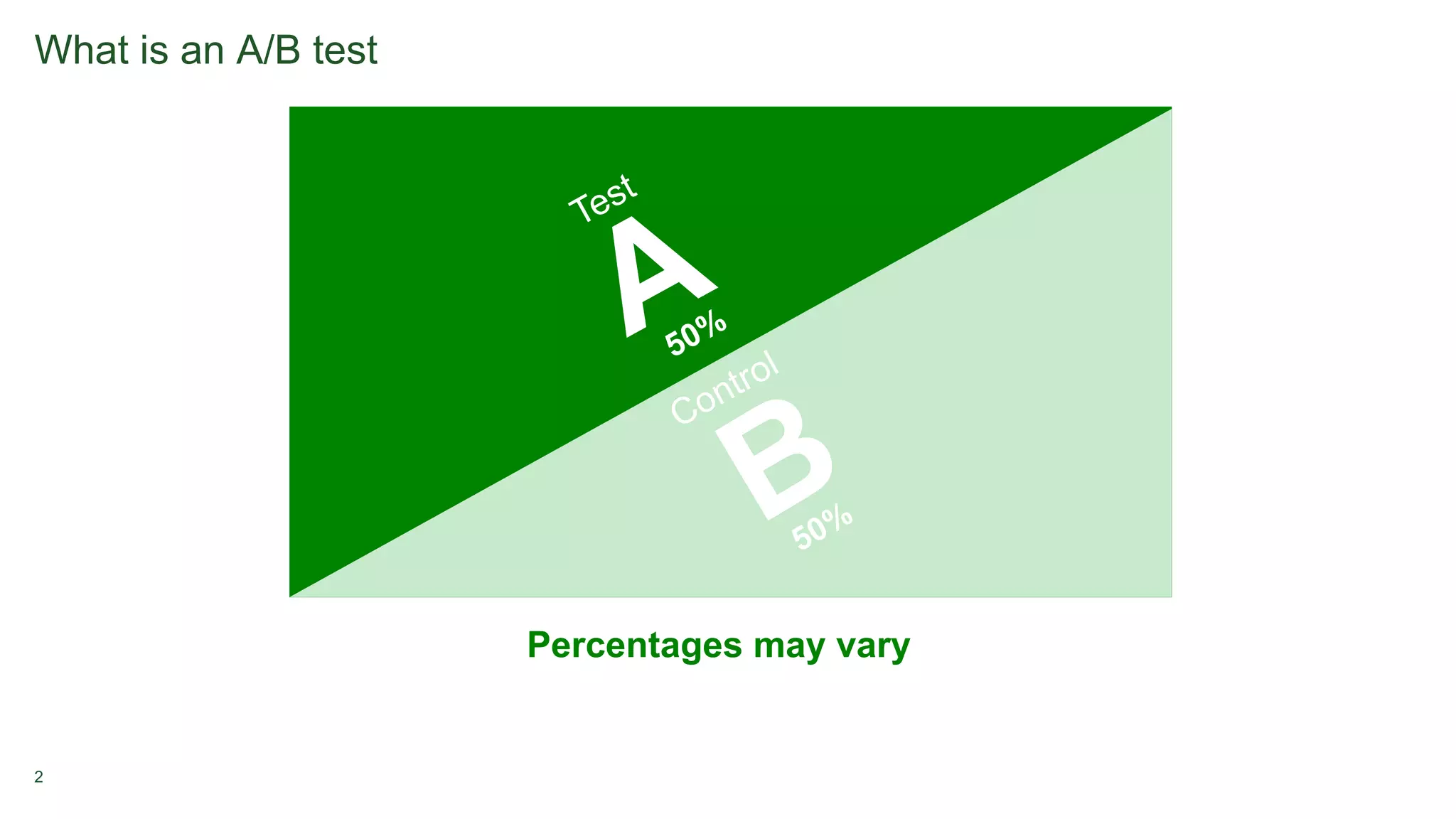
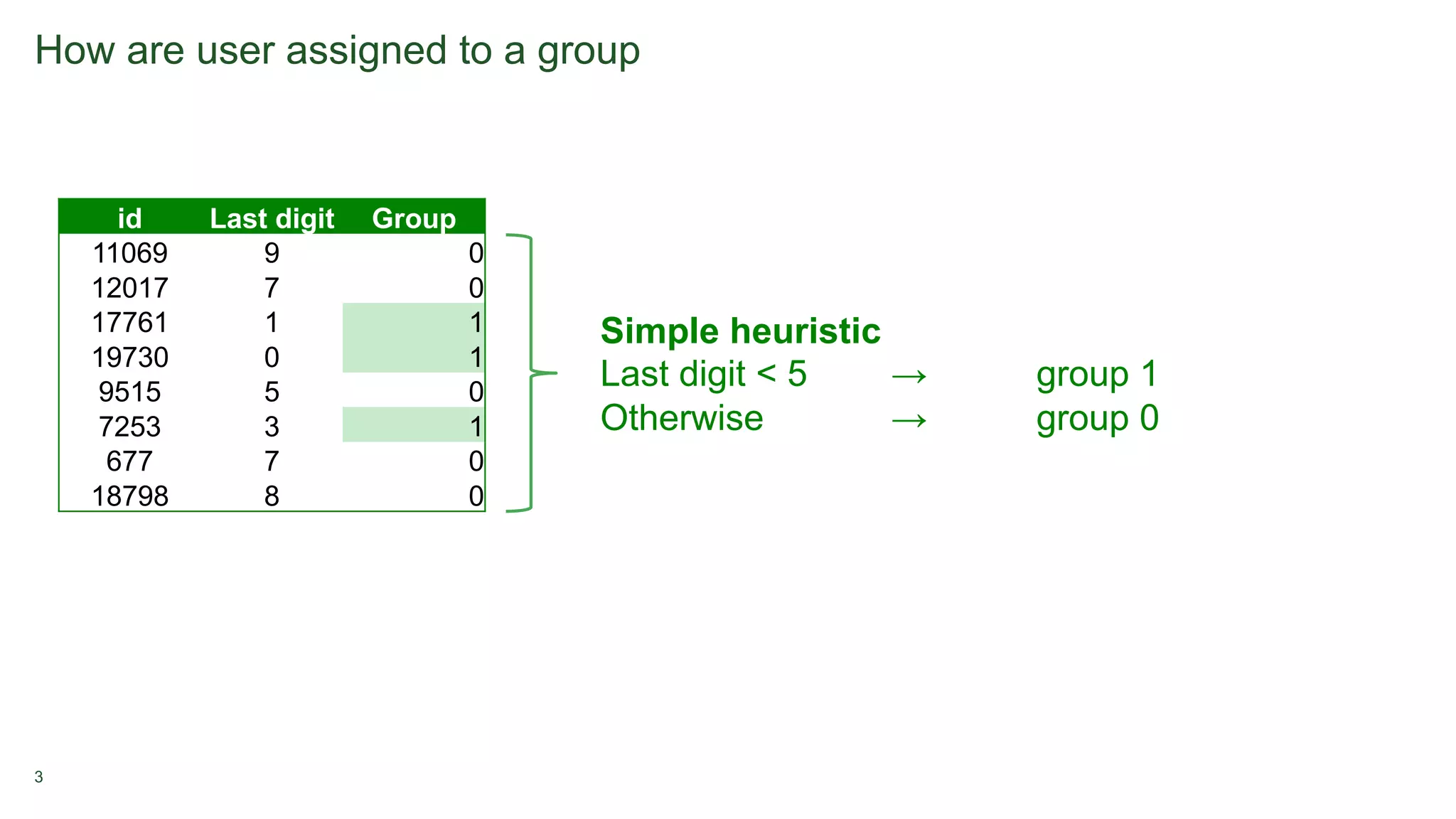
1. A/B testing involves splitting users into a test group that sees a new feature and a control group that sees the original version. Users are typically assigned randomly with equal percentages to each group.
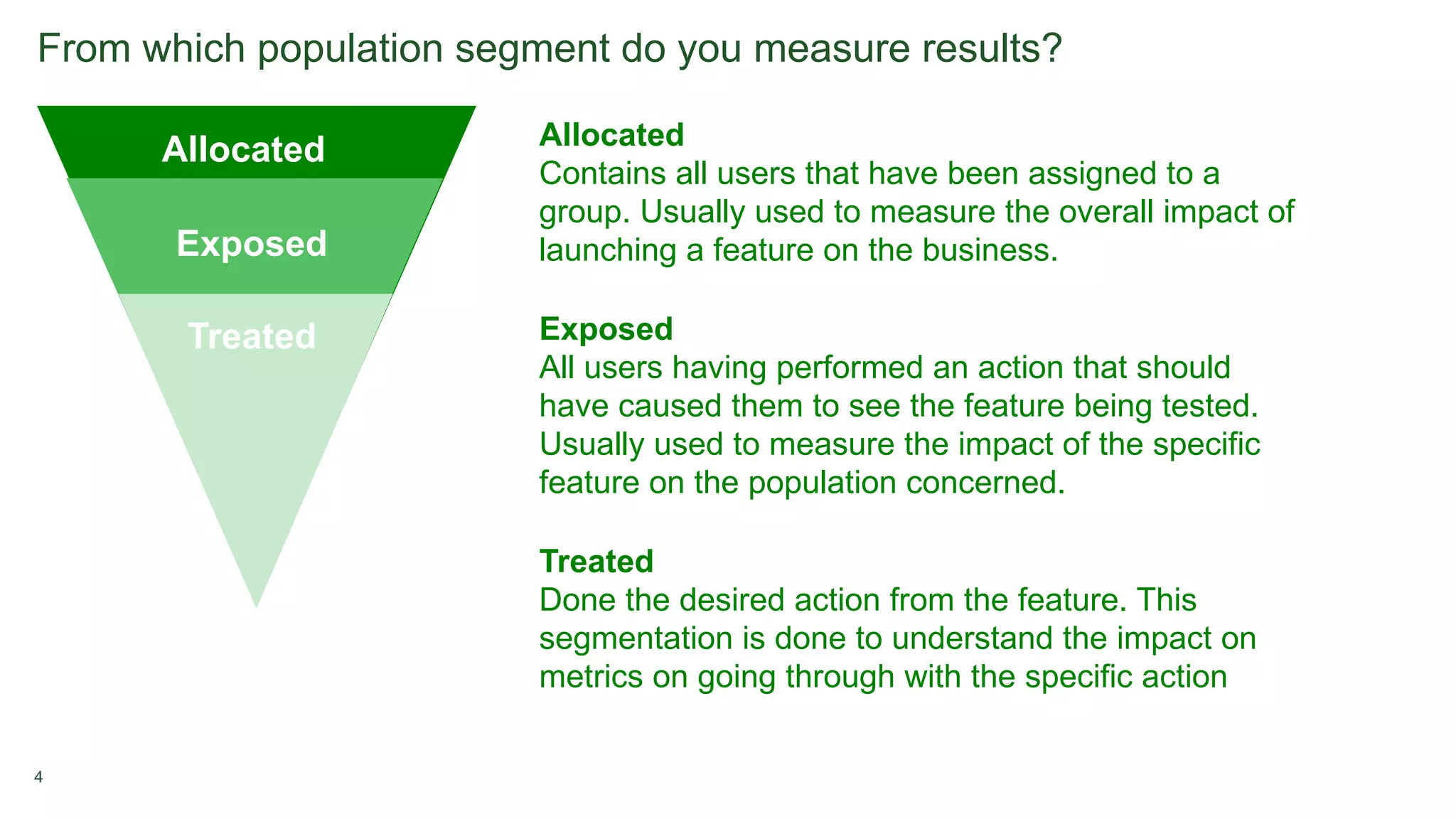
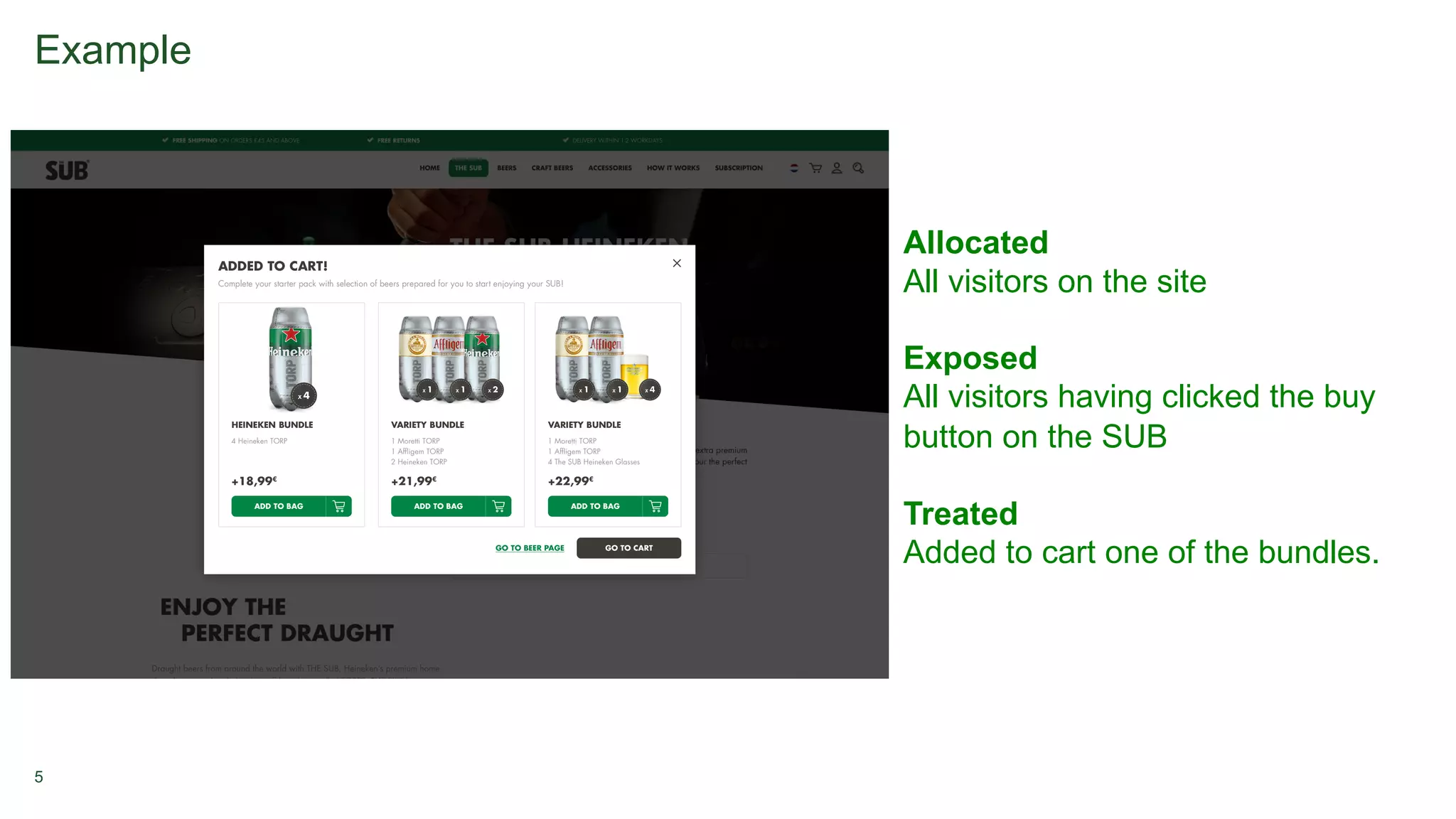
2. Metrics are tracked for both groups to measure the impact of the new feature, such as additions to cart or purchases. Significance testing determines if results are likely real or due to chance.
3. Long-term experiments require holding back some users from the test to measure novelty or learning curve effects over time.