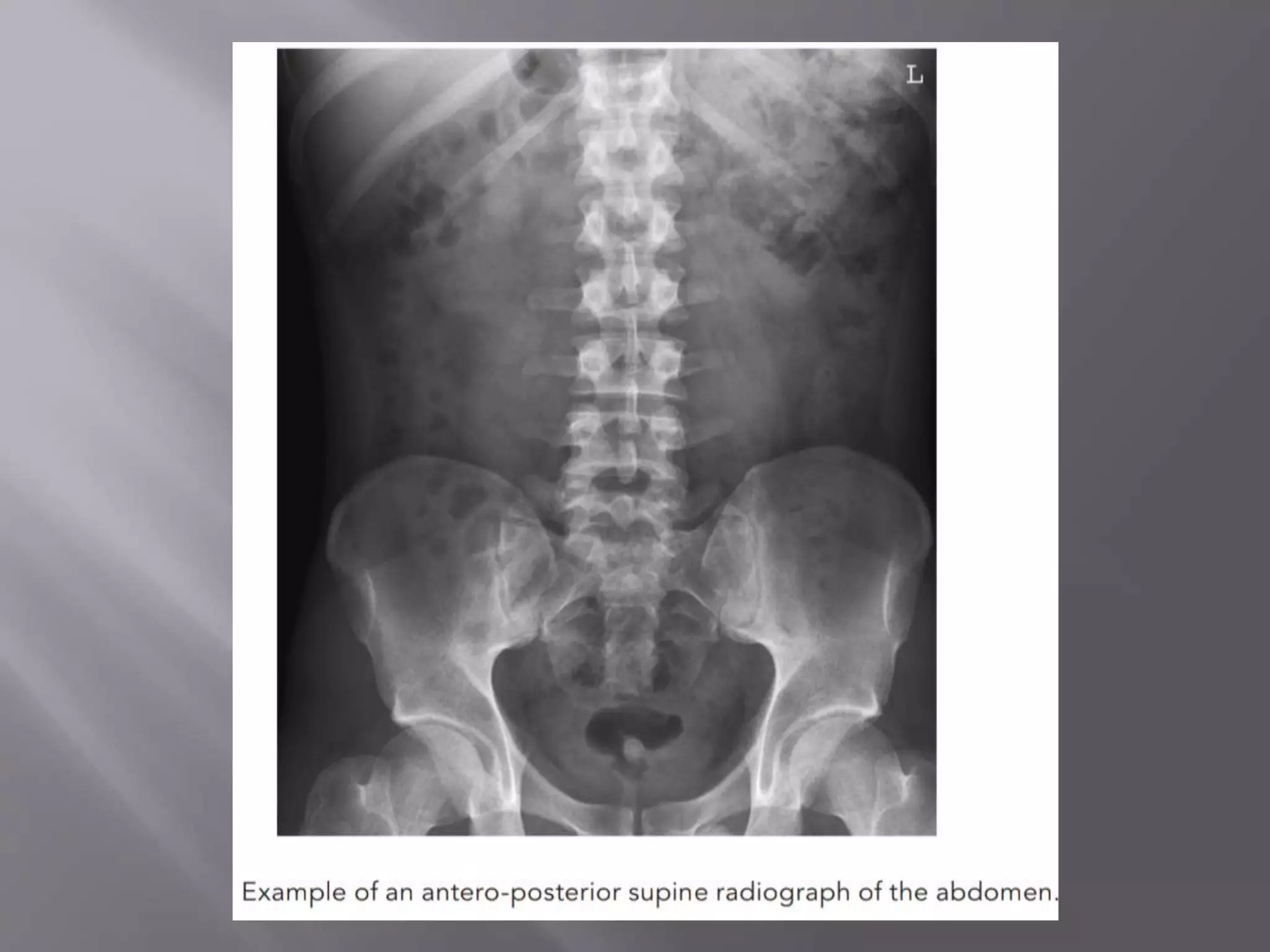
This document provides instructions for performing an abdominal x-ray. It describes positioning the patient supine on the imaging table with their pelvis equidistant from the top. The imaging receptor is placed below the pubic symphysis to include the whole abdomen. The beam is directed to the center of the receptor to include the lateral abdomen margins. The exposure is made on arrested respiration, ideally full expiration. Two images may be needed to ensure full coverage of a large abdomen.