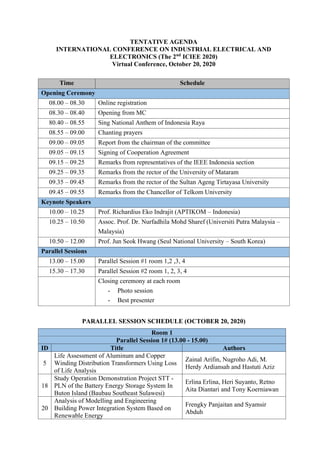
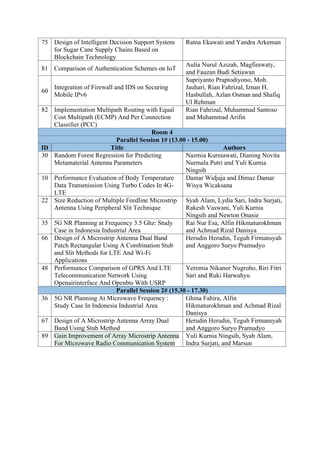
The document is the program and abstract book for the 2nd International Conference on Industrial Electrical and Electronics (ICIEE) being held virtually from October 20-21, 2020. It provides details on the organization of the conference, including the organizing committee, program schedule, and list of presentations to be given in parallel sessions. The opening ceremony will include remarks from representatives of the organizing university and technical sponsors. Three keynote speakers are scheduled to present on topics related to data science and information technology. Parallel presentation sessions will be held after the keynotes.