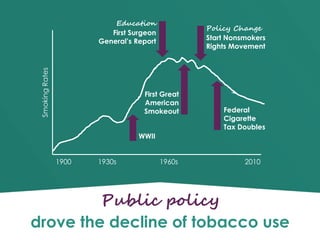
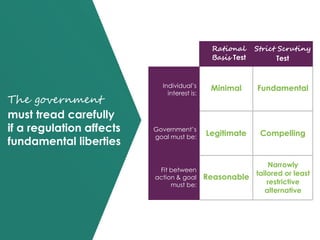
The document discusses the role of law and policy in achieving health equity and protecting public health, emphasizing the government's ability to regulate individual behavior for the common good. It highlights historical examples like tobacco control and outlines the powers and limitations of federal, state, and local governments in public health initiatives. The importance of balancing individual rights and public health needs, with legal frameworks and constitutional considerations, is also examined.