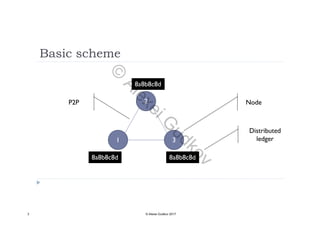
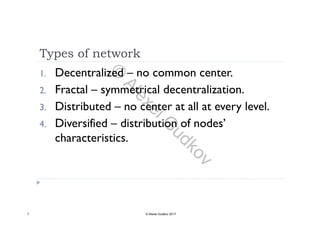
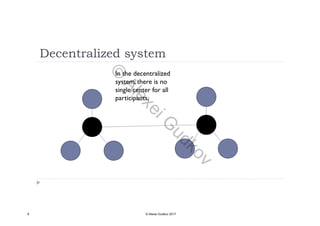
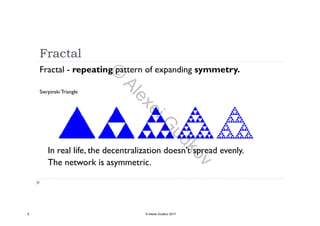
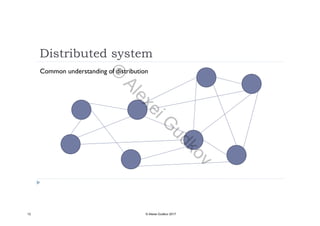
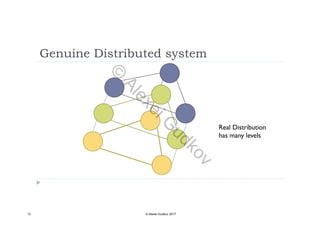
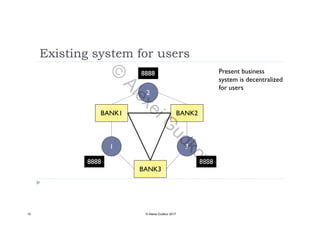
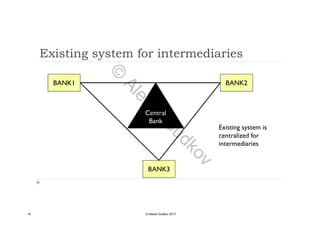
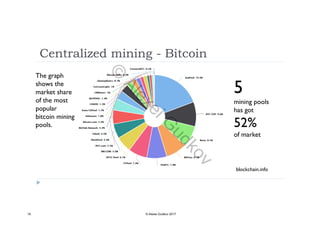
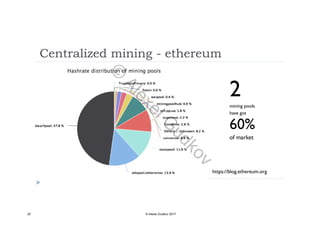
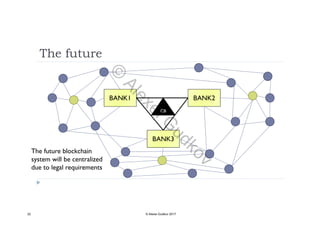
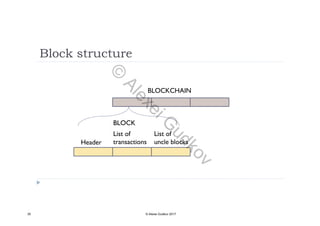
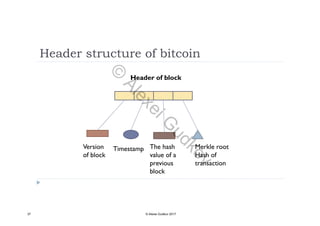
This document discusses key concepts related to decentralized networks and blockchain technology. It begins by describing the basic components of a blockchain network, including nodes that exchange information and maintain an identical and immutable record of historical data. It then explores the differences between decentralized, fractal, distributed, and diversified network types. The document also notes some potential problems with decentralization, such as centralized elements like mining pools, hardware manufacturers, and exchanges. Finally, it provides an overview of distributed ledgers, peer-to-peer networks, and defines blocks and blockchains as sequences of immutable records of transactions.