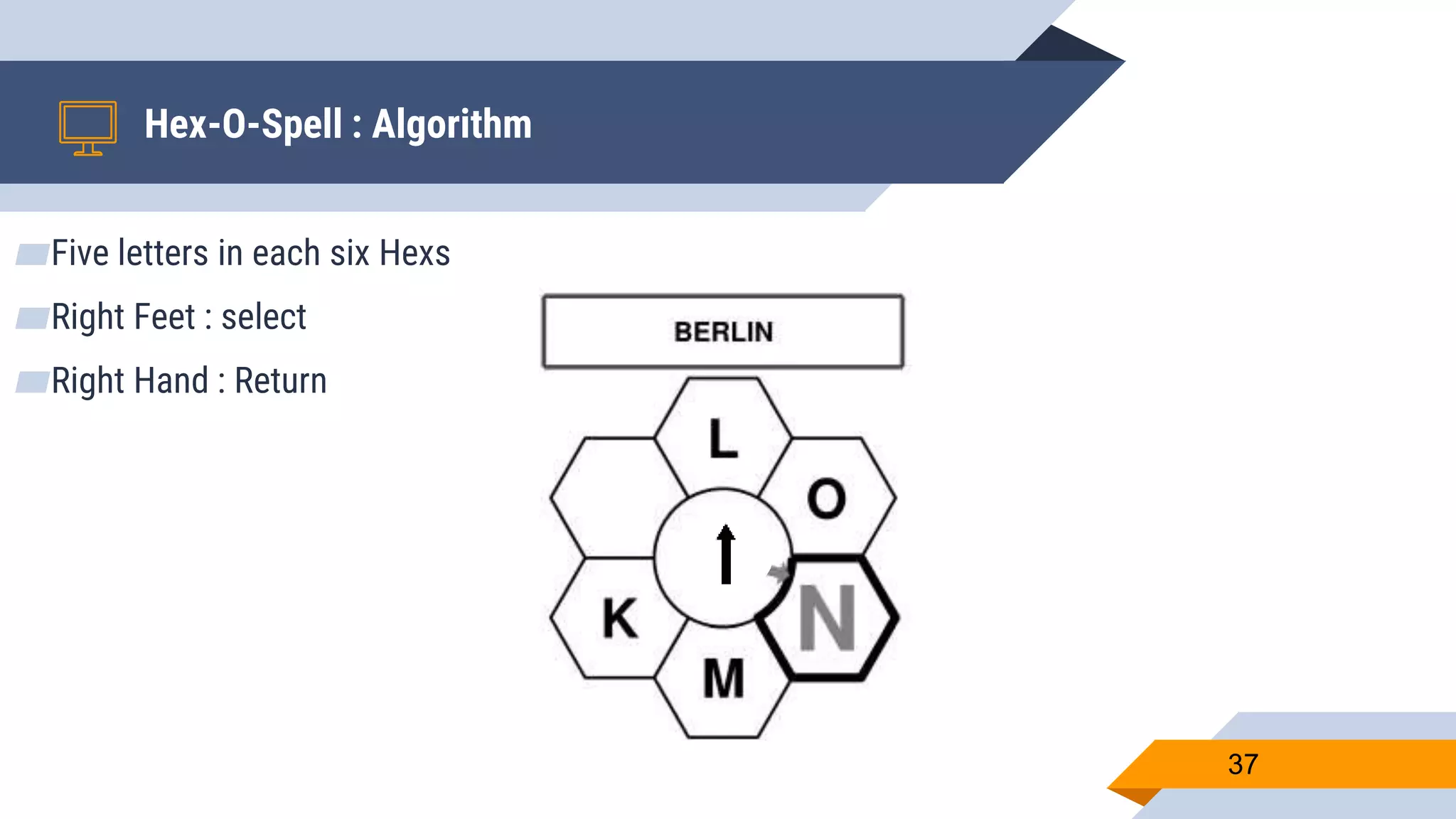
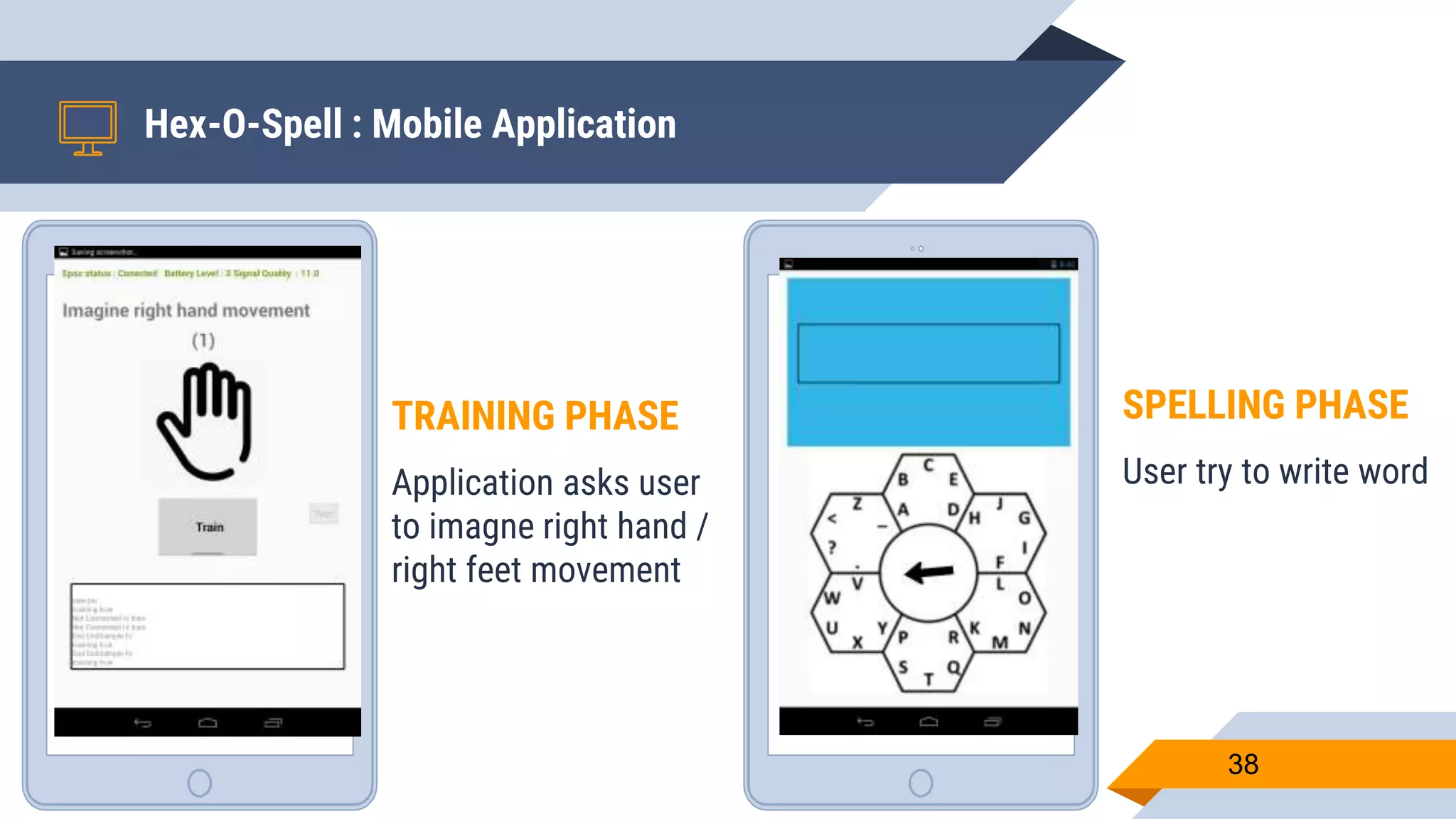
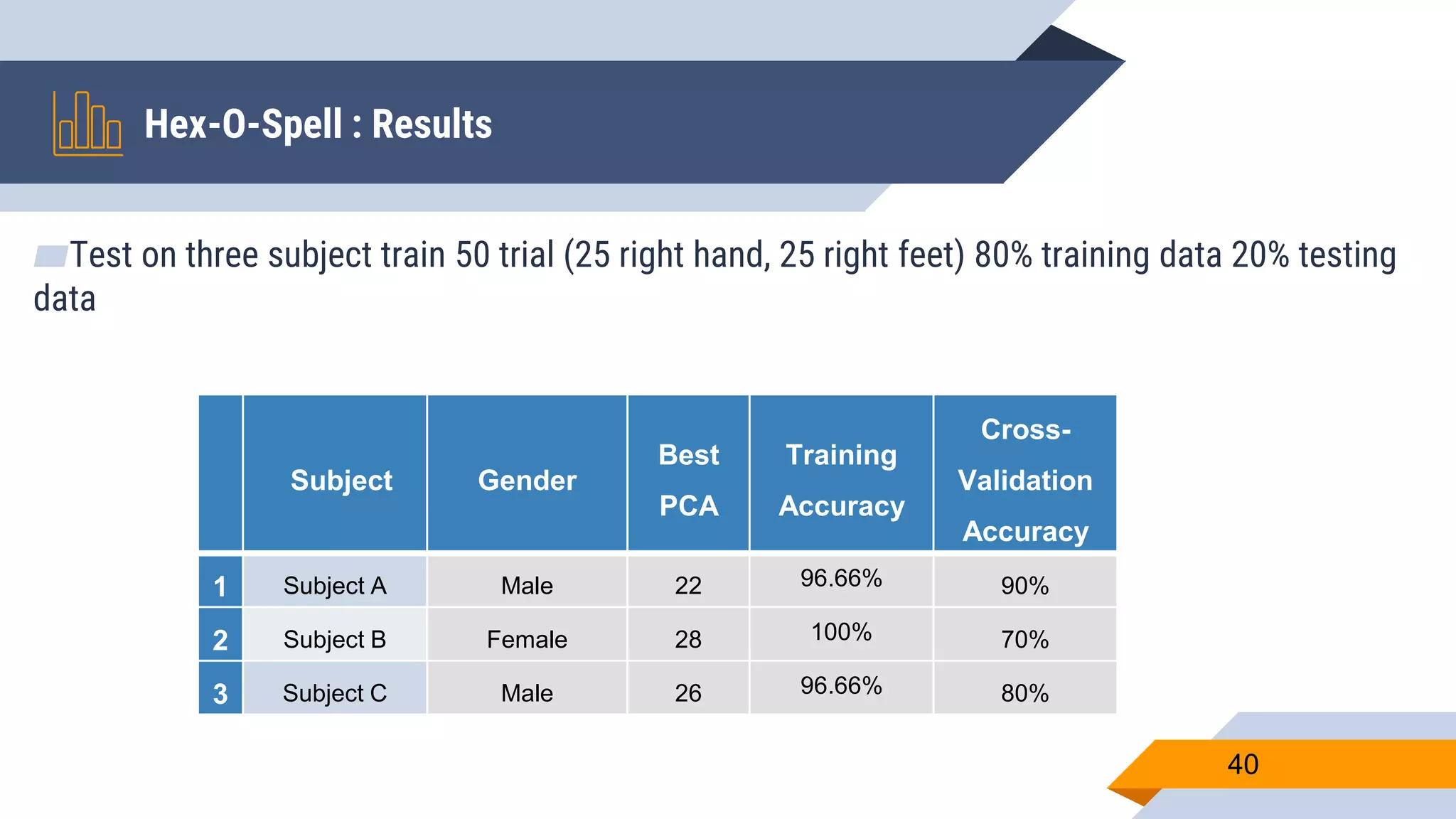
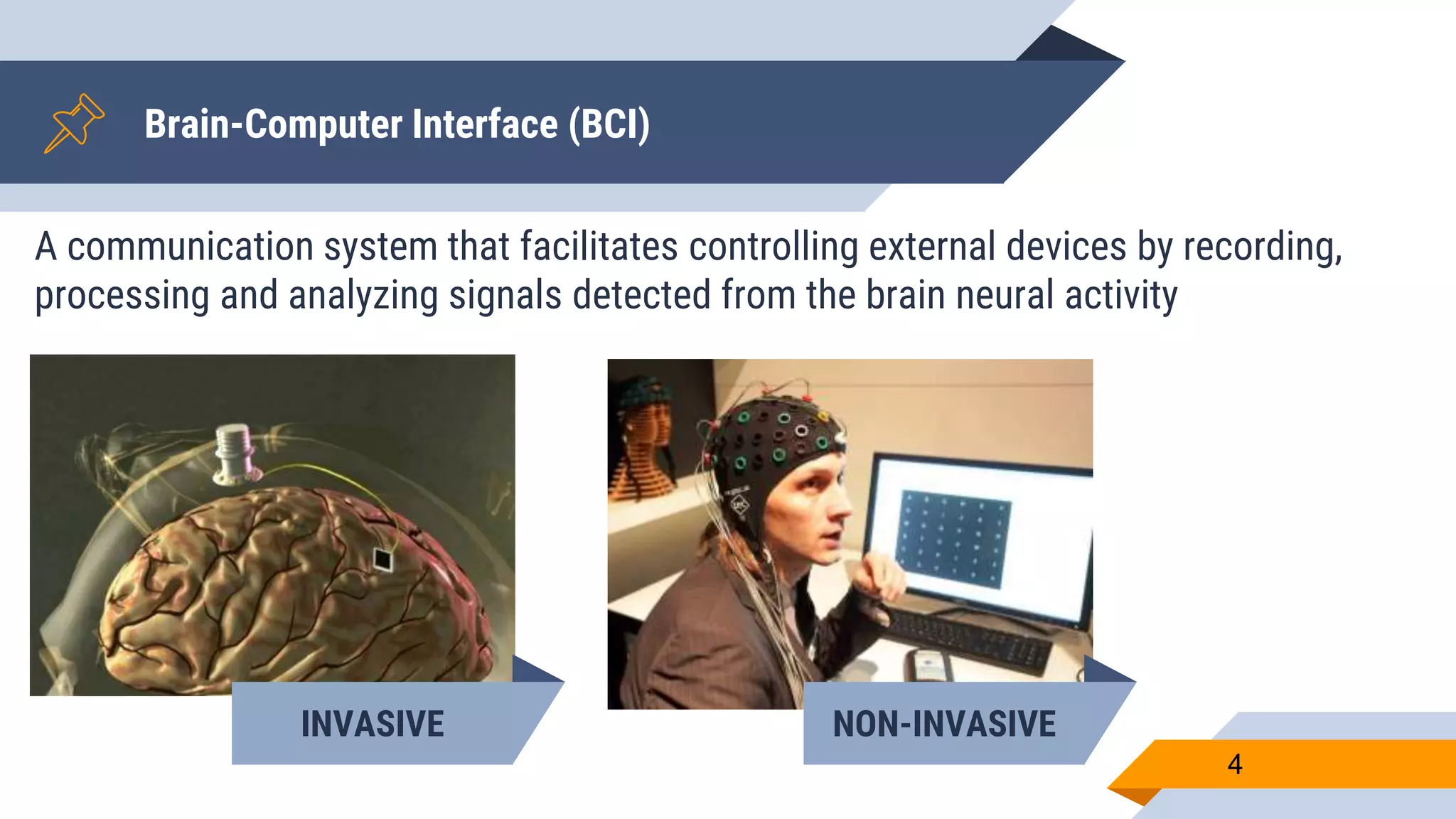
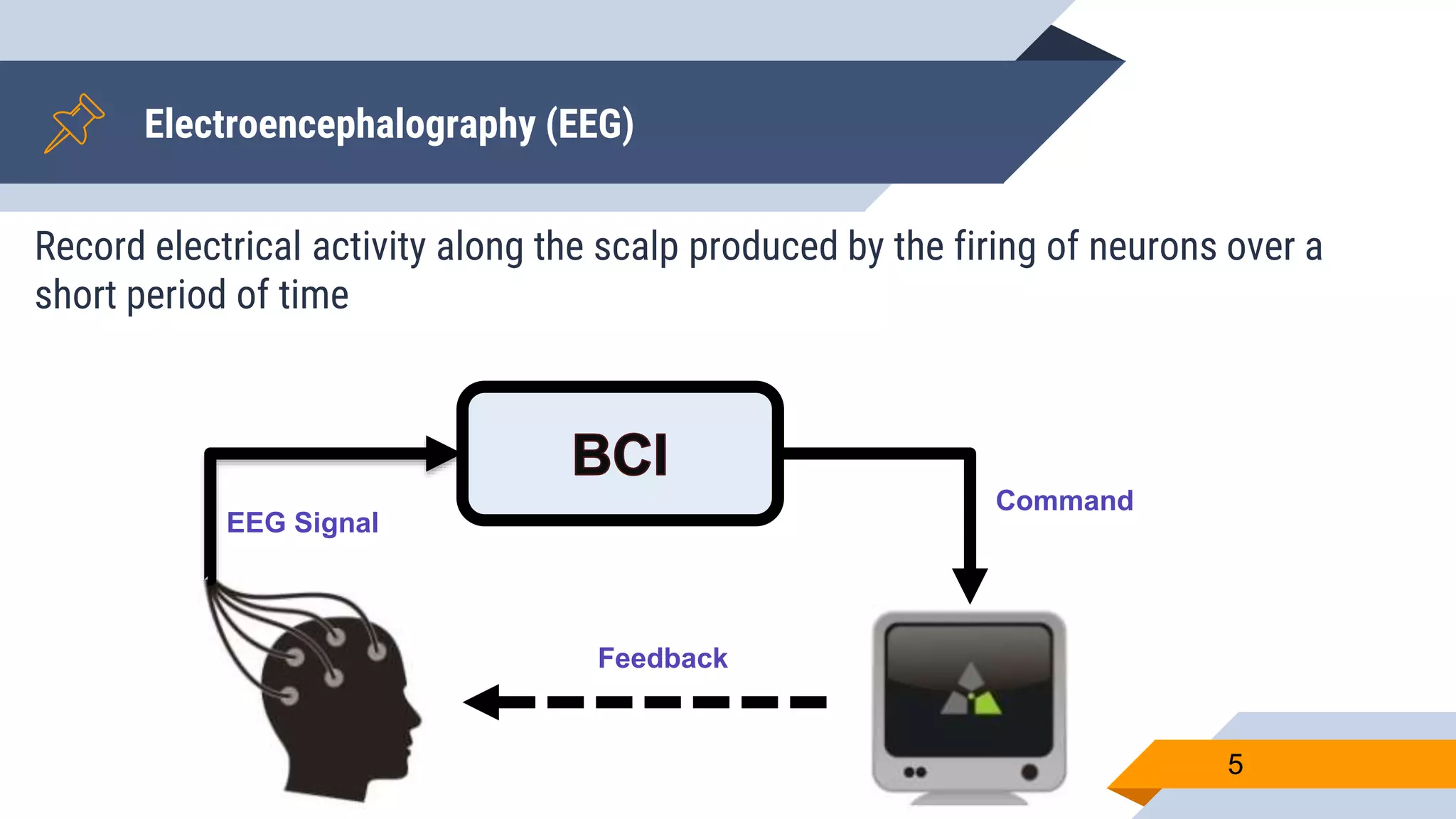
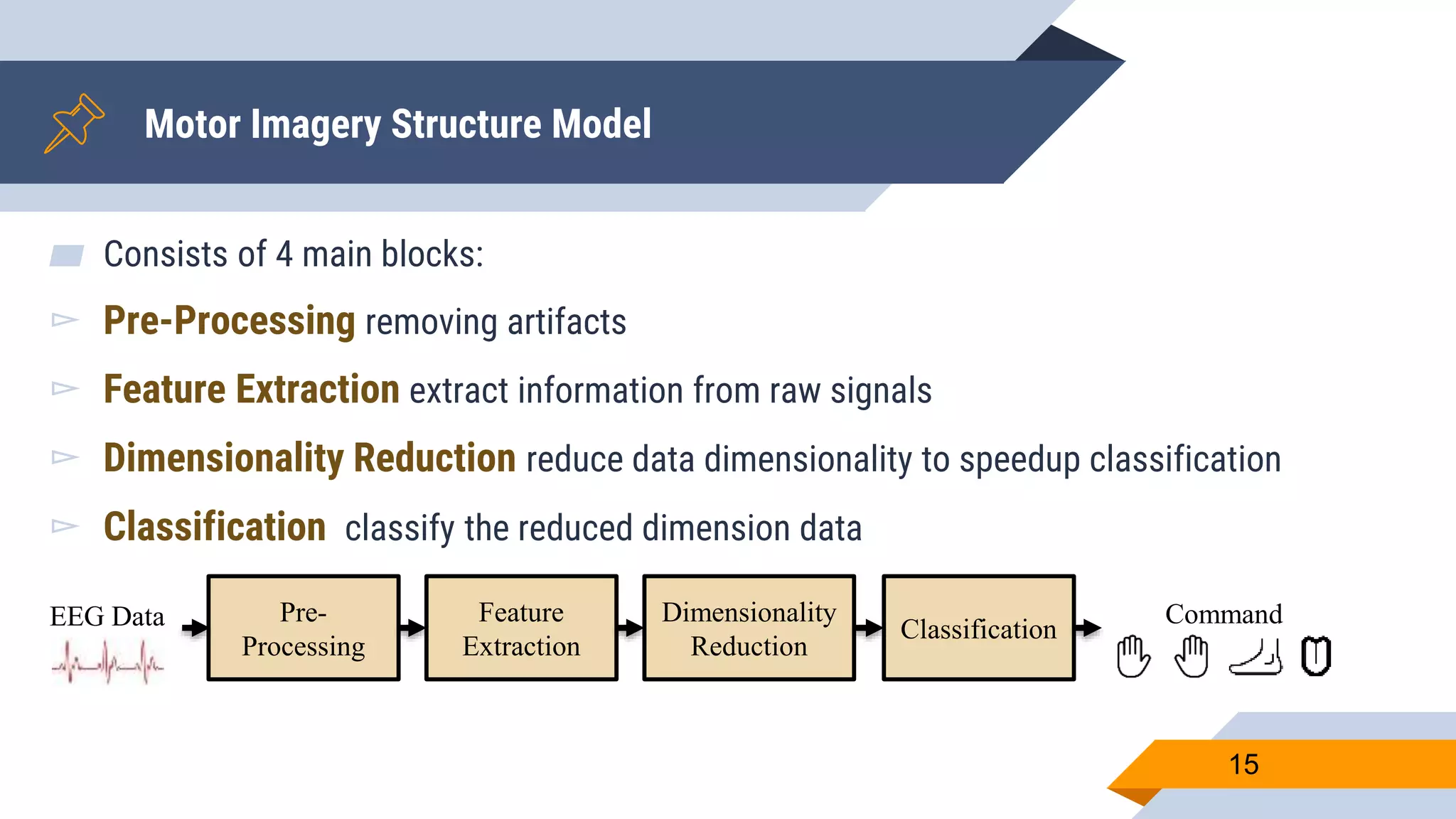
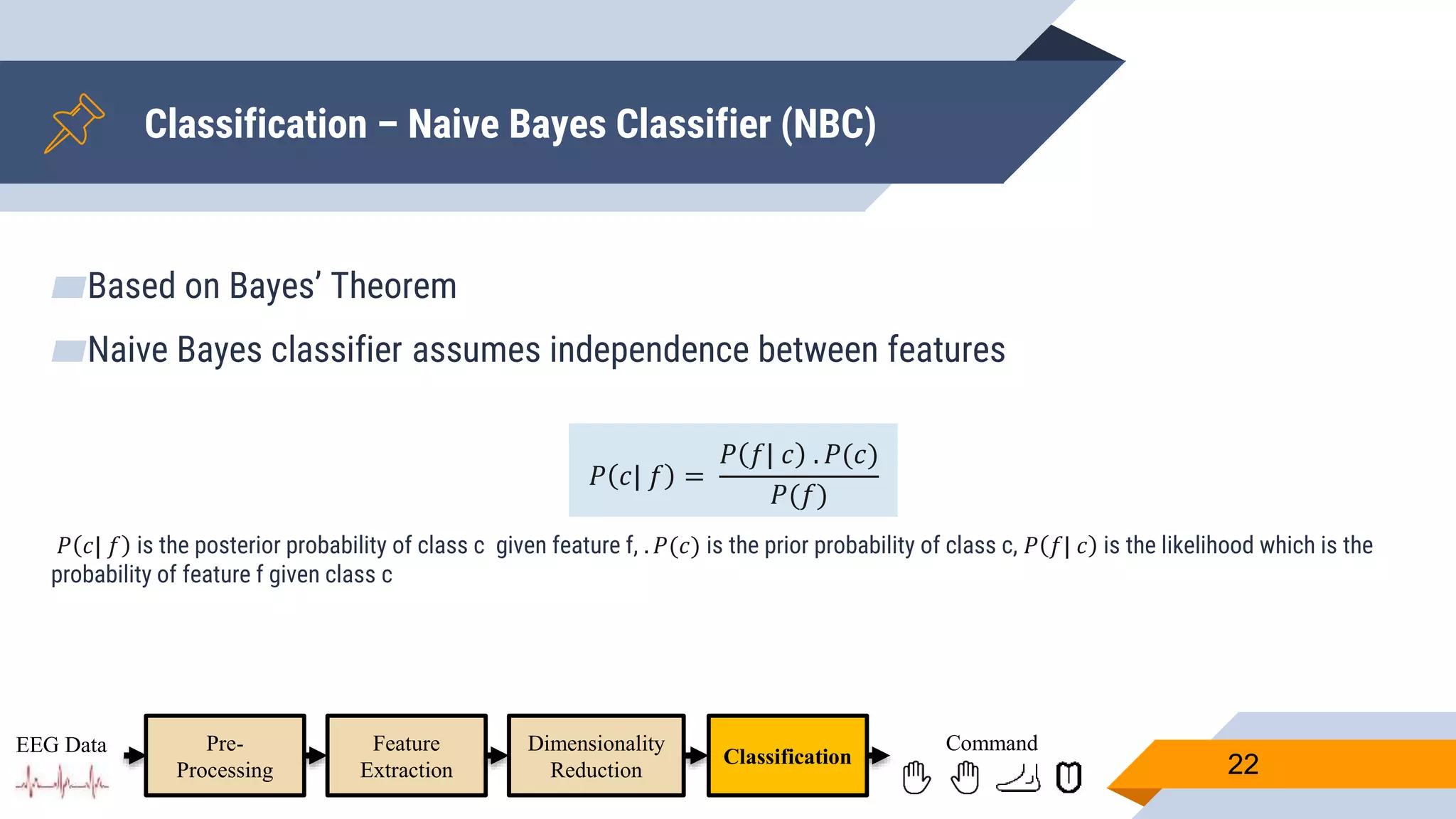
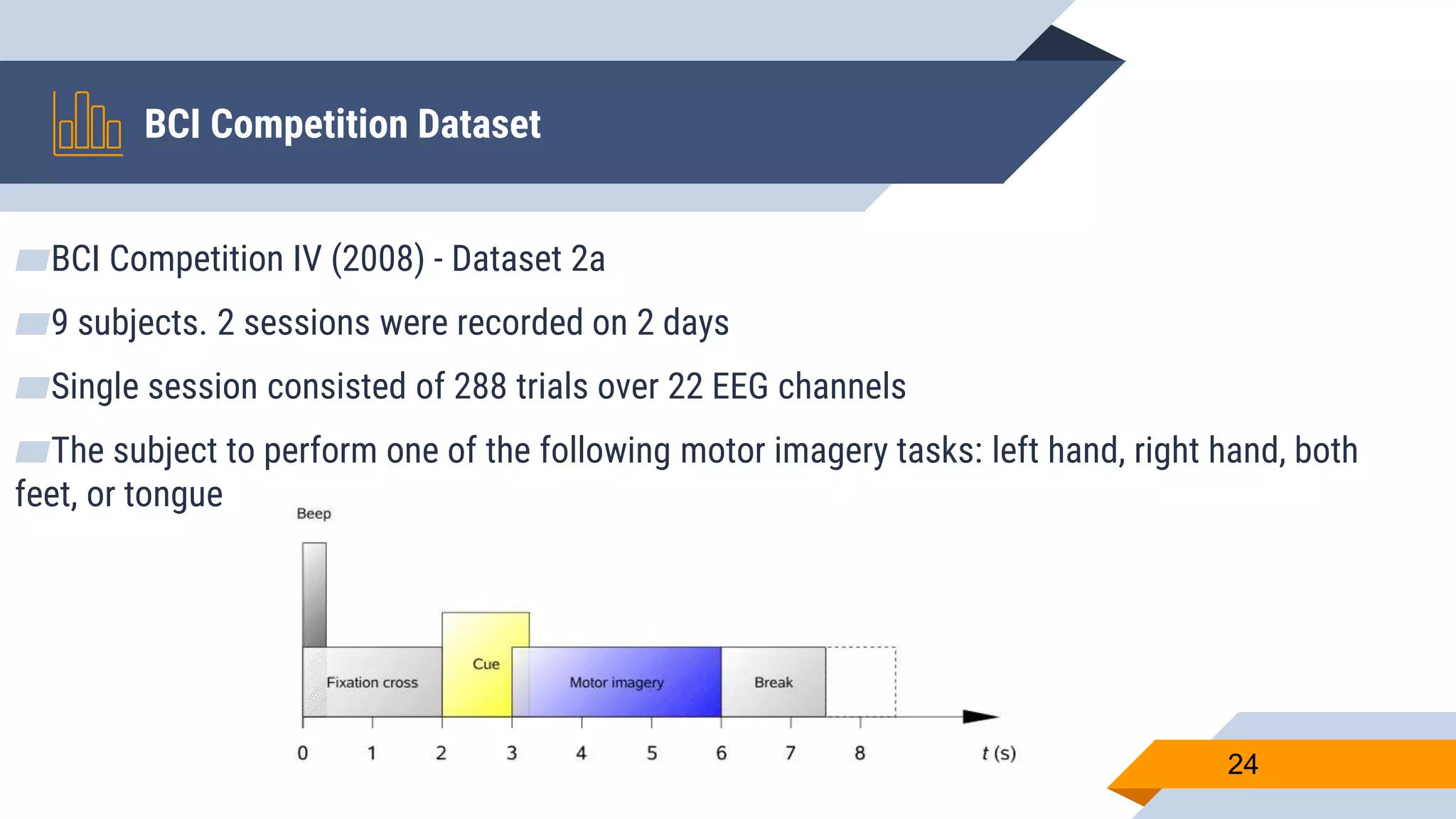
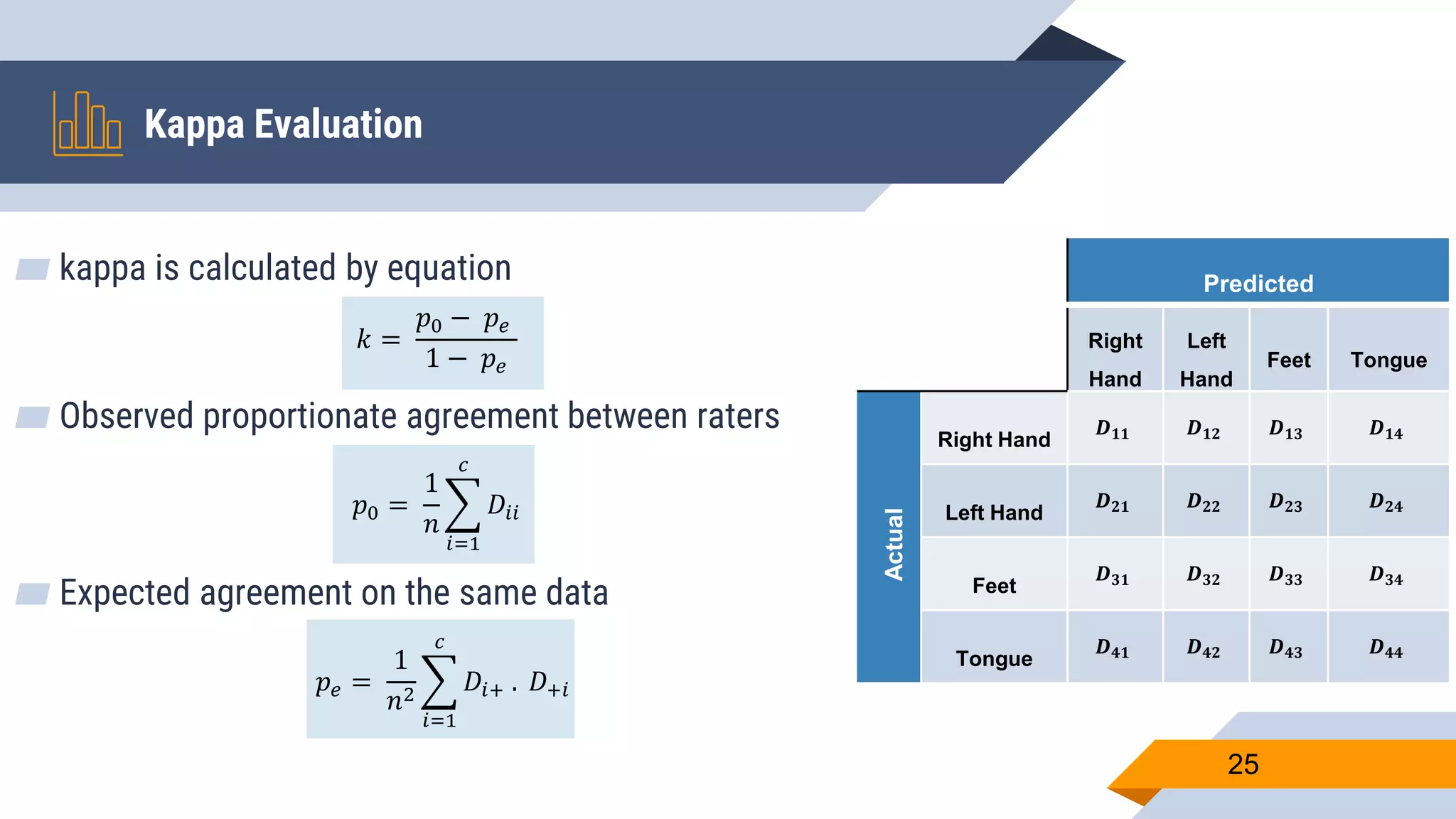
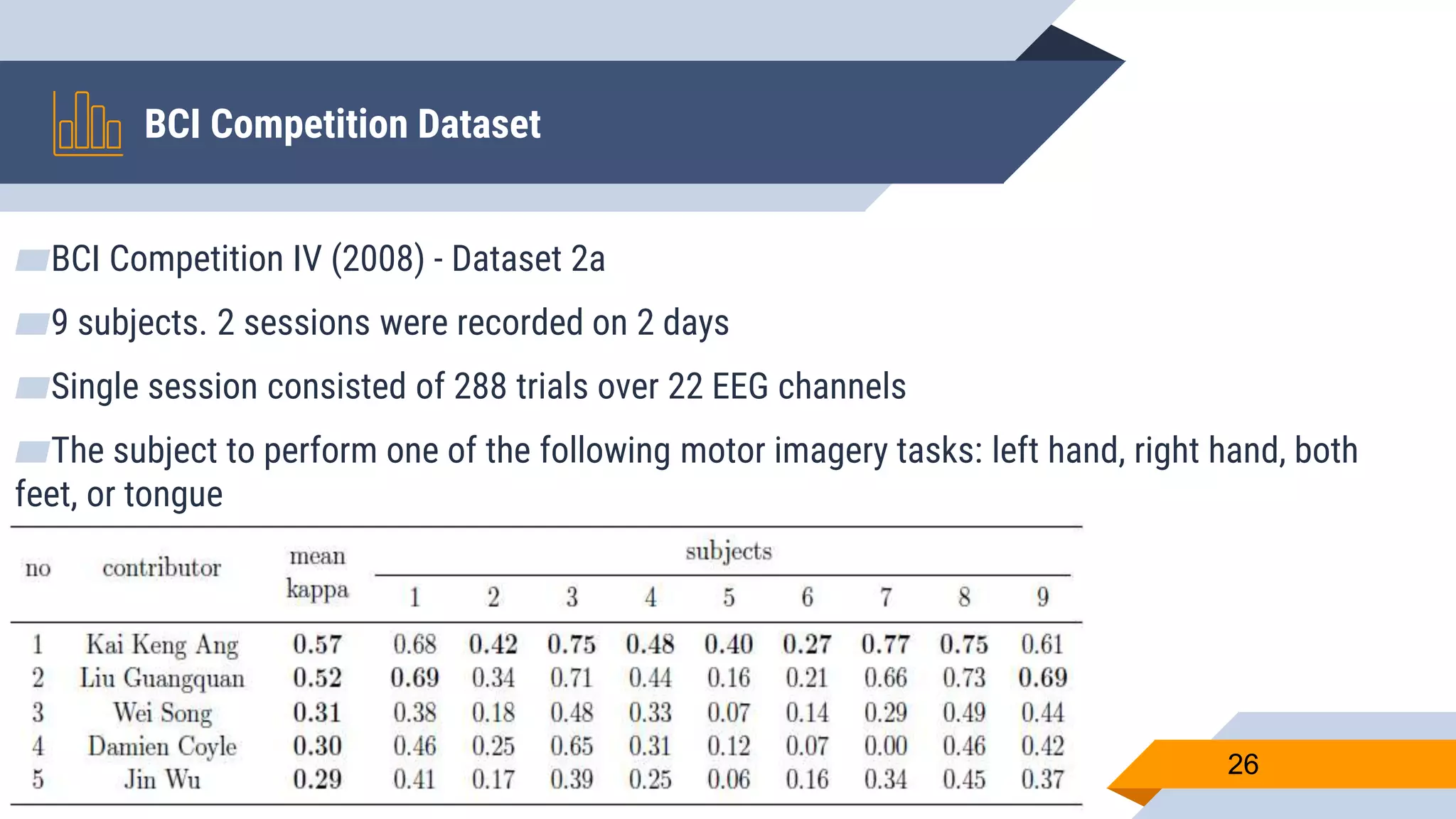
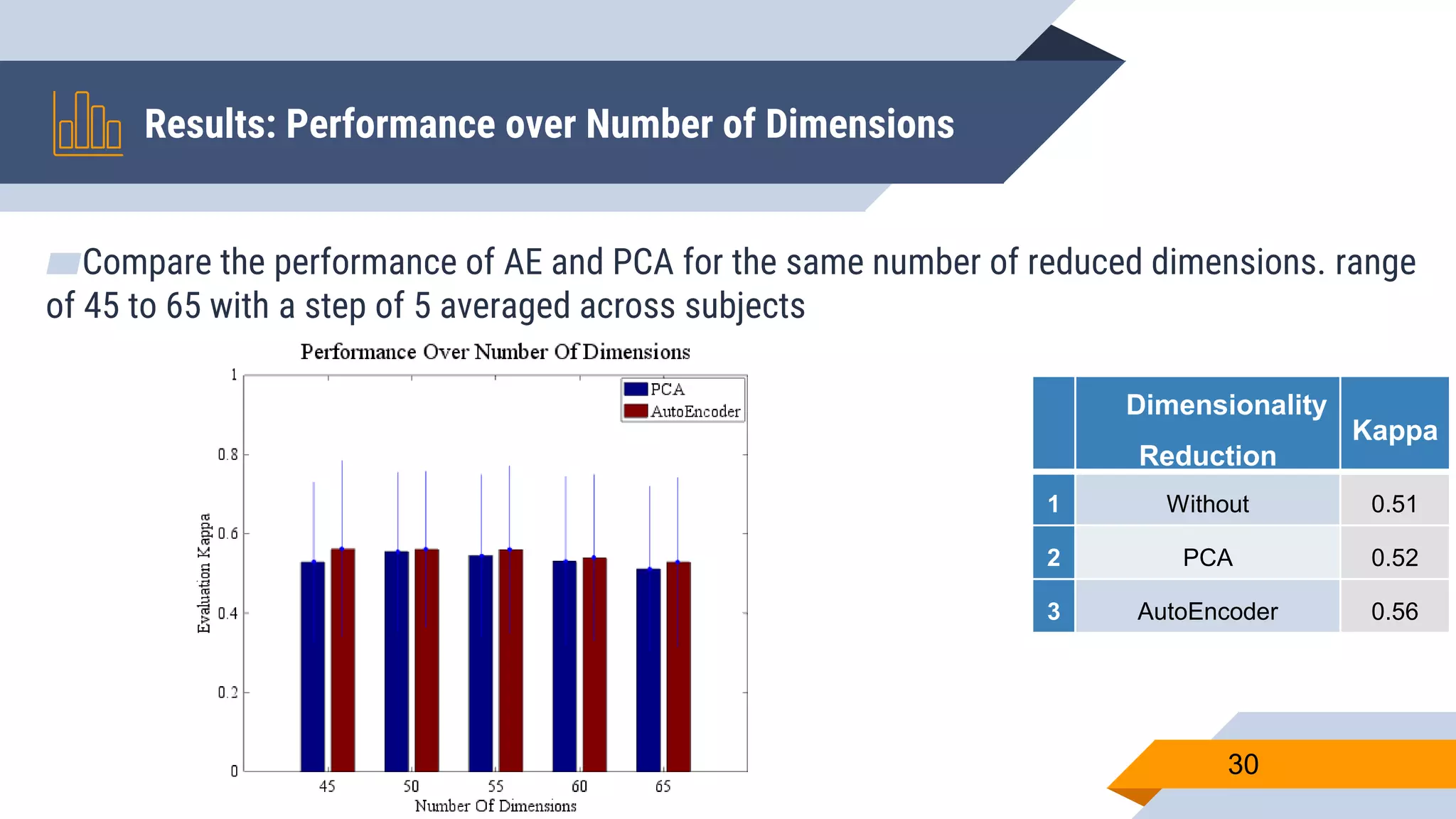
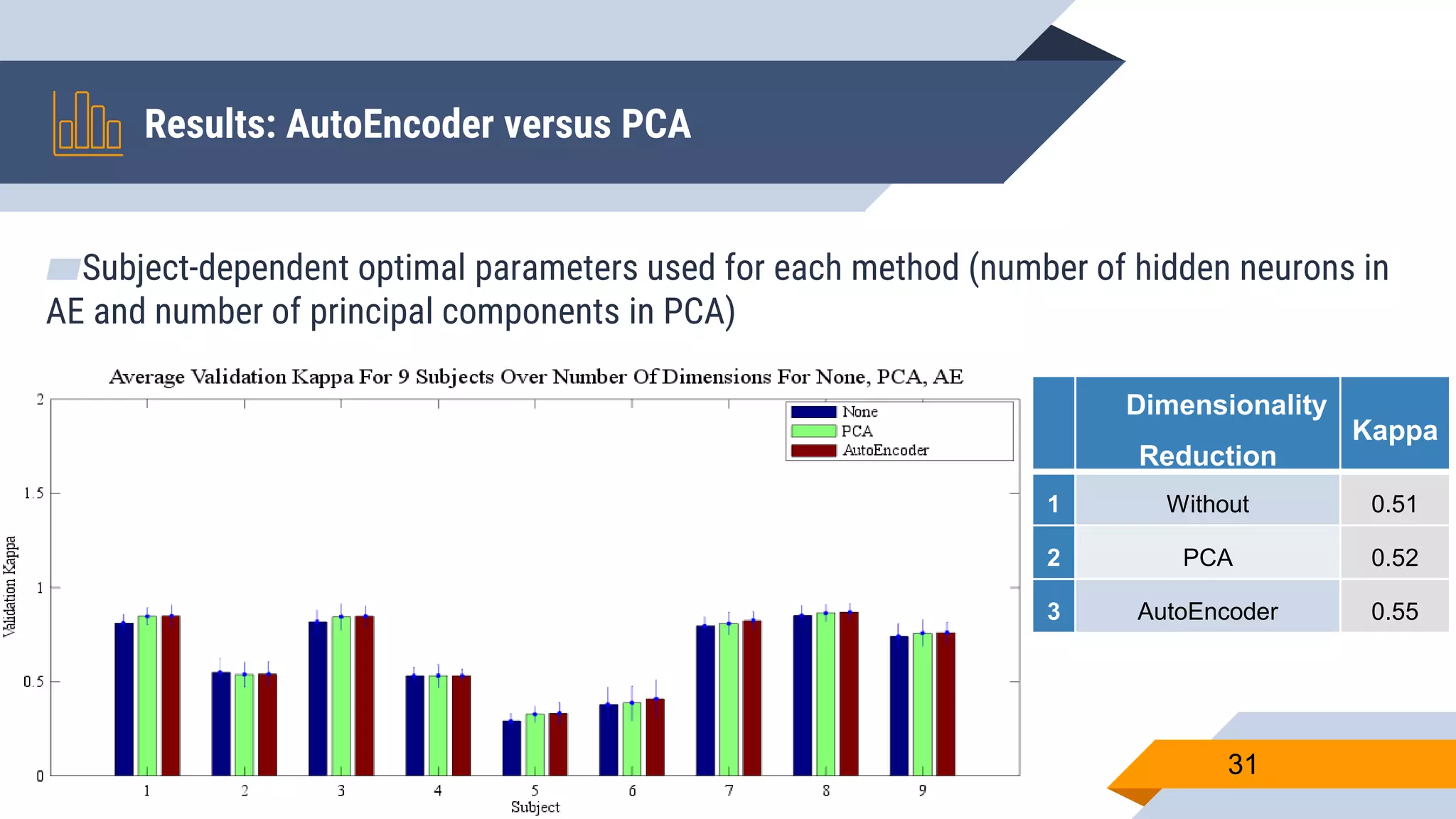
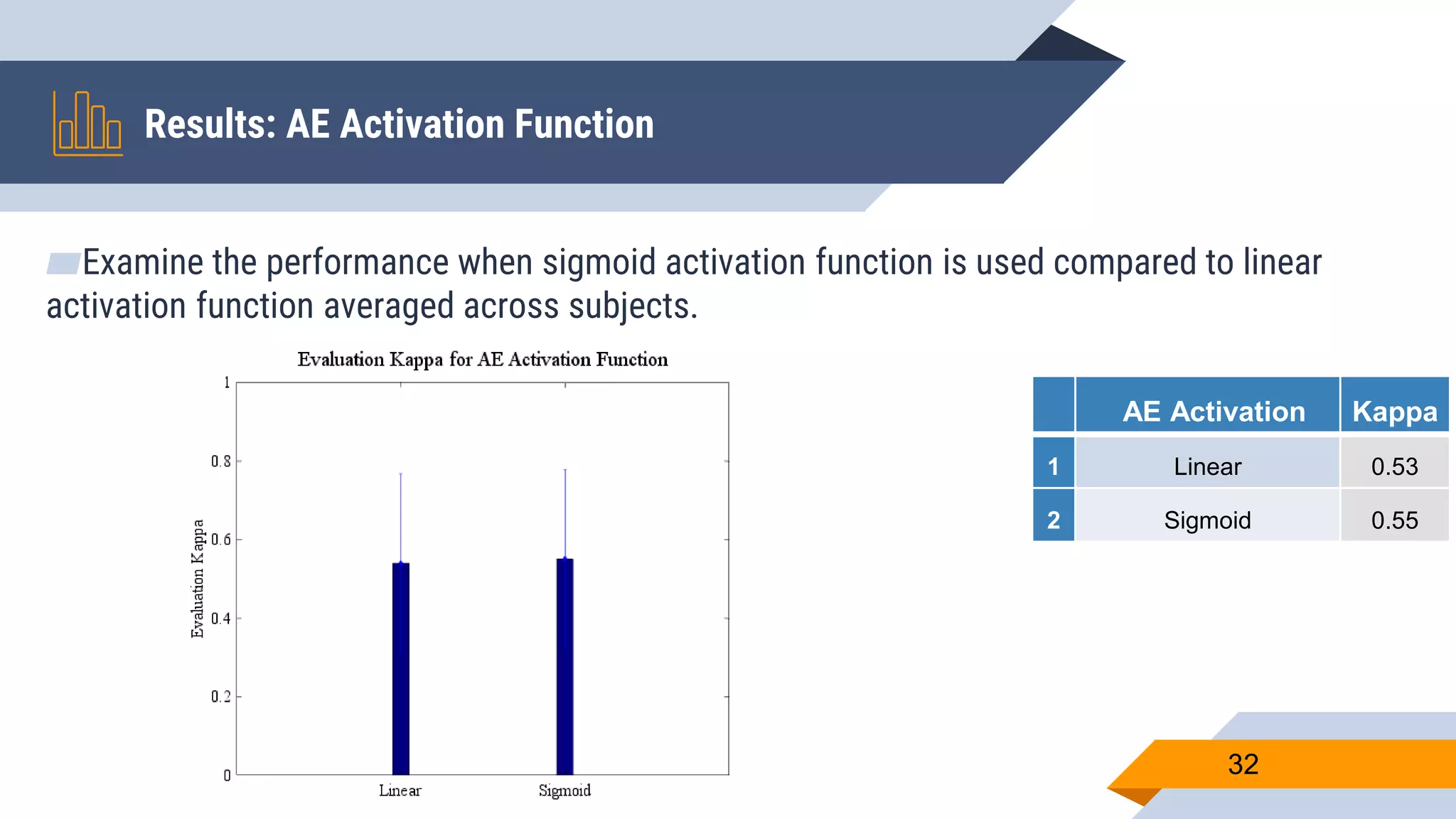
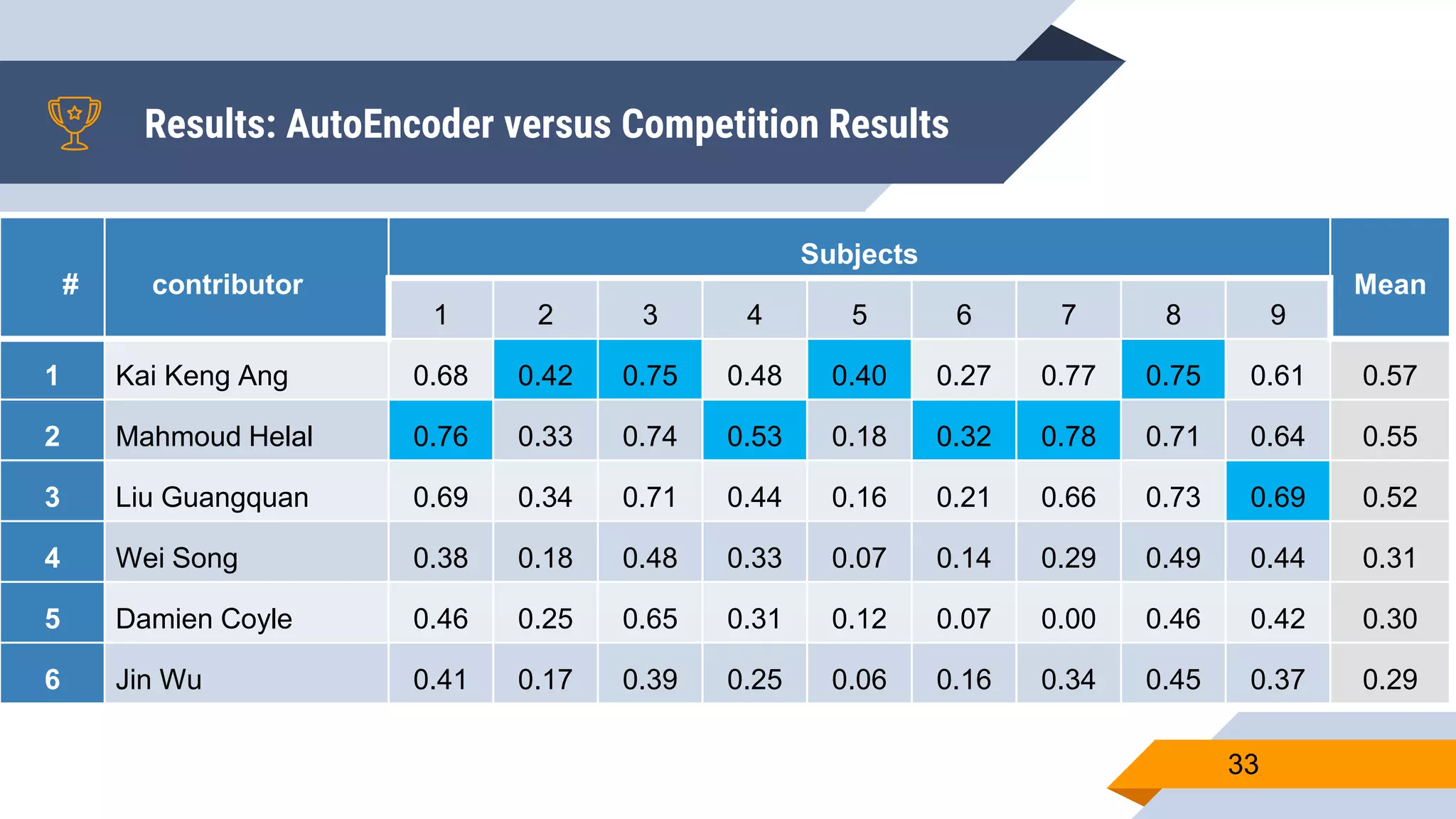
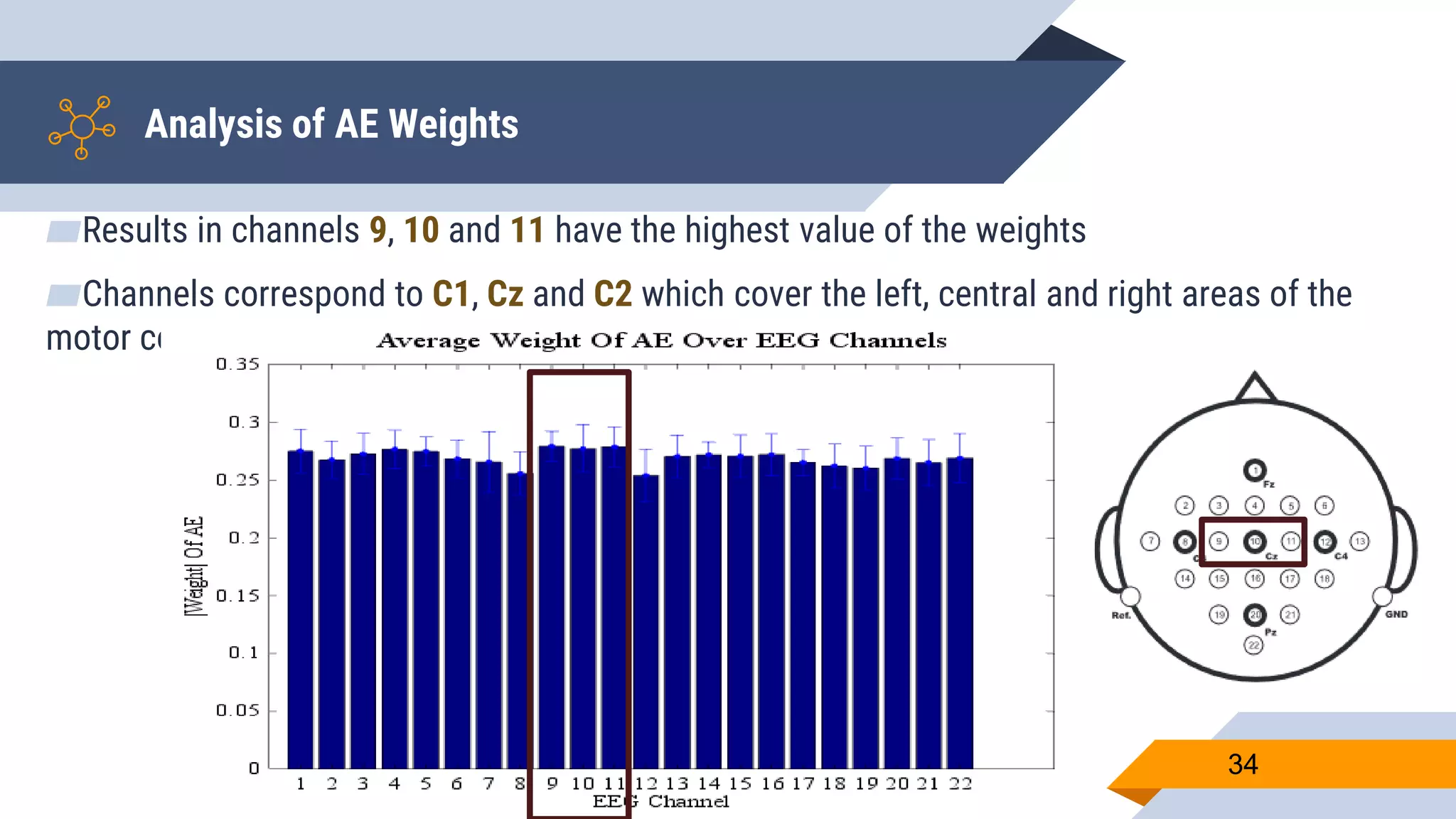
This document presents a motor imagery-based brain-computer interface speller for mobile devices. It introduces a motor imagery structure model consisting of pre-processing, feature extraction, dimensionality reduction, and classification blocks. It develops an autoencoder-based dimensionality reduction method and compares it to PCA. It also develops a Hex-O-Spell mobile application using motor imagery to spell words. Results show the autoencoder approach achieves better performance than PCA. Testing on three subjects demonstrates the utility of the Hex-O-Spell mobile application. Future work involves enhancing the methods and application.






![Event Related Desynchronization (ERD)
▰ Mu [8–13 Hz] and Beta [13–30 Hz] bands
▰ Always correlated with ERS
11
(Neuper et al ,2006)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalseminarpresentation-171108195629/75/A-Brain-Computer-Interface-Speller-for-Smart-Devices-11-2048.jpg)
![Event Related Desynchronization (ERD)
▰ Mu [8–13 Hz] and Beta [13–30 Hz] bands
▰ Always correlated with ERS
12
(Neuper et al ,2006)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalseminarpresentation-171108195629/75/A-Brain-Computer-Interface-Speller-for-Smart-Devices-12-2048.jpg)

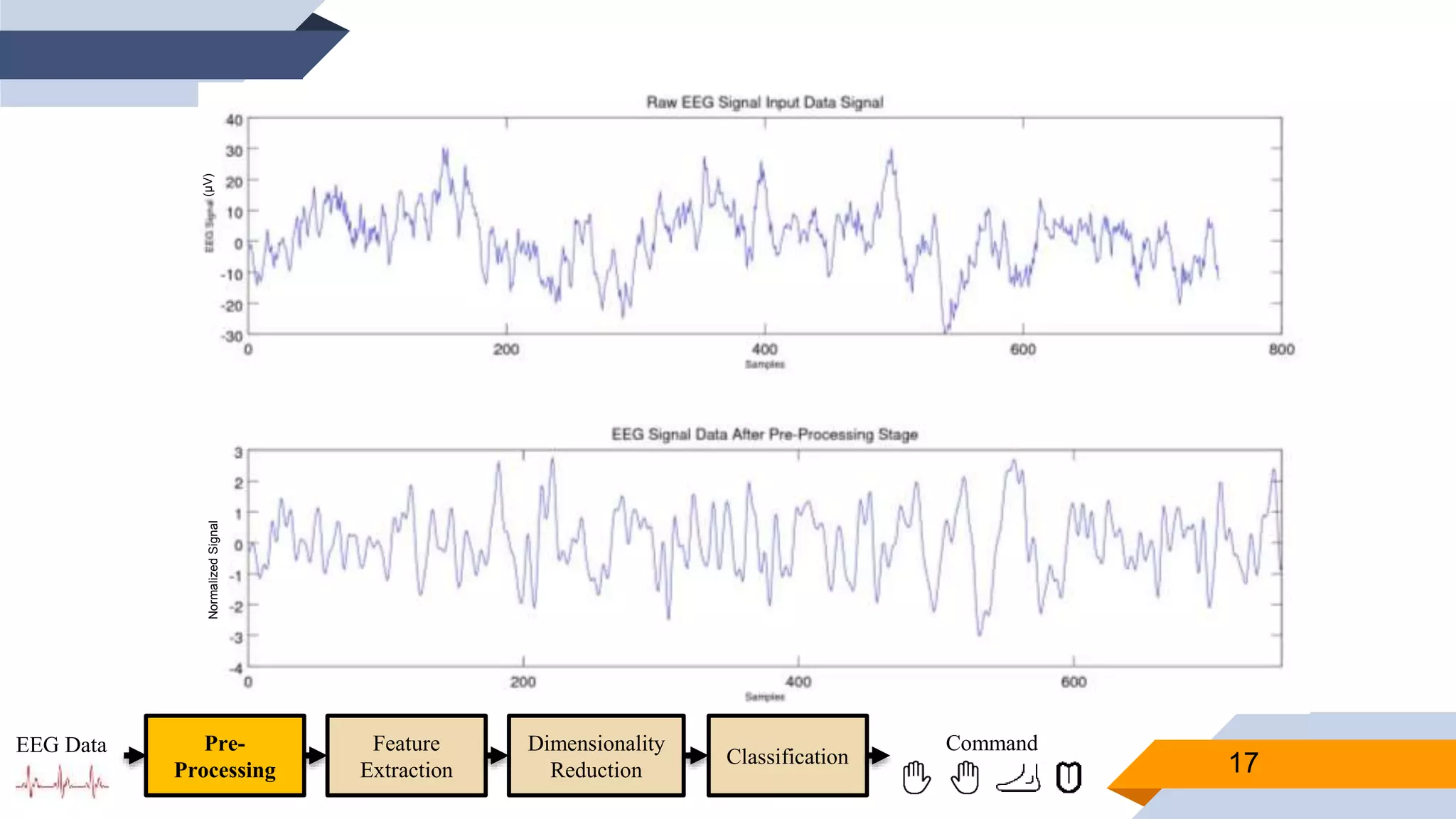
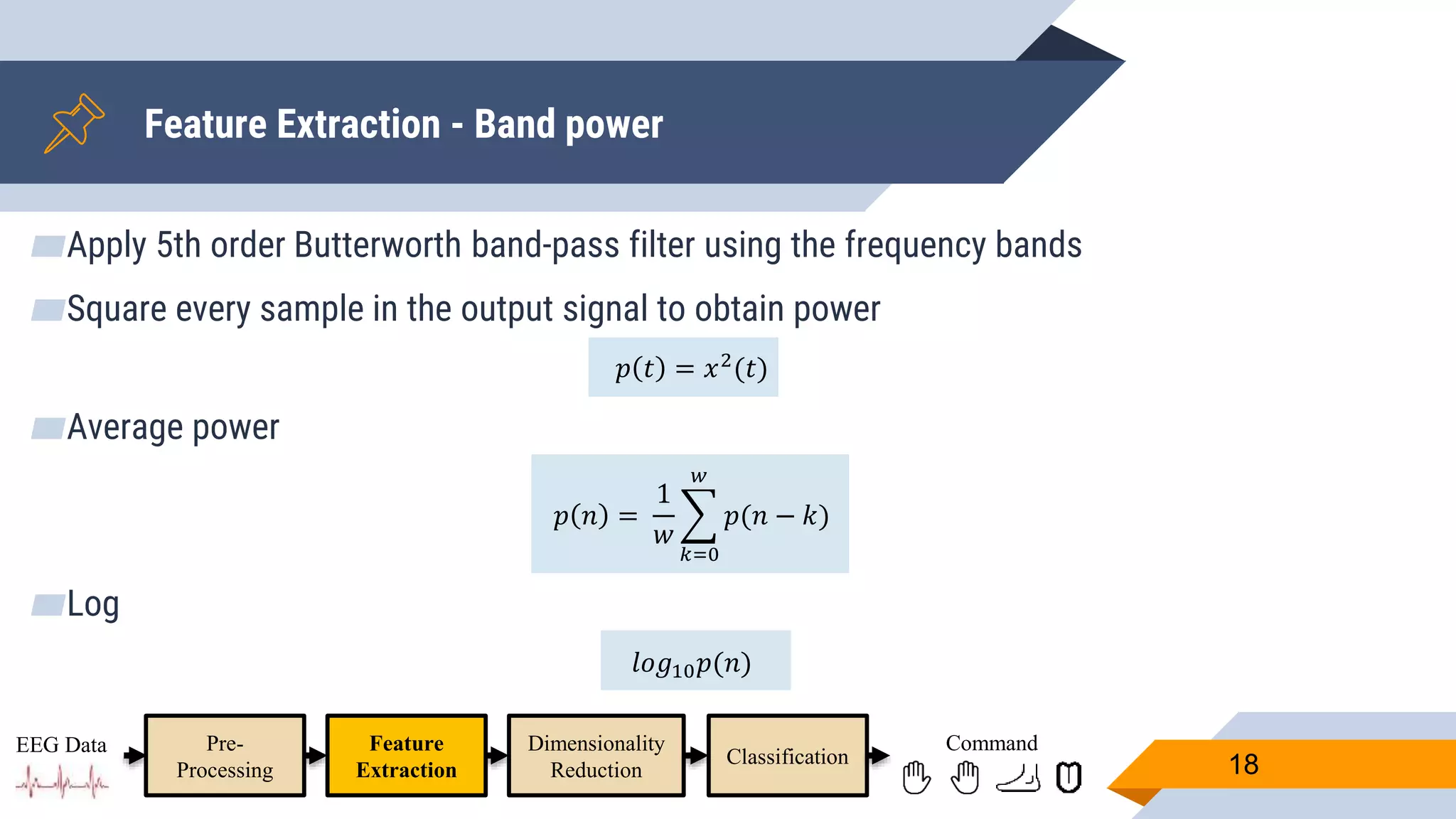
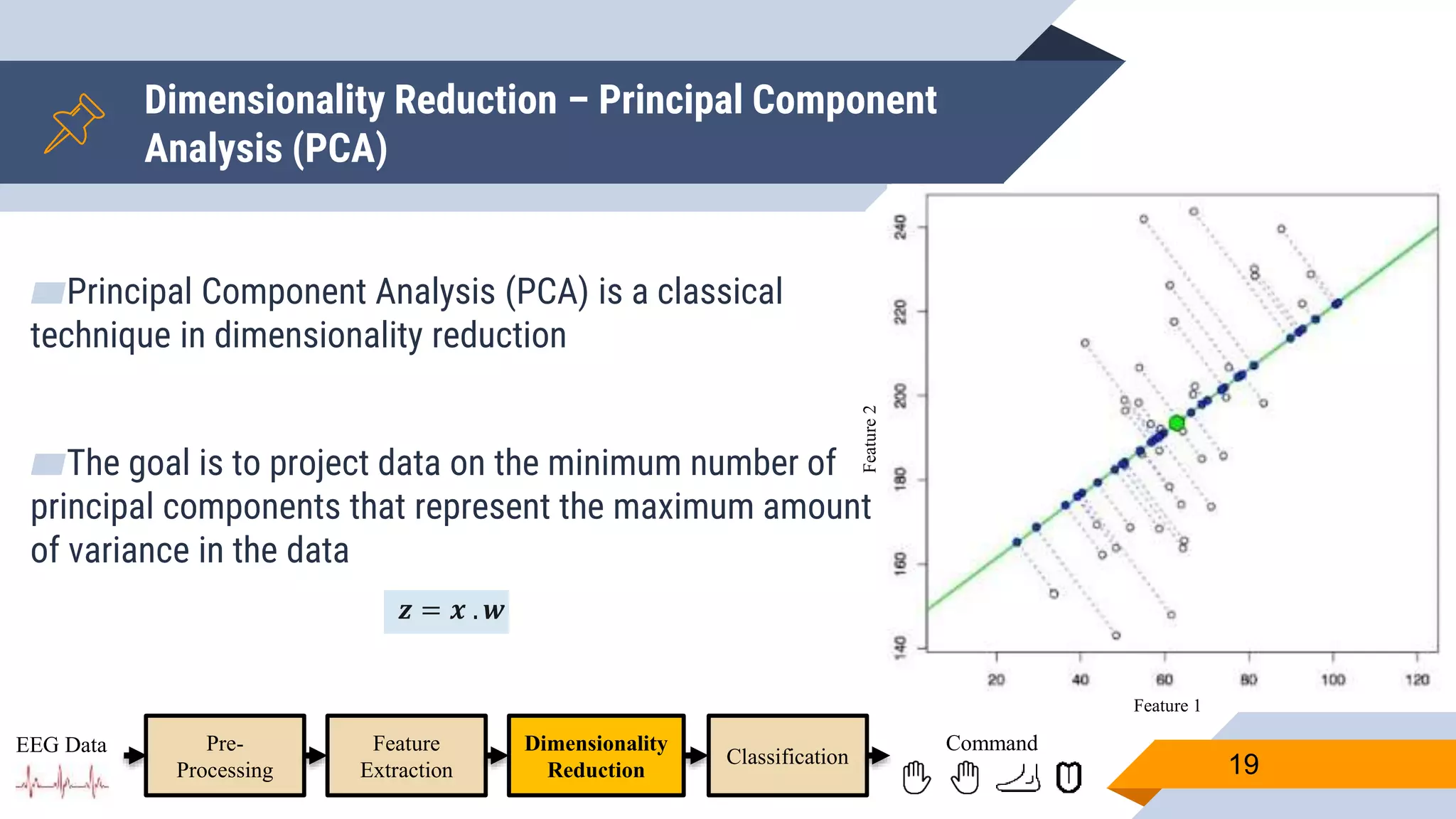
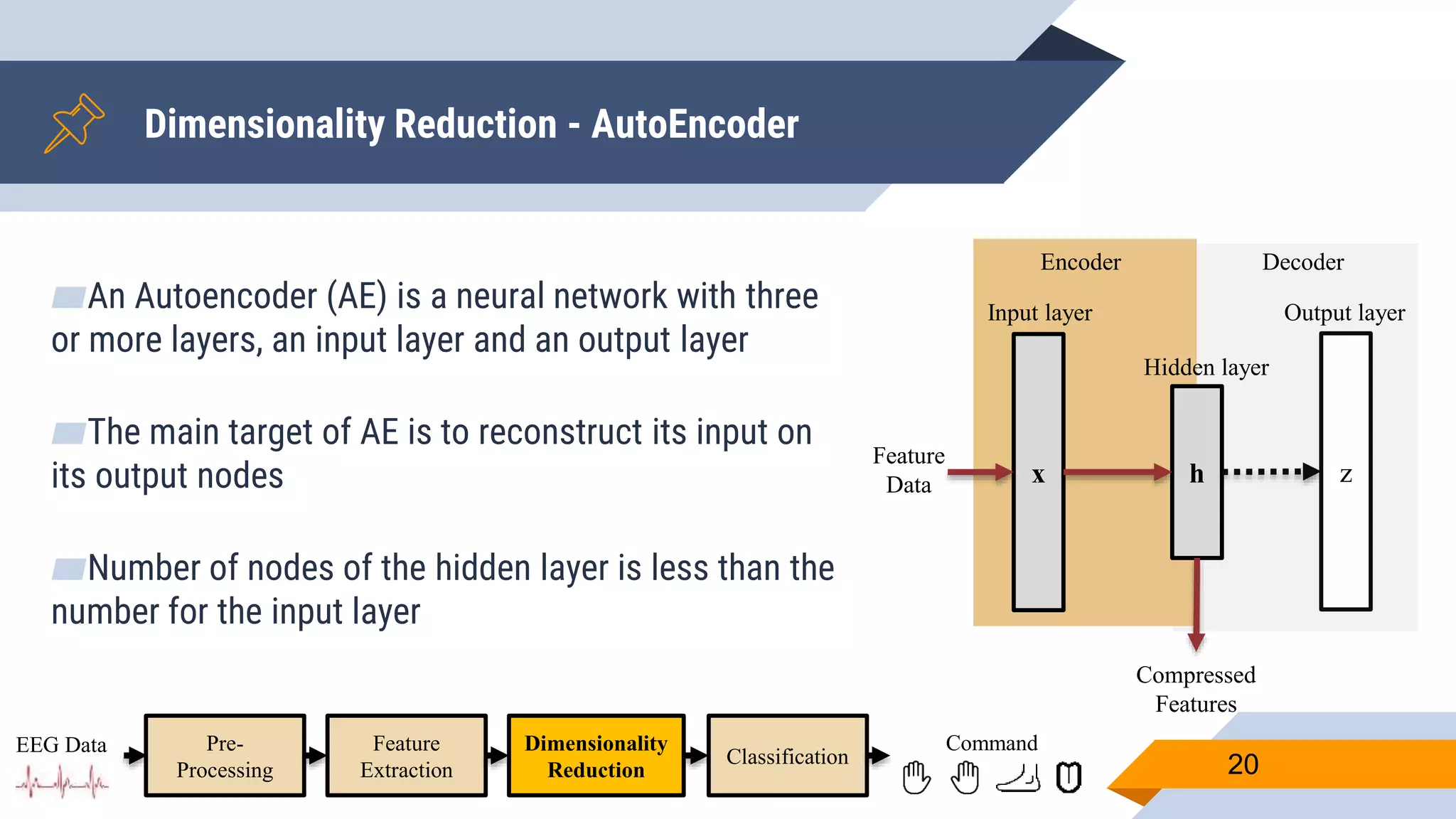
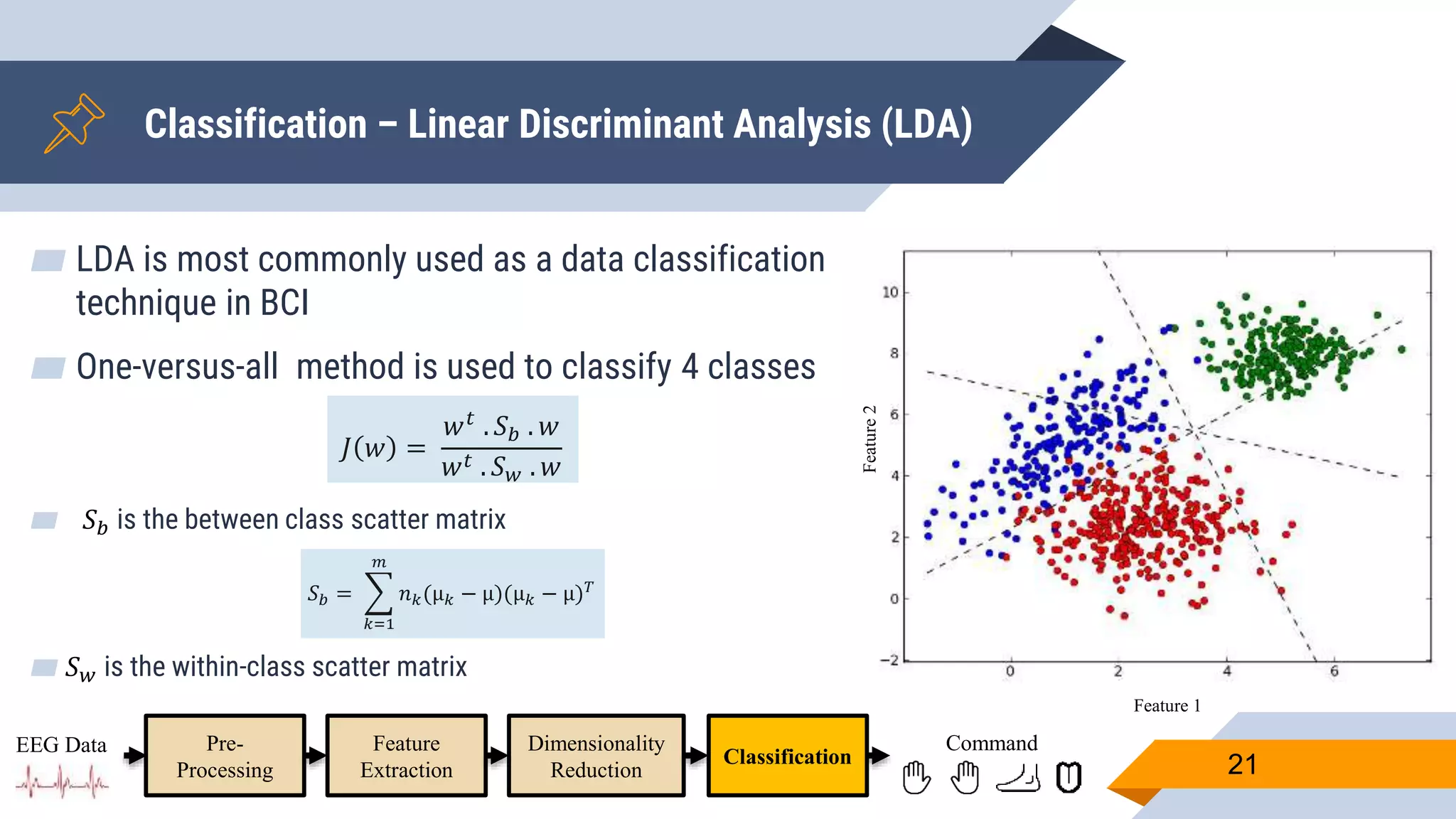
![Pre-Processing
▰ Common Average Reference (CAR) to eliminate external noise
▰ Z-score to adjust values measured from different channels on different scales to a
notionally common scale
▰ Band-pass filter [4-41] Hz to remove eye artifacts and get domain that contains
valuable ERD/RDS information
▰ Down-sample to speedup subsequent processing.
16
Pre-
Processing
Feature
Extraction
Dimensionality
Reduction
Classification
EEG Data Command](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalseminarpresentation-171108195629/75/A-Brain-Computer-Interface-Speller-for-Smart-Devices-16-2048.jpg)

![35
Command
AE 157
BP 1
8-15
BP 2
12-21
BP 3
20-30
LDA 157 Evaluation 157
..
1
2
.
.
157
AE 2 LDA 2 Evaluation 2
AE 1 LDA 1 Evaluation 1
Pre-Processing
EEG Data
Dimensionality ReductionFeature Extraction Classification Evaluation
..
..
Best
Sample
Feature
EEG Signal Flow in Motor Imagery System
[672528x22]
[168132 x 22]
[22 x 228] [228x 45] [228]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalseminarpresentation-171108195629/75/A-Brain-Computer-Interface-Speller-for-Smart-Devices-35-2048.jpg)