected level
of
compensation
Metabolic Acidosis ↓HCO3- ↓PCO2 Hyperventilation
PCO2 = (1.5 ×
[HCO3-]) + 8 ± 2
↓PCO2 = 1.2 ×∆ [HCO3-]
PCO2 = last 2 digits of pH
Metabolic Alkalosis ↑HCO3- ↑PCO2 Hypoventilation
PCO2 = (0.9 × [HCO3-]) +
16 ± 2
↑PCO2 = 0.7 × ∆ [HCO3-]
Respiratory Acidosis ↑PCO2 ↑HCO3-
Acute
Intracellular Buffering
(hemoglobin, intracellular
proteins)
↑[HCO3-] = 1 mEq/L for
every 10 mm Hg ∆PCO2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbasedisorders2-230829081008-977190ff/75/ACID-BASE-DISORDERS-2-pptx-16-2048.jpg)
![Primary
disorder
Initial chemical
change
Compensatory
response
Compensatory
Mechanism
Expected level
of compensation
Chronic
Generation of
new HCO3- due
to the increased
excretion of
ammonium.
↑[HCO3-] = 3.5
mEq/L for every
10 mm Hg
∆PCO2
Respiratory
Alkalosis
↓PCO2 ↓HCO3-
Acute
Intracellular
Buffering
↓[HCO3-] = 2
mEq/L for every
10 mm Hg
∆PCO2
Chronic
Decreased
reabsorption of
HCO3-, decreased
excretion of
ammonium
↓[HCO3-] =4
mEq/L for every
10 mm Hg
∆PCO2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbasedisorders2-230829081008-977190ff/75/ACID-BASE-DISORDERS-2-pptx-17-2048.jpg)
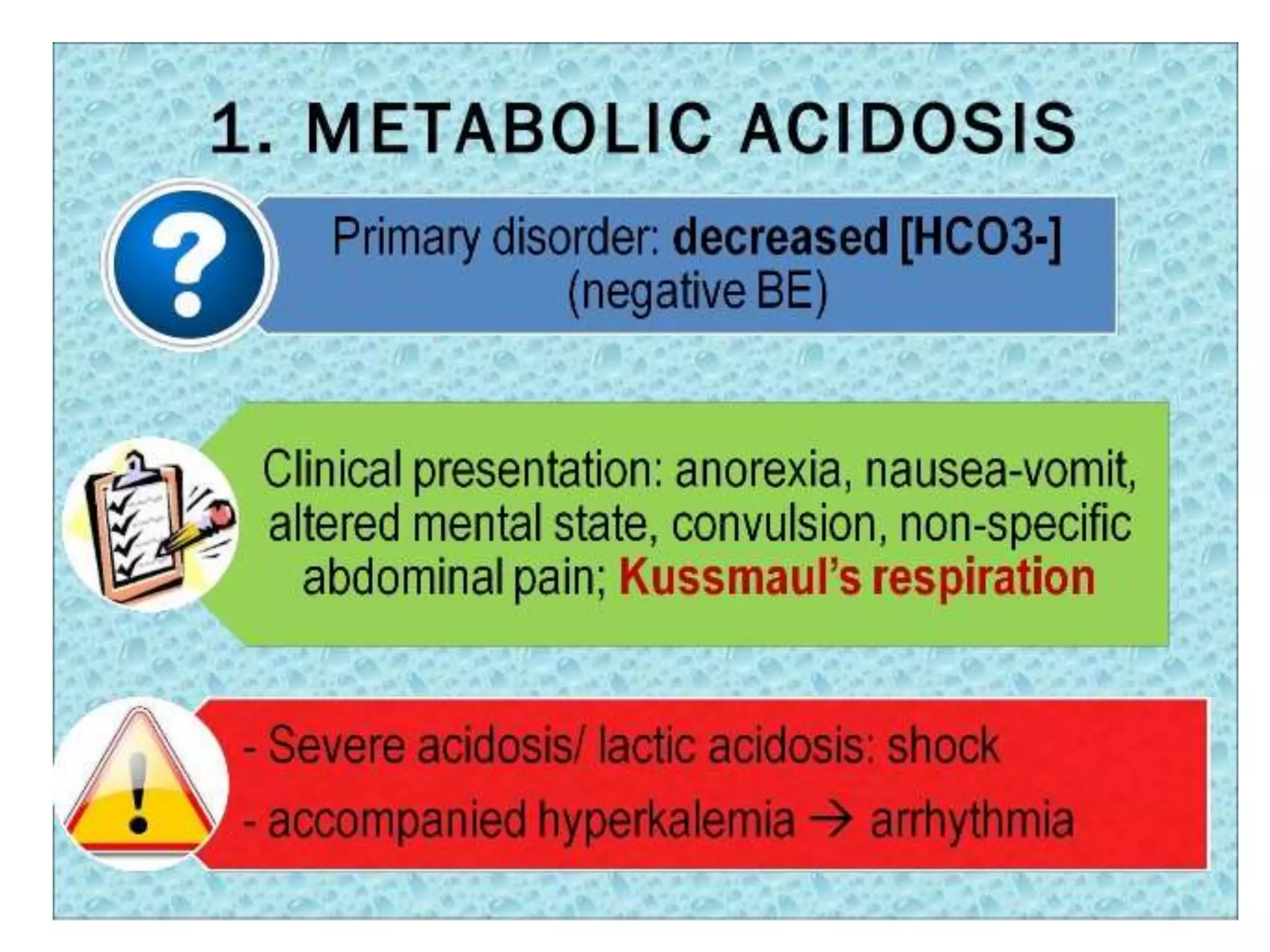
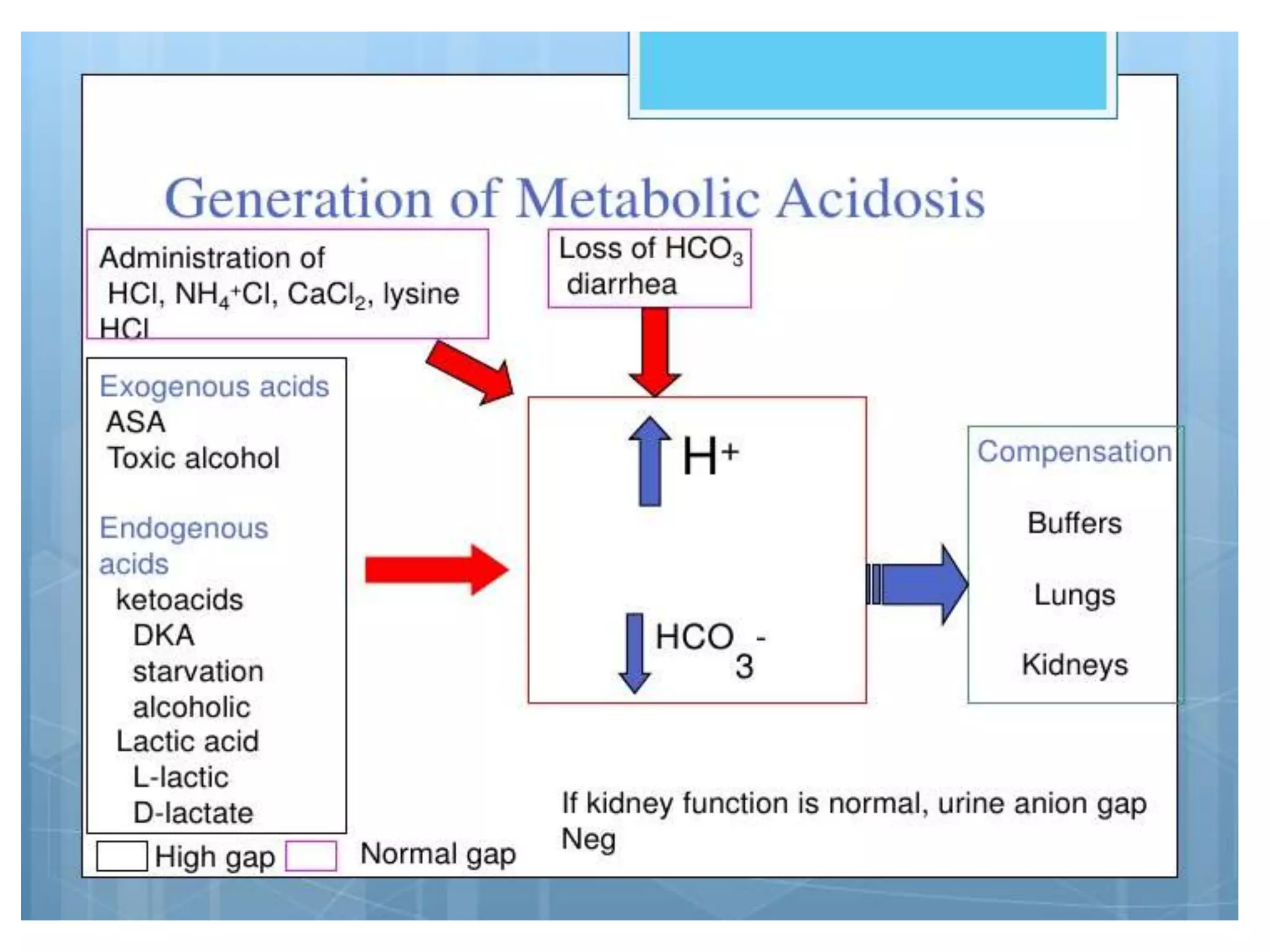















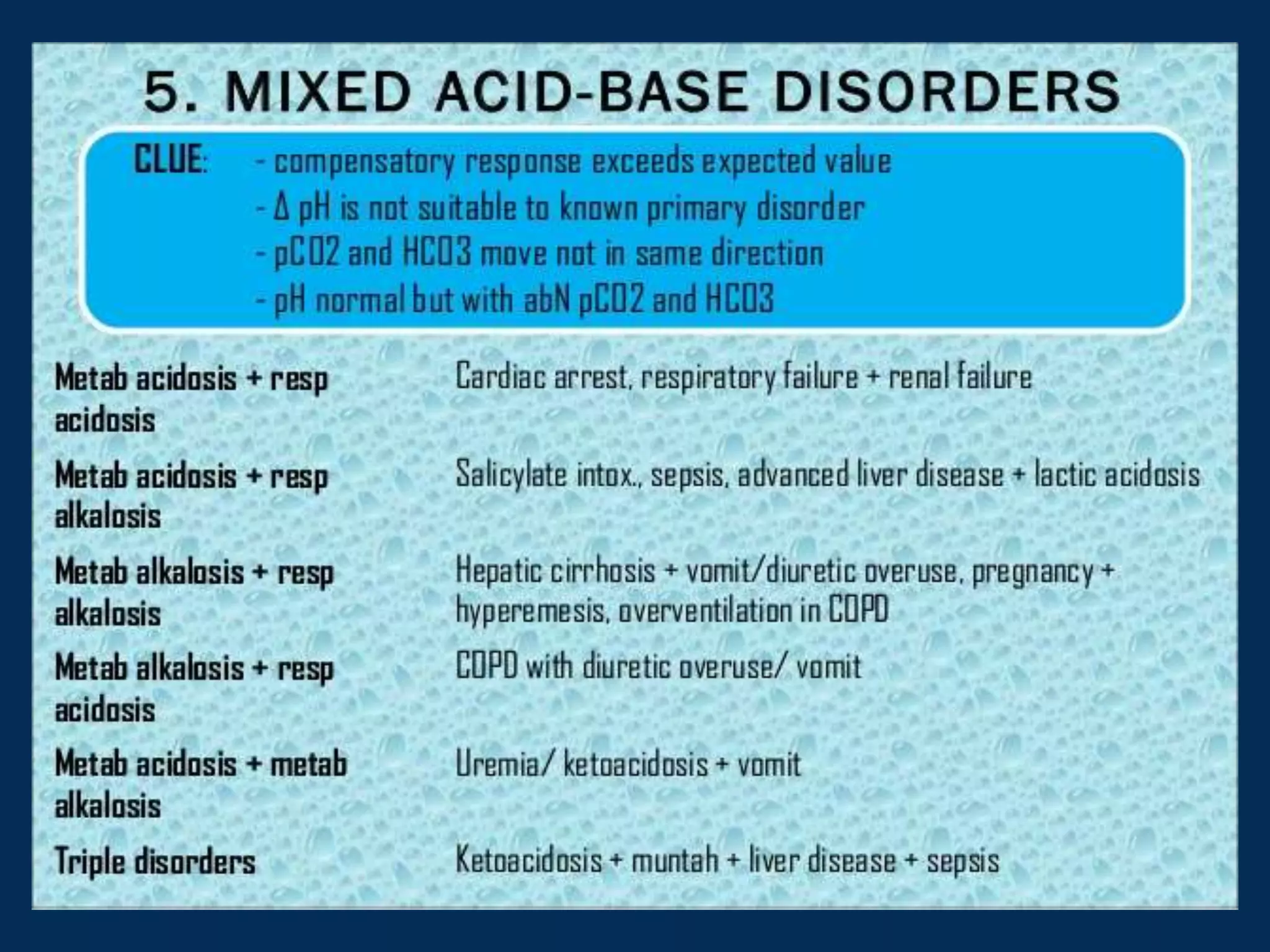






![Below is table summarizing compensatory
responses and their mechanisms
Primary
disorder
Initial chemical
change
Compensatory
response
Compensatory
Mechanism
Expected level
of
compensation
Metabolic Acidosis ↓HCO3- ↓PCO2 Hyperventilation
PCO2 = (1.5 ×
[HCO3-]) + 8 ± 2
↓PCO2 = 1.2 ×∆ [HCO3-]
PCO2 = last 2 digits of pH
Metabolic Alkalosis ↑HCO3- ↑PCO2 Hypoventilation
PCO2 = (0.9 × [HCO3-])
+ 16 ± 2
↑PCO2 = 0.7 × ∆ [HCO3-]
Respiratory Acidosis ↑PCO2 ↑HCO3-
Acute
Intracellular Buffering
(hemoglobin, intracellular
proteins)
↑[HCO3-] = 1 mEq/L for
every 10 mm Hg ∆PCO2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbasedisorders2-230829081008-977190ff/75/ACID-BASE-DISORDERS-2-pptx-42-2048.jpg)
![Primary
disorder
Initial chemical
change
Compensatory
response
Compensatory
Mechanism
Expected level
of compensation
Chronic
Generation of new
HCO3- due to the
increased
excretion of
ammonium.
↑[HCO3-] = 3.5
mEq/L for every
10 mm Hg ∆PCO2
Respiratory
Alkalosis
↓PCO2 ↓HCO3-
Acute
Intracellular
Buffering
↓[HCO3-] = 2
mEq/L for every
10 mm Hg ∆PCO2
Chronic
Decreased
reabsorption of
HCO3-, decreased
excretion of
↓[HCO3-] =4
mEq/L for every
10 mm Hg ∆PCO2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidbasedisorders2-230829081008-977190ff/75/ACID-BASE-DISORDERS-2-pptx-43-2048.jpg)









