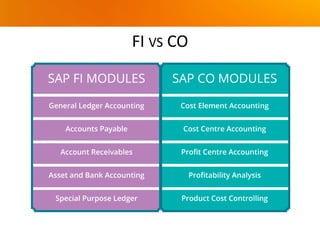
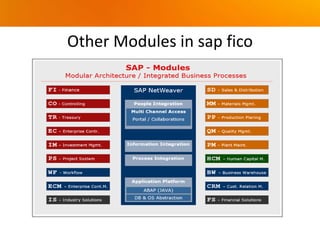
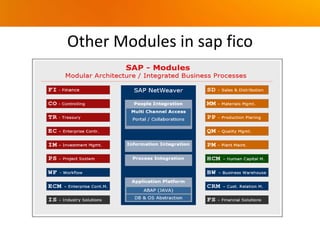
The document provides an overview of SAP FICO (Finance and Controlling) modules. It discusses the history and versions of SAP ECC, the differences between FI (Finance) and CO (Controlling) modules, benefits of cloud vs on-premises deployment, other SAP FICO modules, SAP S/4HANA, types of SAP projects, and the stages of an SAP implementation based on the ASAP methodology.