A Comprehensive Guide to Oral Biopsy | top 10 dental colleges in Bangalore
- 1. A Comprehensive Guide to Oral Biopsy | top 10 dental colleges in bangalore In the vast landscape of dentistry and oral pathology, the role of oral biopsy emerges as a beacon of diagnostic clarity amidst the complexities of oral lesions. With its ability to unveil the underlying histopathological features of oral abnormalities, oral biopsy serves as an indispensable tool for clinicians in the diagnosis and management of a wide array of oral conditions. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of oral biopsy, exploring its significance, procedural nuances, clinical applications, and emerging trends. Understanding Oral Biopsy And Its Significance An oral biopsy involves the surgical removal of a small tissue sample from the oral cavity for microscopic examination. This procedure is typically performed under local anaesthesia, ensuring minimal discomfort for the patient. The collected tissue is then subjected to histopathological analysis, which is scrutinised by a pathologist under a microscope. The examination aims to identify cellular abnormalities, inflammatory changes, or neoplastic growths present within the tissue. Oral biopsy stands as a cornerstone in the diagnosis and management of oral lesions, ranging from benign entities to potentially malignant or malignant conditions. Unlike clinical examination alone, which may provide valuable insights into the nature of oral lesions, histopathological evaluation through biopsy offers a definitive diagnosis, thereby guiding appropriate treatment interventions. Moreover, oral biopsy plays a pivotal role in prognostication, aiding clinicians in assessing the aggressiveness and potential for malignant transformation of certain oral lesions.
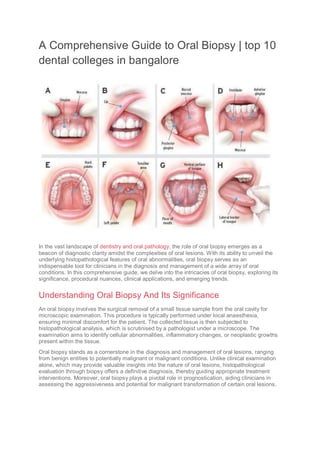
- 2. Understanding the Diagnostic Process of Oral Biopsies The diagnostic process of oral biopsies is a critical component of oral pathology, providing essential information for the accurate diagnosis and subsequent management of various oral lesions. This process involves a systematic approach encompassing clinical evaluation, lesion identification, biopsy selection, tissue sampling, histopathological analysis, and interpretation of findings. Let’s explore each step in detail: Clinical Evaluation: The diagnostic journey begins with a comprehensive clinical examination of the oral cavity. Dentists, oral surgeons, or oral pathologists carefully assess the patient’s medical history, oral hygiene status, and any associated symptoms or complaints. During the examination, attention is focused on identifying abnormal lesions, including ulcers, white or red patches, lumps, swellings, or other mucosal changes. Lesion Identification: Suspicious oral lesions are identified based on their clinical presentation, location, size, and associated features. Lesions that exhibit concerning characteristics such as irregular borders, induration, ulceration, rapid growth, bleeding, or associated pain may raise suspicion for malignancy or other significant pathology. Lesions are categorised according to their clinical appearance, which helps guide the selection of appropriate biopsy techniques. Biopsy Selection: The selection of the biopsy technique depends on various factors, including the size, location, and clinical appearance of the lesion, as well as the suspected diagnosis and patient preferences. Common biopsy techniques include incisional biopsy, excisional biopsy, punch biopsy, shave biopsy, and brush biopsy. Each technique has its advantages and limitations, and the choice of biopsy method is tailored to the individual patient’s needs and the nature of the lesion. Tissue Sampling: Once the decision to perform a biopsy is made, the next step involves obtaining a representative tissue sample from the lesion. Local anaesthesia is typically administered to ensure patient comfort during the procedure. Using appropriate instruments, such as a scalpel, punch biopsy tool, or brush biopsy device, a sample of the lesion is collected, ensuring adequate depth and breadth for histopathological analysis. Hemostasis is achieved as necessary to minimise bleeding and facilitate specimen collection. Histopathological Analysis: The harvested tissue specimen is submitted to the pathology laboratory for histopathological examination. The specimen undergoes a series of processing steps, including fixation, embedding, sectioning, staining, and microscopic evaluation. Histopathological analysis allows for the assessment of cellular morphology, tissue architecture, and pathological changes within the lesion. Common findings may include inflammation, dysplasia, carcinoma, fibrosis, cystic changes, or specific tumour types. Interpretation of Findings: The histopathological findings are interpreted by skilled oral pathologists, who provide a comprehensive report detailing the diagnosis, histological features, and any relevant prognostic information. The final diagnosis guides subsequent treatment decisions, including the need for further surgical intervention, medical management, or multidisciplinary care. In cases of malignancy, the histopathological diagnosis may also influence staging, prognosis, and treatment planning. This process is essential for accurate diagnosis, prognosis, and subsequent management of various oral lesions, ultimately contributing to improved patient outcomes in the field of oral pathology and dentistry. Types of Oral Biopsies Oral biopsies encompass a variety of techniques used to obtain tissue samples from oral lesions for diagnostic evaluation. The choice of biopsy type depends on factors such as the size and
- 3. location of the lesion, the suspected diagnosis, and the clinician’s preference. Here are some common types of oral biopsies: Incisional Biopsy In an incisional biopsy, a portion of the lesion is surgically excised for histopathological examination. Indications: Incisional biopsies are typically performed for larger lesions or those with indeterminate clinical features. Procedure: After administering local anaesthesia, a scalpel is used to incise and remove a representative section of the lesion. Hemostasis is achieved, and the incision is closed with sutures. Excisional Biopsy Excisional biopsies are the removal of the entire lesion. Indications: Excisional biopsies are preferred for smaller lesions or those suspected to be benign.
- 4. Procedure: Following local anaesthesia, the entire lesion is surgically excised, ensuring clear margins. The excised tissue is then submitted for histopathological analysis. Punch Biopsy Punch biopsies involve the use of a circular cutting tool to obtain a cylindrical tissue sample. Indications: Punch biopsies are suitable for small, accessible lesions, especially on the gingiva or palate. Procedure: After anaesthesia, a punch biopsy instrument is used to remove a core of tissue from the lesion. The sampled tissue is then sent for histopathological examination. Shave Biopsy Shave biopsies involve the superficial removal of tissue layers from the surface of the lesion. Indications: Shave biopsies are performed for superficial lesions or those with well- defined borders. Procedure: After anaesthesia, a scalpel or razor blade is used to shave off a thin layer of tissue from the surface of the lesion. The shaved tissue is collected and sent for histopathological analysis. Brush Biopsy (Oral Cytology) Brush biopsies involve the collection of cells from the surface of the lesion using a specialised brush or cytology brush. Indications: Brush biopsies are used for lesions that are difficult to access or when traditional biopsy methods are not feasible. Procedure: A cytology brush is gently rubbed against the lesion’s surface to collect cellular material. The collected cells are then transferred onto a glass slide, fixed, stained, and examined under a microscope for cytological abnormalities. Incisional Laser Biopsy Laser-assisted biopsy involves the use of a laser to incise and remove tissue from the lesion. Indications: Laser biopsy may be preferred for lesions located in areas with limited access or for patients who may benefit from reduced bleeding and postoperative discomfort. Procedure: Laser energy is delivered to incise and remove a portion of the lesion. The excised tissue is then collected and sent for histopathological analysis. Each type of oral biopsy has its advantages and limitations, and the choice of biopsy technique depends on various factors, including the nature of the lesion, patient factors, and clinician
- 5. expertise. The ultimate goal of oral biopsy is to obtain an accurate diagnosis, which guides subsequent treatment decisions and improves patient outcomes. Emerging Trends and Future Directions: Advancements in technology and research continue to shape the landscape of oral biopsy, with emerging trends focused on enhancing diagnostic accuracy, minimising invasiveness, and optimising patient outcomes. Molecular techniques such as immunohistochemistry, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), and next-generation sequencing hold promise in elucidating the molecular signatures of oral lesions, thereby refining diagnostic criteria and prognostic stratification. Furthermore, non-invasive diagnostic modalities such as salivary biomarkers, optical coherence tomography (OCT), and confocal microscopy are being explored as adjuncts to traditional biopsy techniques, offering potential benefits in early detection and surveillance of oral lesions. Sum Up In conclusion, oral biopsy stands as a cornerstone in the diagnosis and management of oral pathology, offering invaluable insights into the histopathological features of oral lesions. By unravelling the mysteries of oral pathology, oral biopsy empowers clinicians to make informed treatment decisions, prognostic assessments, and personalised patient care plans. As we navigate the evolving landscape of oral healthcare, the role of oral biopsy remains indispensable in our quest for early detection, accurate diagnosis, and improved patient outcomes in the realm of oral medicine and dentistry. To ensure that our students at RajaRajeswari Dental College & Hospital learn the significance of oral biopsy, the Department of oral & Maxillofacial Pathology and microbiology organised an intern study club seminar where the department pioneers delivered lectures on the diagnosis and significance of oral biopsy. If you are intrigued by the subjects of dentistry visit us and learn more.