Embed presentation






![With these two accents there is a
slight nuance in the pronunciation in
French.
• é [ e] like in café (note the sense
of the stroke for acute)
• è [ ε] like in mère (note the sense
of the stroke for grave)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/accentsinfrench-101103183734-phpapp01/85/Accents-in-french-8-320.jpg)

![These are the different ways these
sounds can be spelt:
• [ e] du thé, une épée, s’appeler,
chez
• [ε] chère, le chêne, une princesse,
une reine, une baie](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/accentsinfrench-101103183734-phpapp01/85/Accents-in-french-10-320.jpg)
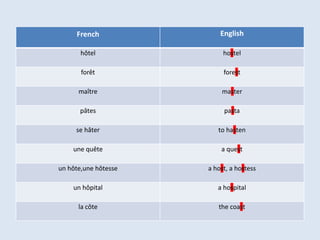
The hat accent, or circumflex accent (^), is placed on top of vowels in French words and does not change the pronunciation of the vowel. It indicates that the word originally contained an 's' in the middle ages that has since disappeared. This is useful for English speakers to know as the 's' is often still present in the English equivalent word. For example, hôtel comes from hostel and maître from master. The accent is also why the verb être is conjugated with an e or s starting sound. Additionally, the accents é and è produce slight pronunciation differences in French, with é sounding like the e in café and è like the e in mère, though these sounds can be spelled







![With these two accents there is a
slight nuance in the pronunciation in
French.
• é [ e] like in café (note the sense
of the stroke for acute)
• è [ ε] like in mère (note the sense
of the stroke for grave)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/accentsinfrench-101103183734-phpapp01/85/Accents-in-french-8-320.jpg)

![These are the different ways these
sounds can be spelt:
• [ e] du thé, une épée, s’appeler,
chez
• [ε] chère, le chêne, une princesse,
une reine, une baie](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/accentsinfrench-101103183734-phpapp01/85/Accents-in-french-10-320.jpg)