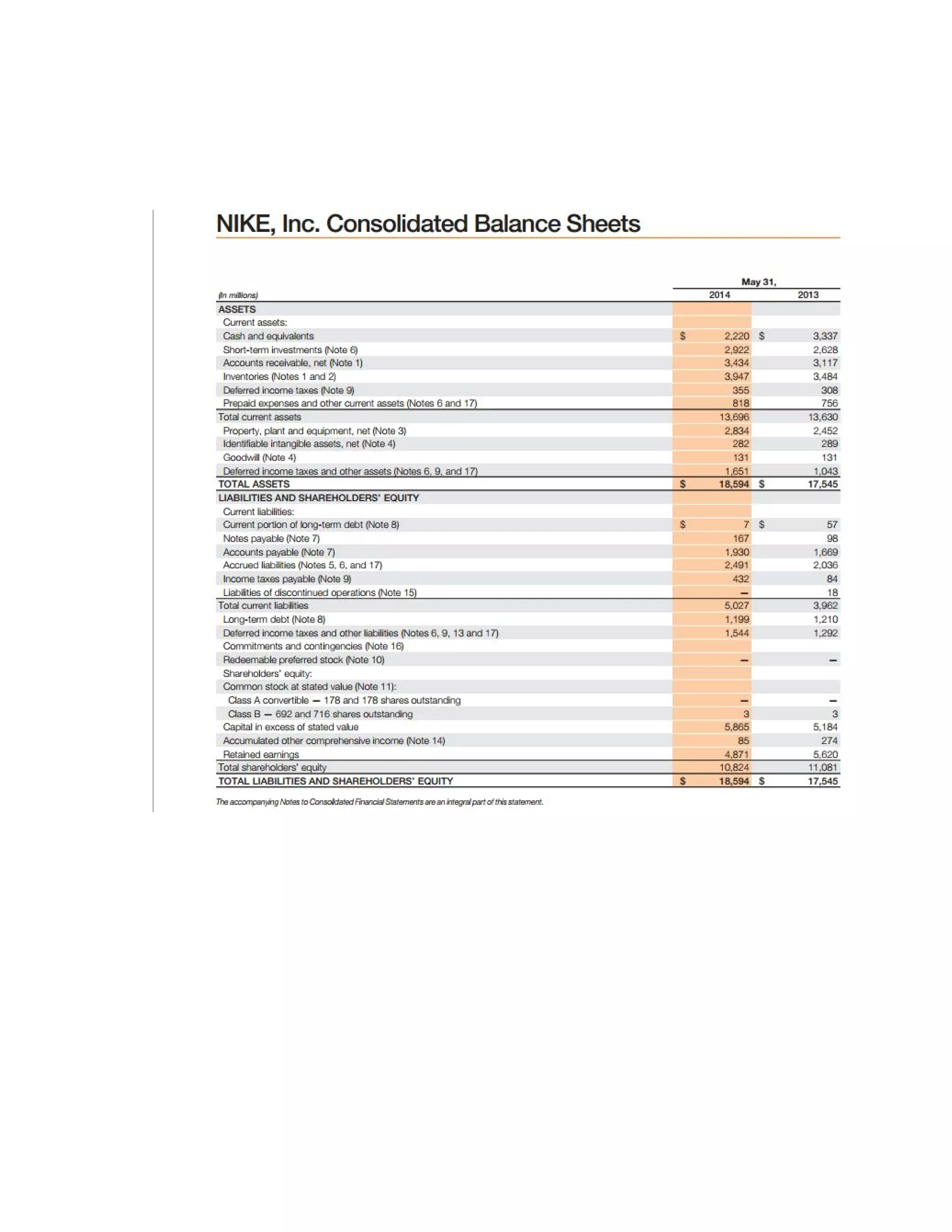
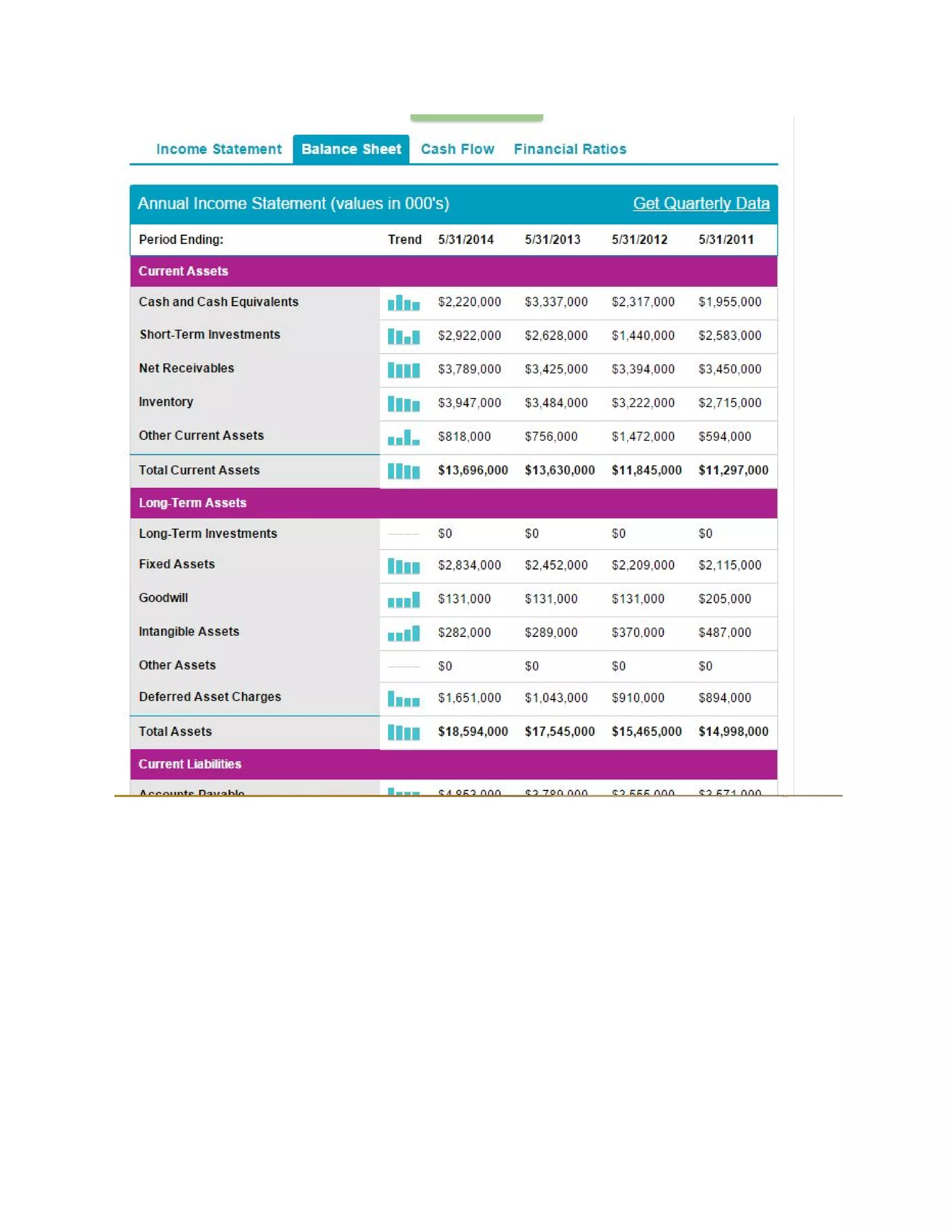
This document analyzes the financial performance of Nike from 2013-2014. It includes an analysis of profitability ratios like return on equity and net profit margin, stability ratios like working capital ratio and debt ratios, and a price-earnings ratio. While some ratios like gross profit margin and return on equity increased from 2013-2014, other ratios declined like ability to control expenses. Overall, Nike remained financially stable but the document recommends not purchasing shares due to the long payback period.












![REFERENCE
1. NKE Key Financial Ratios. (2015, June 1). Retrieved June 2, 2015, from
http://www.nasdaq.com/symbol/nke/financials?query=ratios
2. Jones, D. (2015, May 26). The footwear and apparel giant is set to report an
upside fiscal fourth quarter in late June. Nike Shares Could Run Up to $120,
p. 1. Retrieved June 2, 2015, from
http://online.barrons.com/articles/nikesharescouldrunupto1201432663
122
3. Schaefer, S. (2015, May 11). The World's Most Valuable Brands. Forbes,
77.
4. Gibson, C., & Gibson, C. (2001). Financial reporting and analysis: Using
financial accounting information (8th ed., p. 307). Cincinnati, Ohio,
Hamilton City: SouthWestern College Pub.
5. Anon, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://investors.nike.com/files/doc_financials/2014/docs/nike2014form10
K.pdf [Accessed 1 Jun. 2015].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/accountreport-150624091839-lva1-app6892/75/Accountreport-15-2048.jpg)