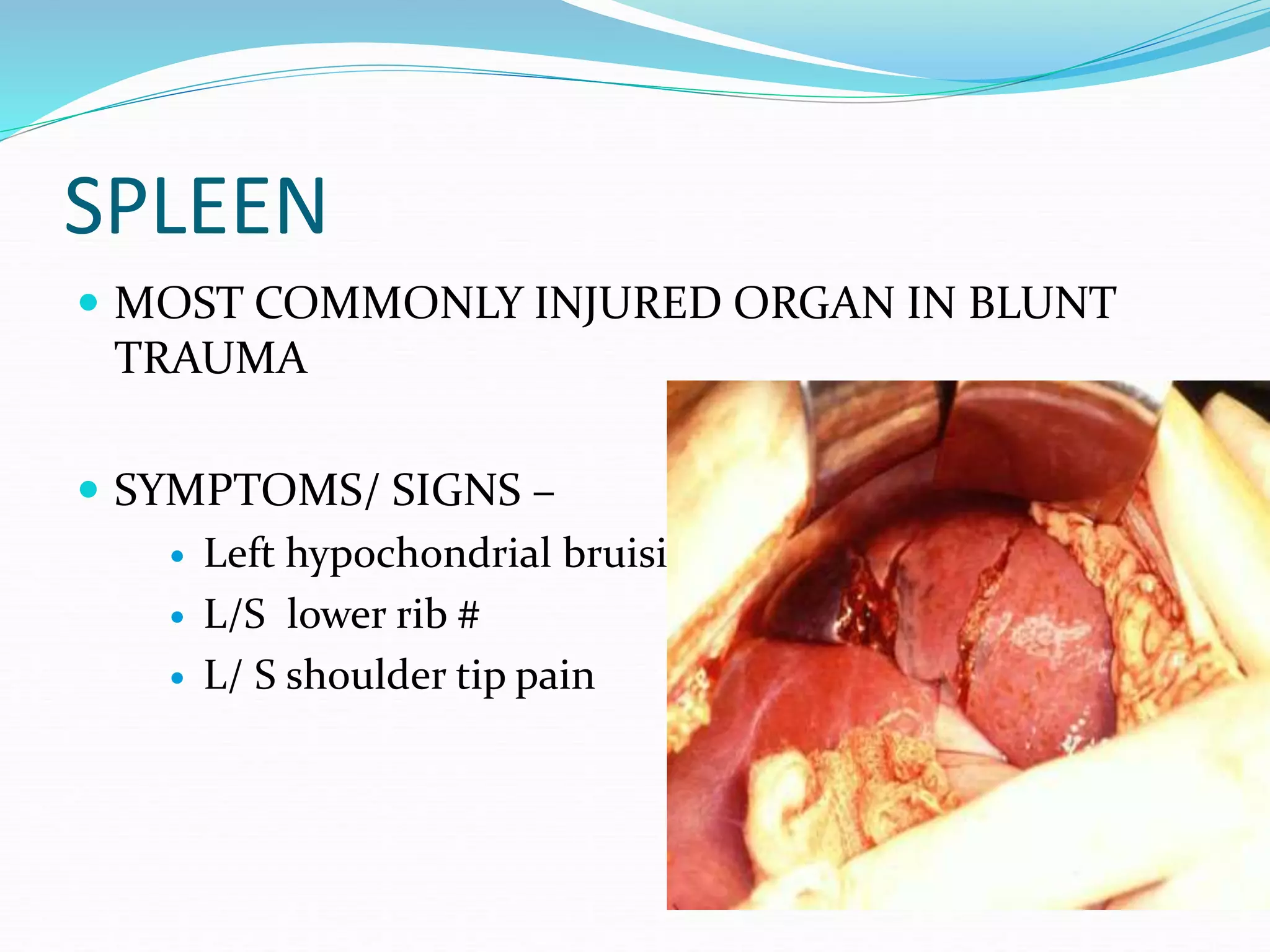
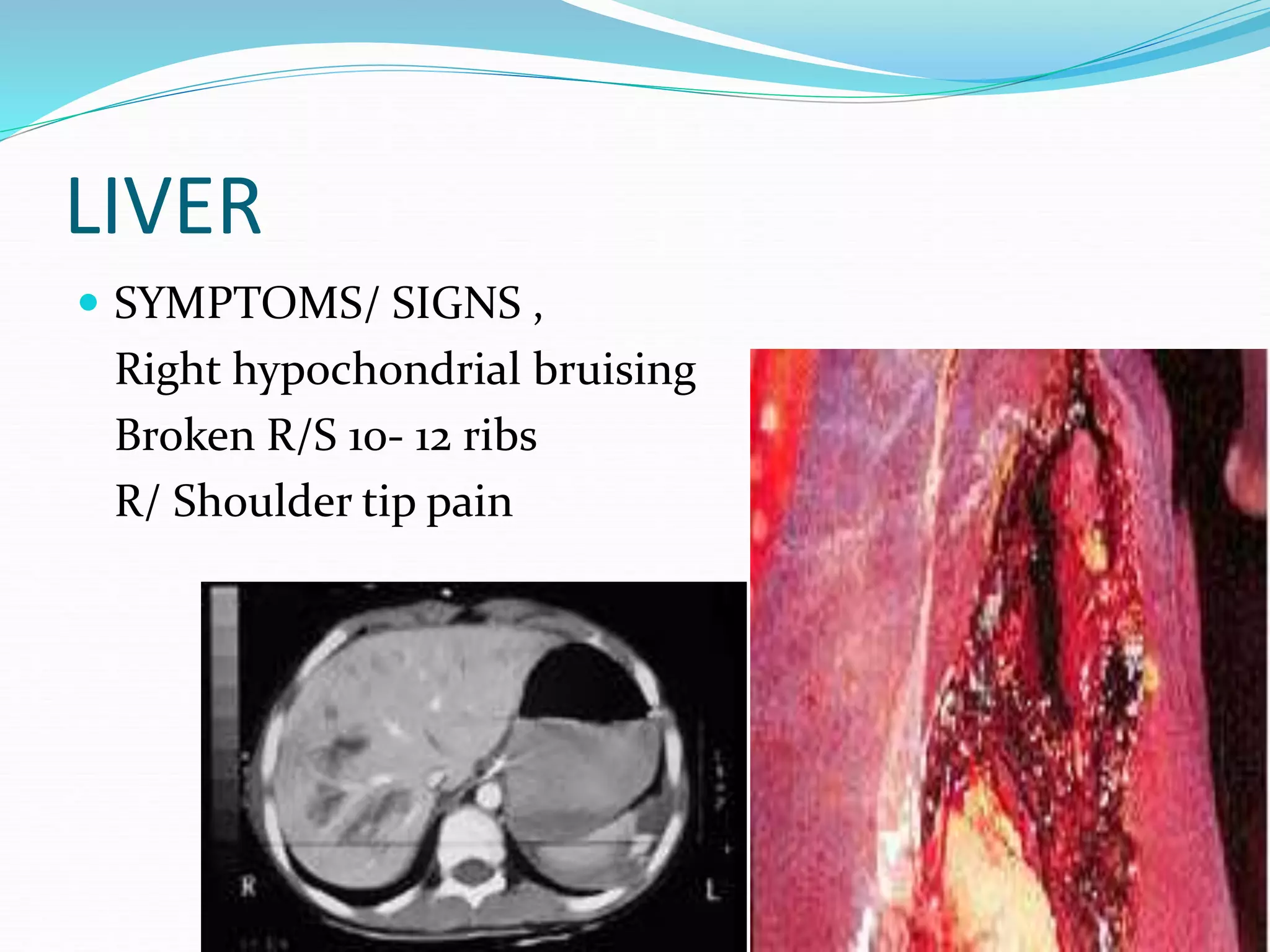
This document summarizes abdominal and pelvic trauma. It describes the commonly injured organs from blunt and penetrating trauma, including the liver, spleen, small bowel, and kidneys. Signs and symptoms and management strategies are provided for each organ. In general, exploratory laparotomy is indicated for hemodynamic instability, peritonitis, suspected organ injury on imaging, or deterioration; otherwise close observation or radiological interventions may be appropriate depending on the specific organ involved and patient stability.