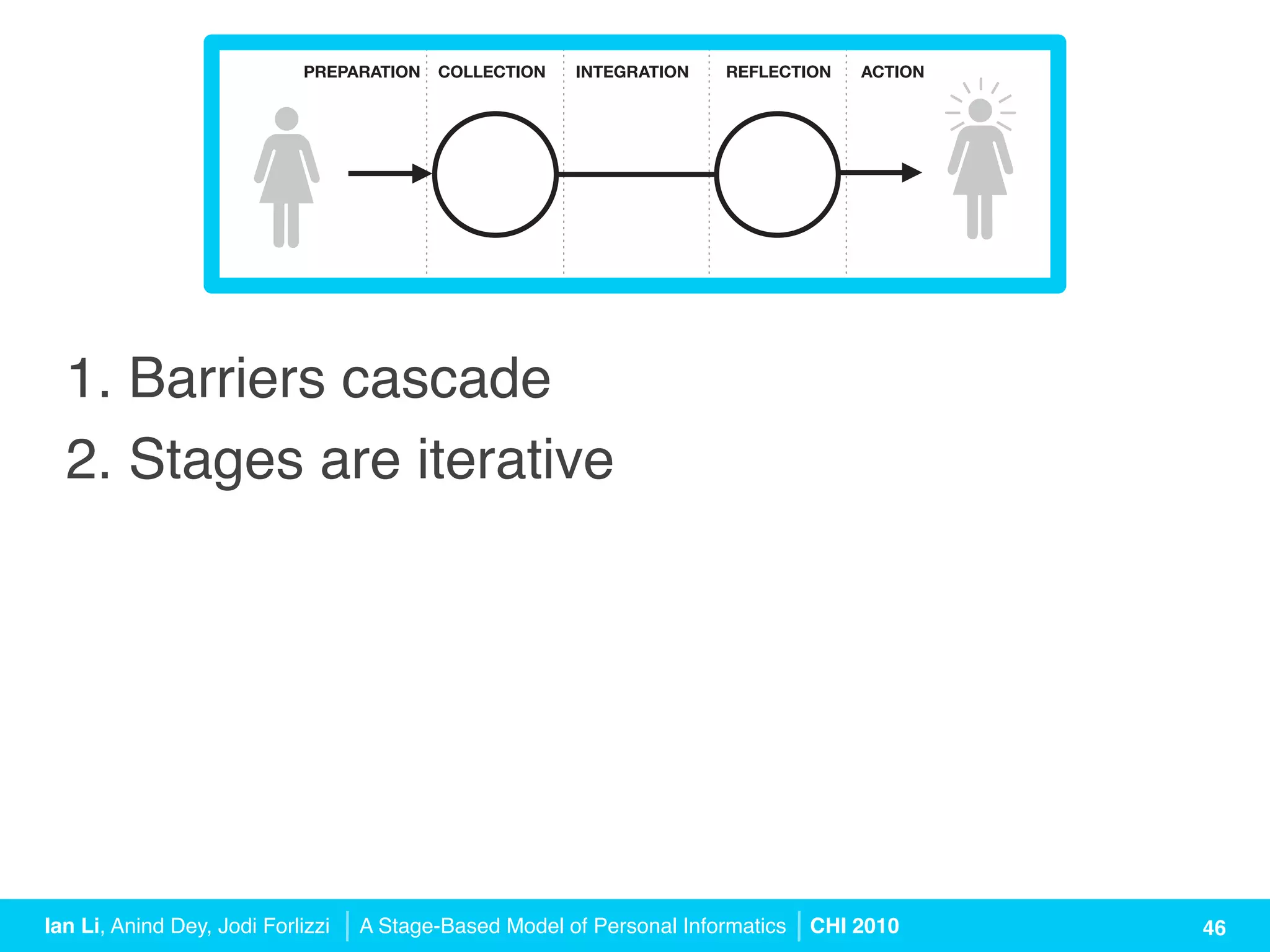
The document presents a stage-based model of personal informatics systems, which aims to help individuals collect and reflect on personal data to gain self-knowledge. It outlines five stages: preparation, collection, integration, reflection, and action, highlighting various barriers users face at each stage. The model emphasizes the iterative nature of these stages and offers design guidelines to enhance user experience in personal informatics tools.











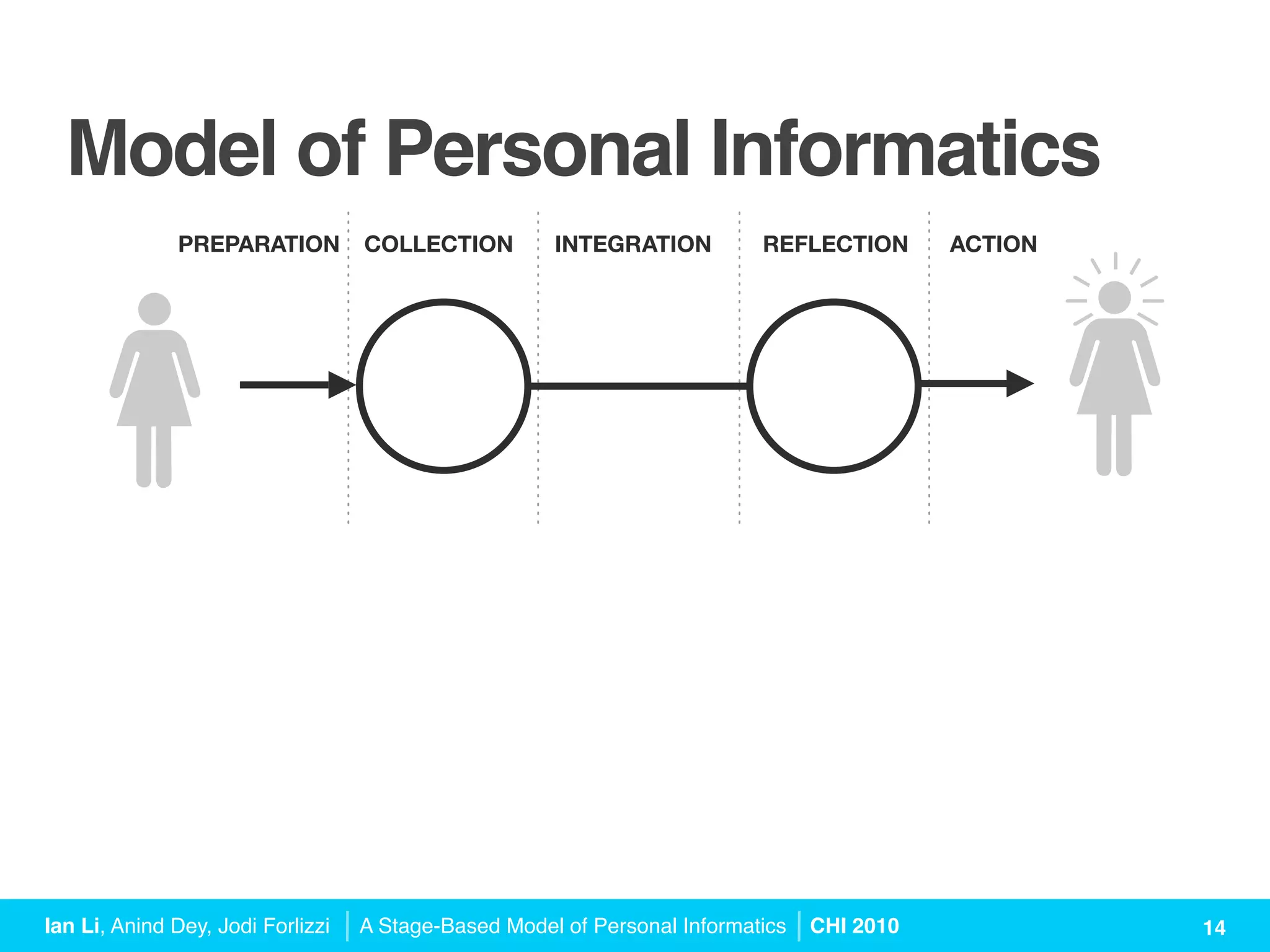


















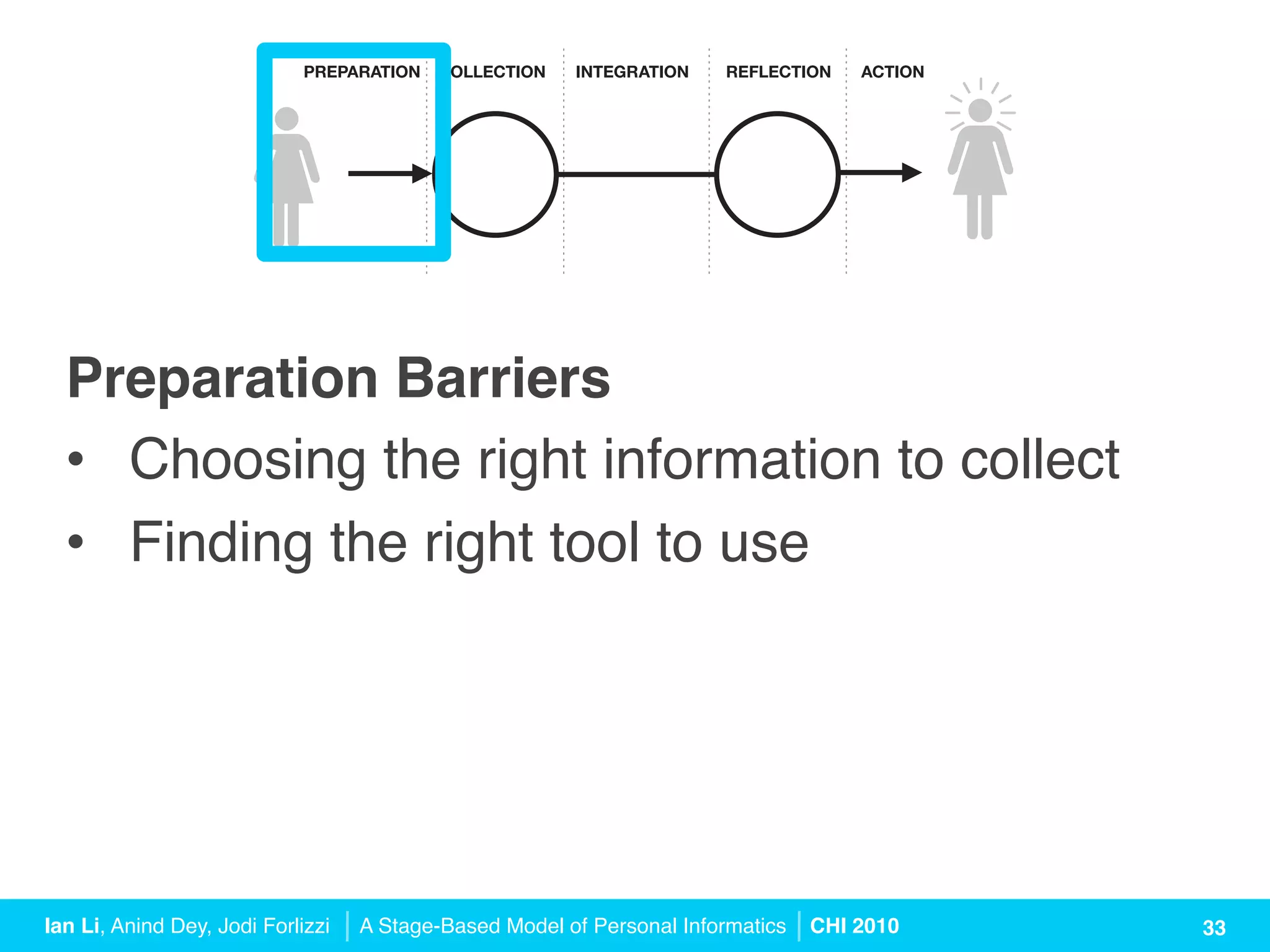





![PREPARATION COLLECTION INTEGRATION REFLECTION ACTION
Integration Barriers
“Itʼd be neat if I could
• Organization
graph [the data]
• Scattered straight from the web
site instead of
visualizations
manually typing in the
• Transcribing data
data to a
• Multiple inputs
spreadsheet.”
Ian Li, Anind Dey, Jodi Forlizzi A Stage-Based Model of Personal Informatics CHI 2010
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pi-draft5web-pptx-100412194411-phpapp02/75/A-Stage-Based-Model-of-Personal-Informatics-Systems-CHI-2010-Talk-39-2048.jpg)