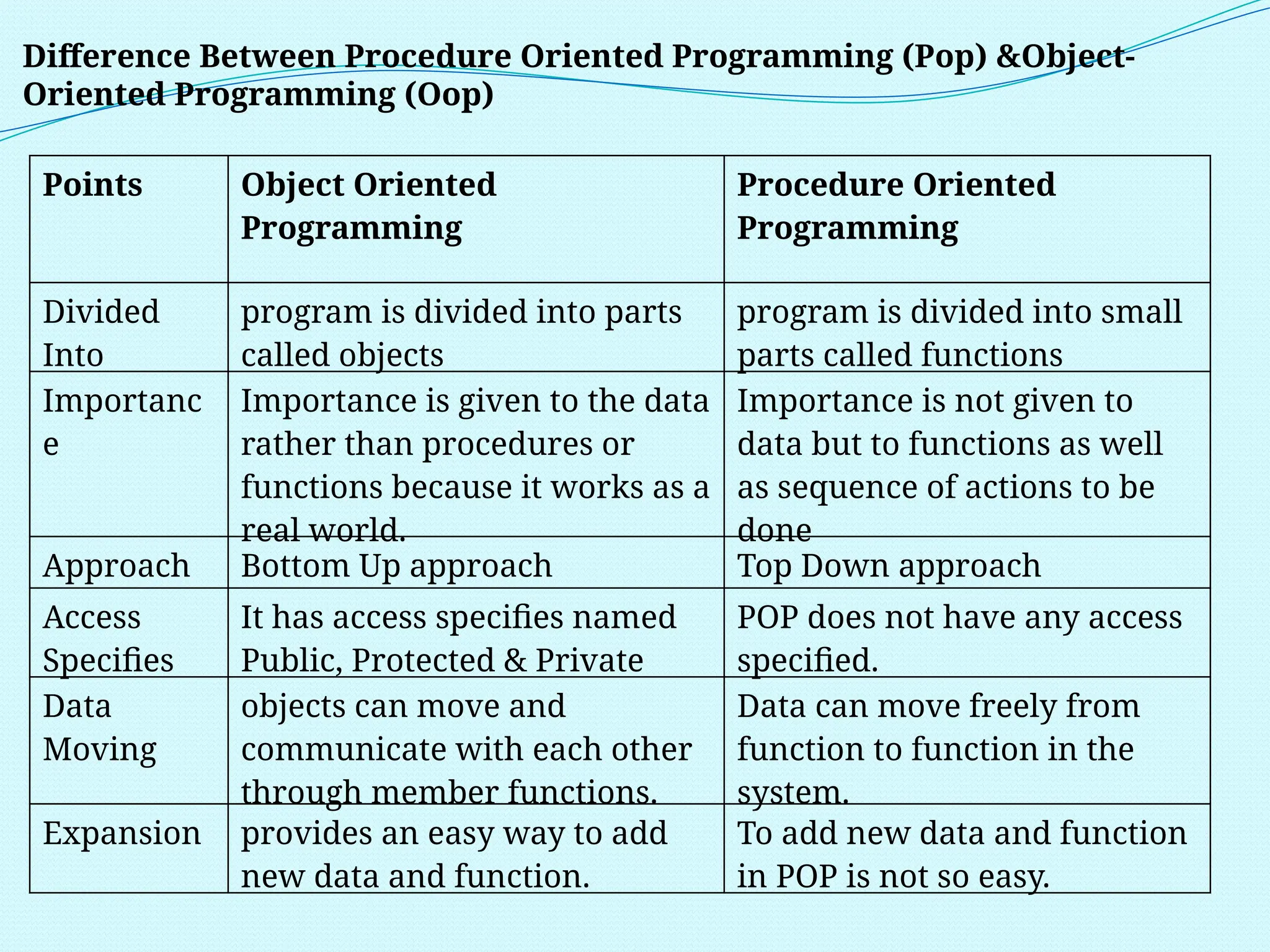
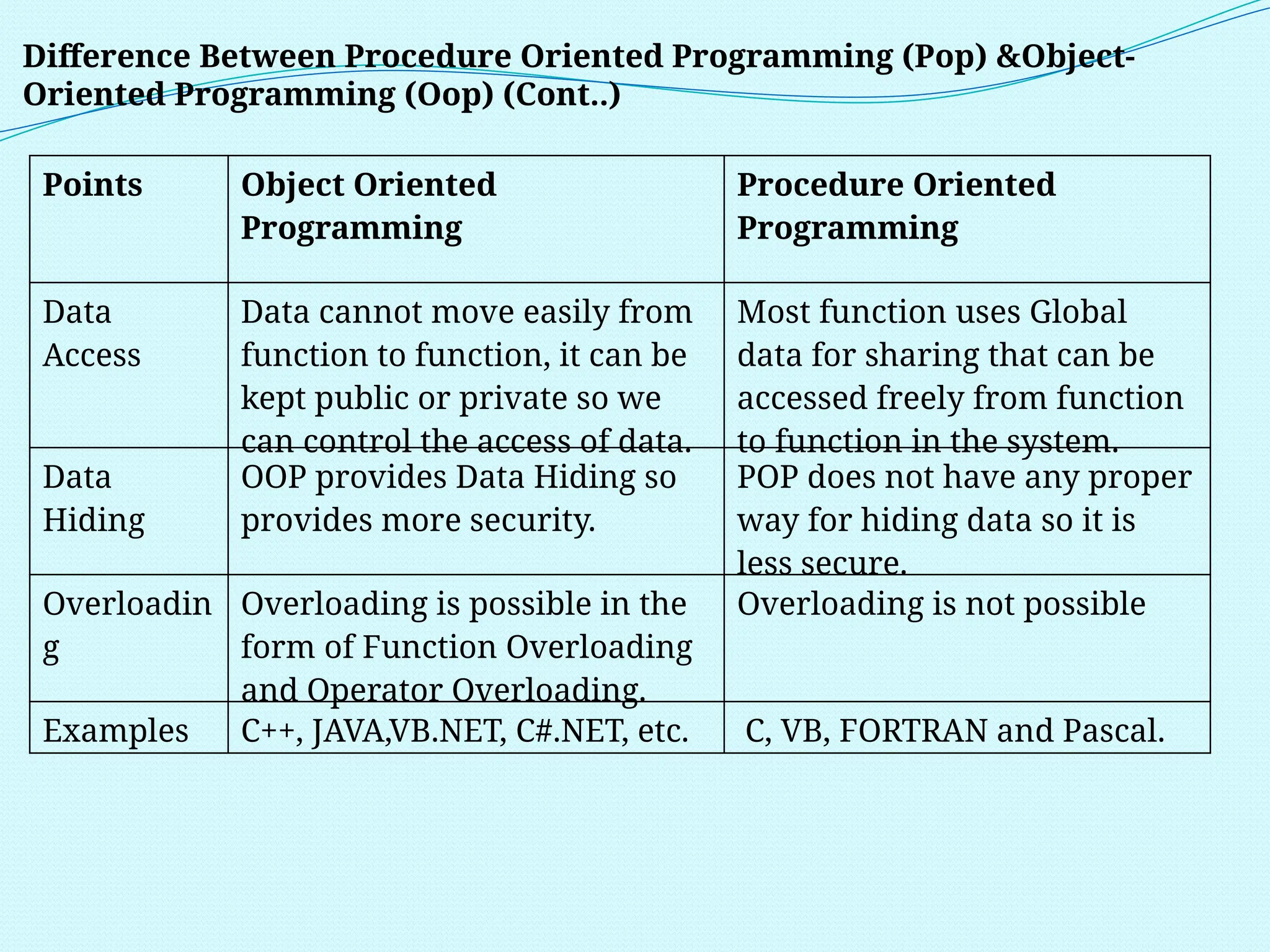
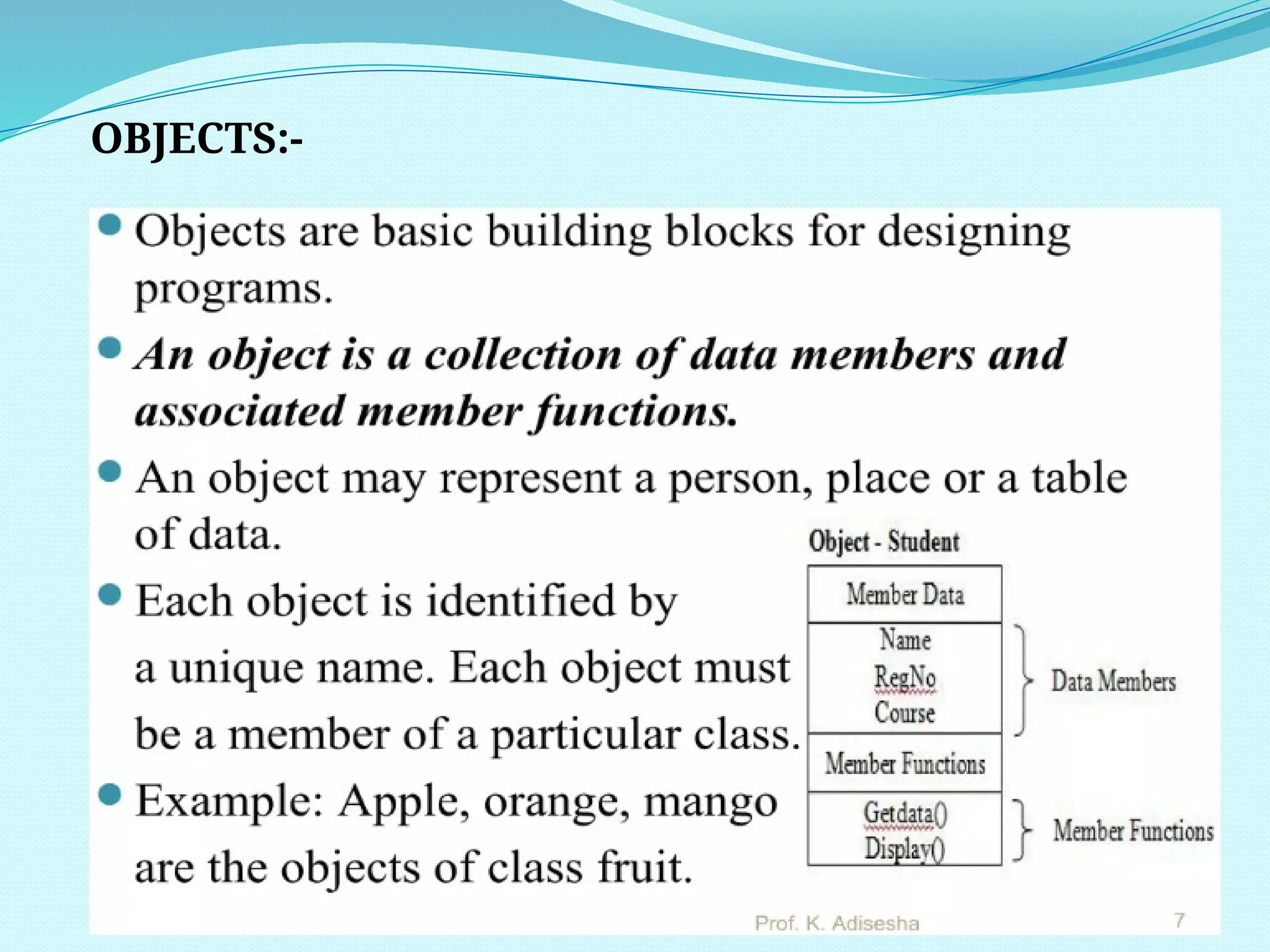
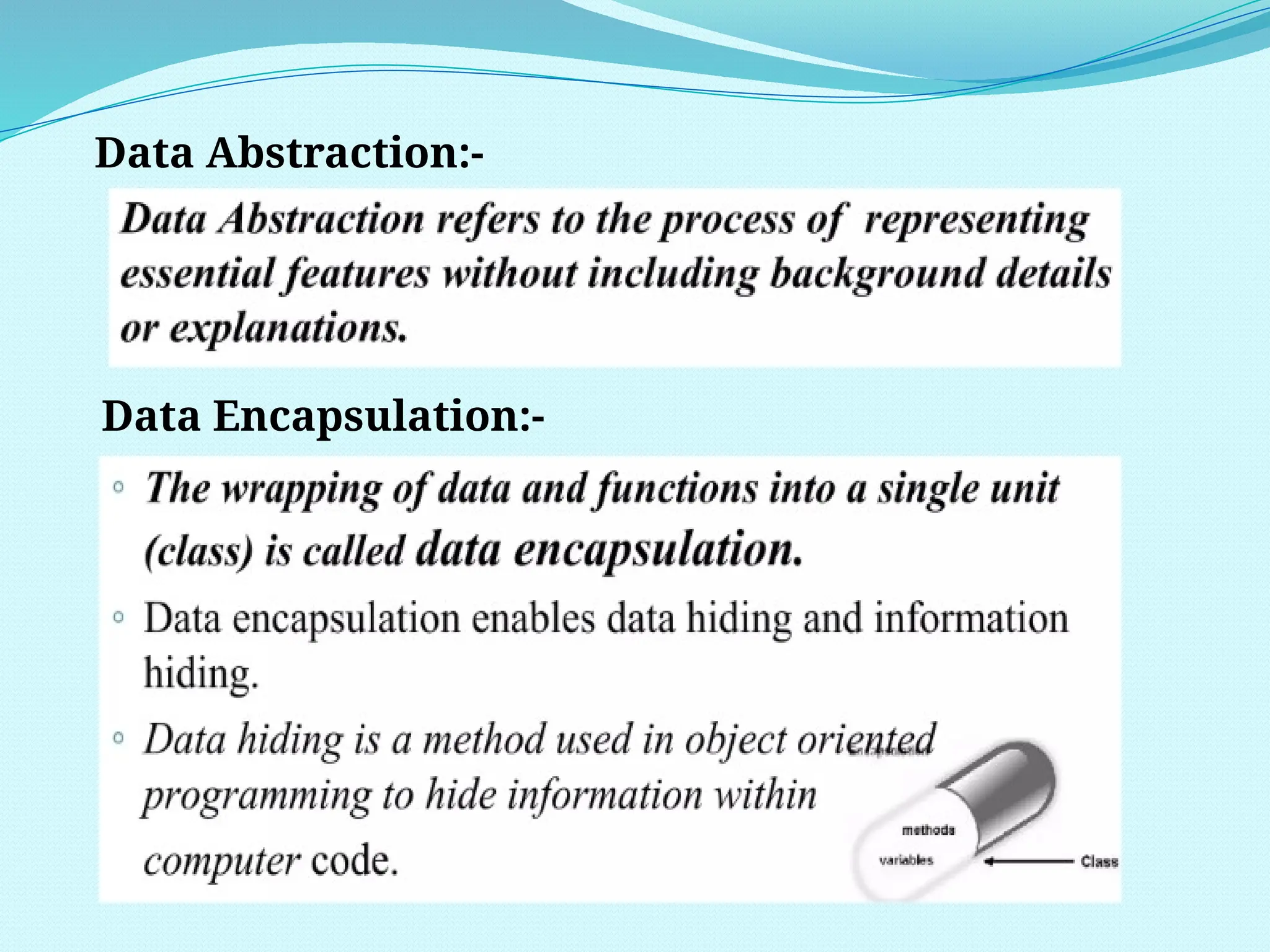
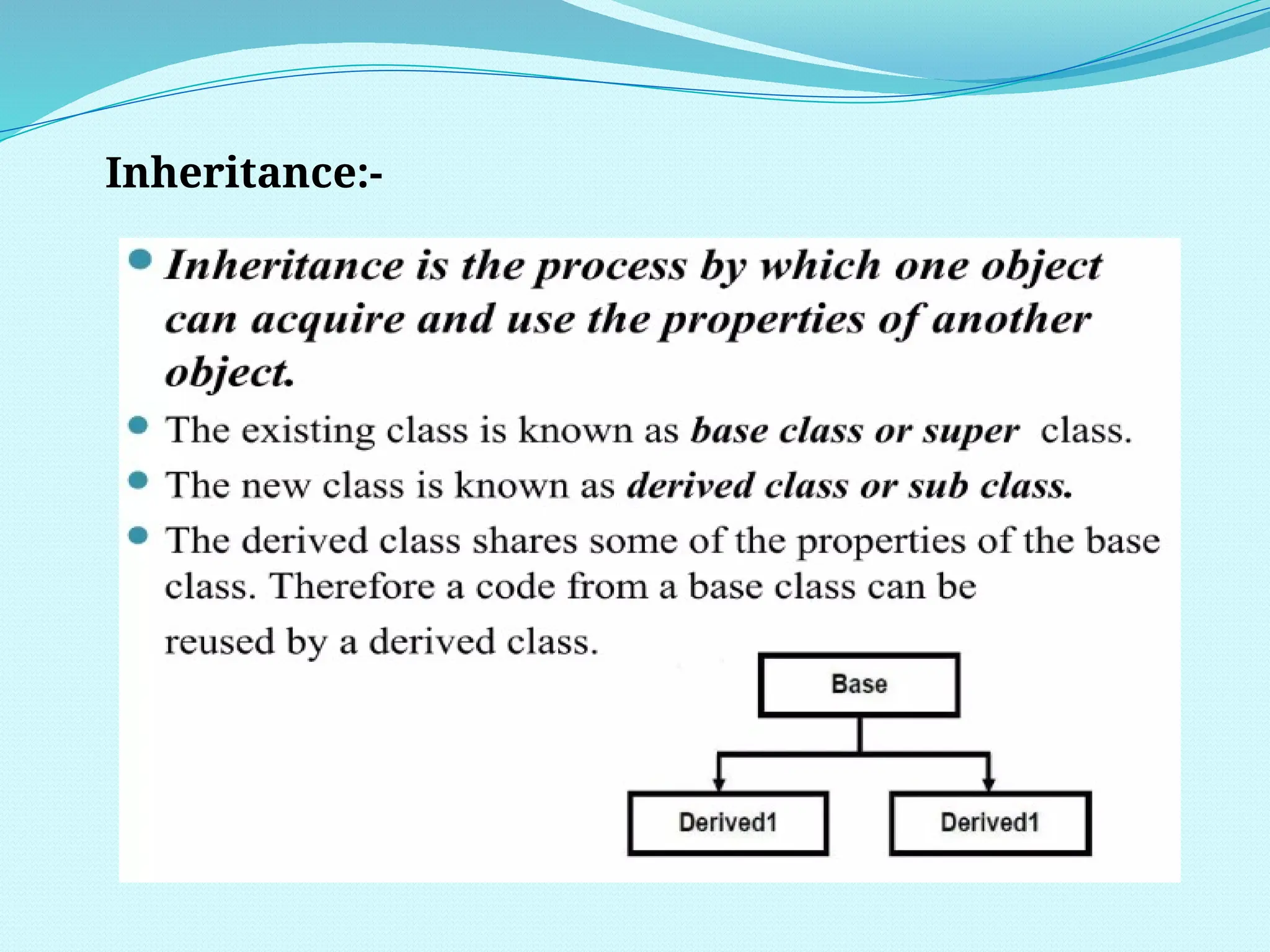
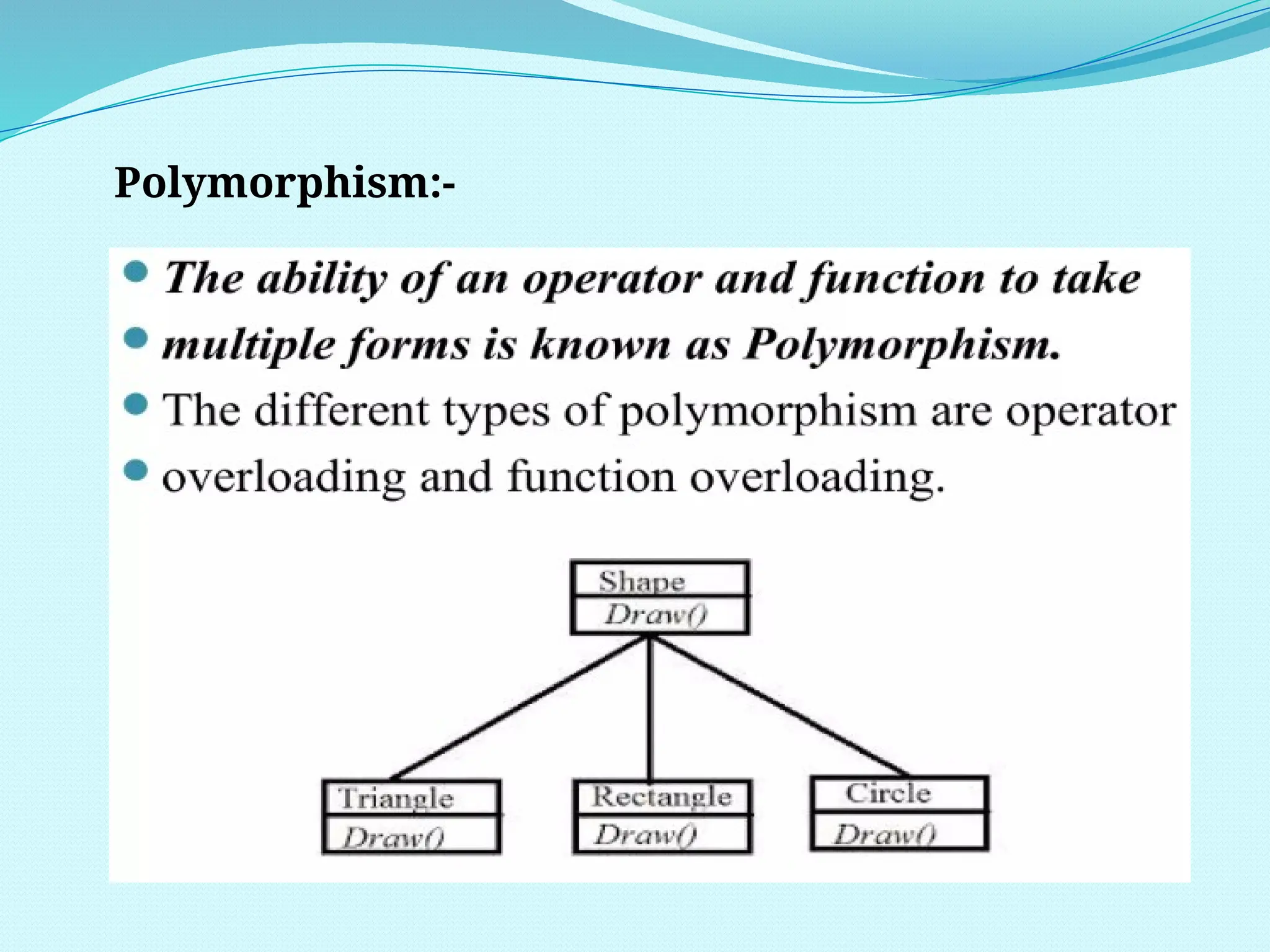
The document outlines the differences between Procedure Oriented Programming (POP) and Object Oriented Programming (OOP), highlighting aspects like program structure, data handling, and expansion capabilities. OOP emphasizes data over procedures, offering advantages such as enhanced software reuse, security, and better performance, while POP focuses on functions and global data access. It also discusses merits and demerits of OOP, such as the need for proper planning and design, potential for larger program sizes, and difficulties in converting real-world problems into an object-oriented model.