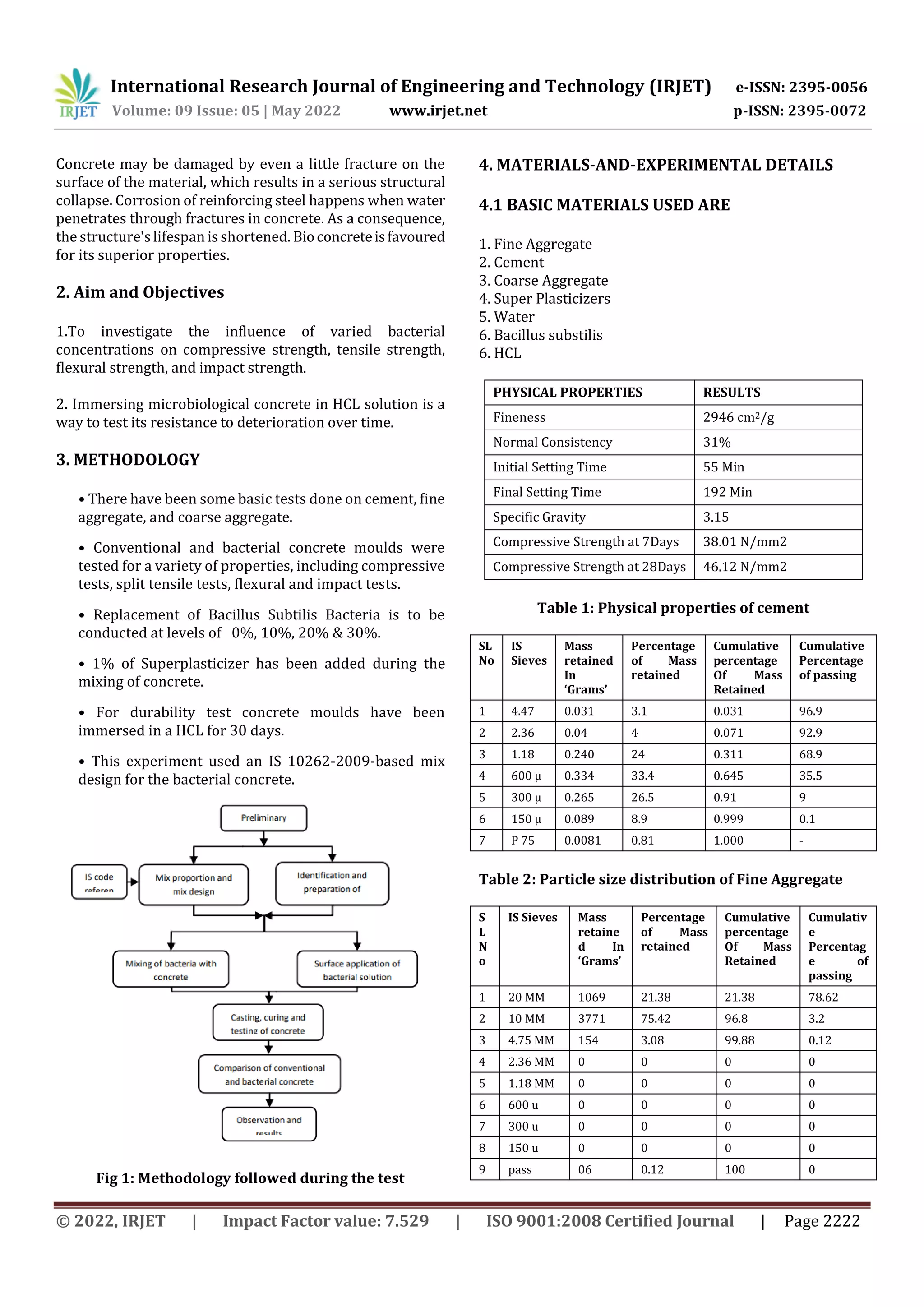
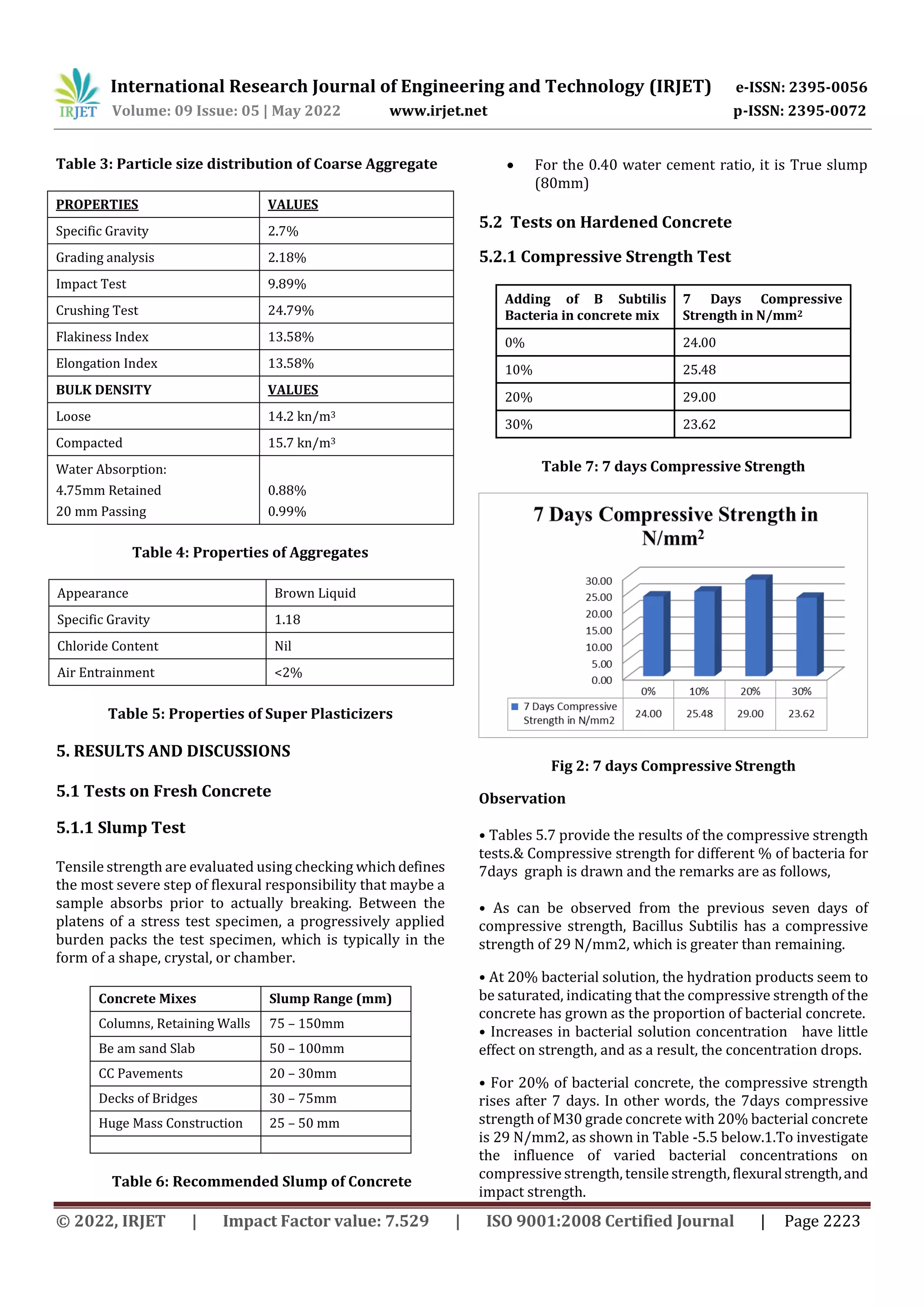
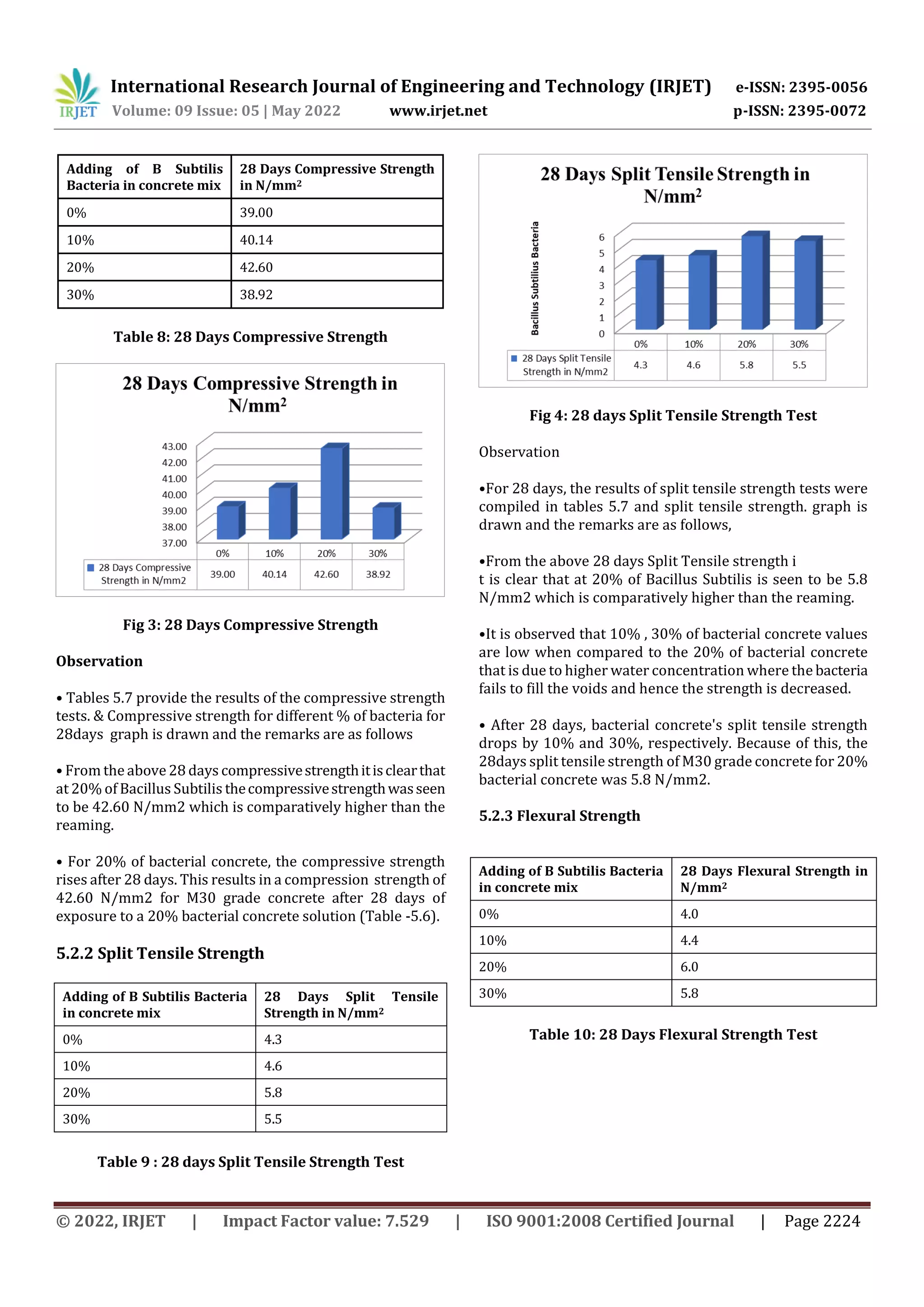
This study investigated the strength and durability properties of concrete containing Bacillus subtilis bacteria. Concrete mixtures were prepared with bacterial concentrations of 0%, 10%, 20%, and 30%. Specimens were tested after 7 and 28 days of curing. The 20% bacterial concrete achieved the highest compressive strength, split tensile strength, and flexural strength at both curing ages. Additionally, the 20% bacterial concrete performed best in durability testing where specimens were immersed in HCL for 30 days, maintaining the highest residual compressive strength. The results indicate that Bacillus subtilis bacteria can improve the strength and durability of concrete, with an optimal concentration of 20%.