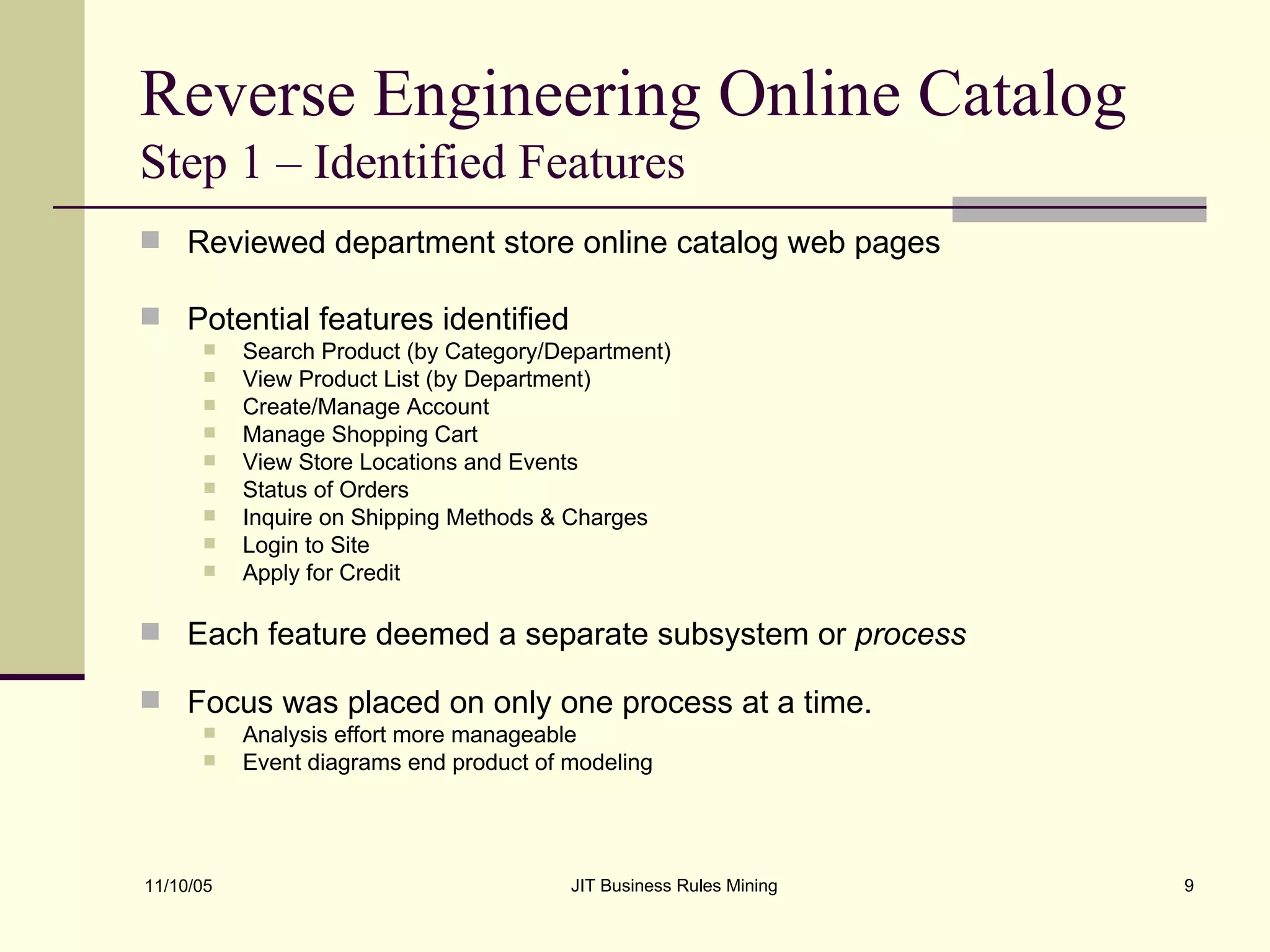
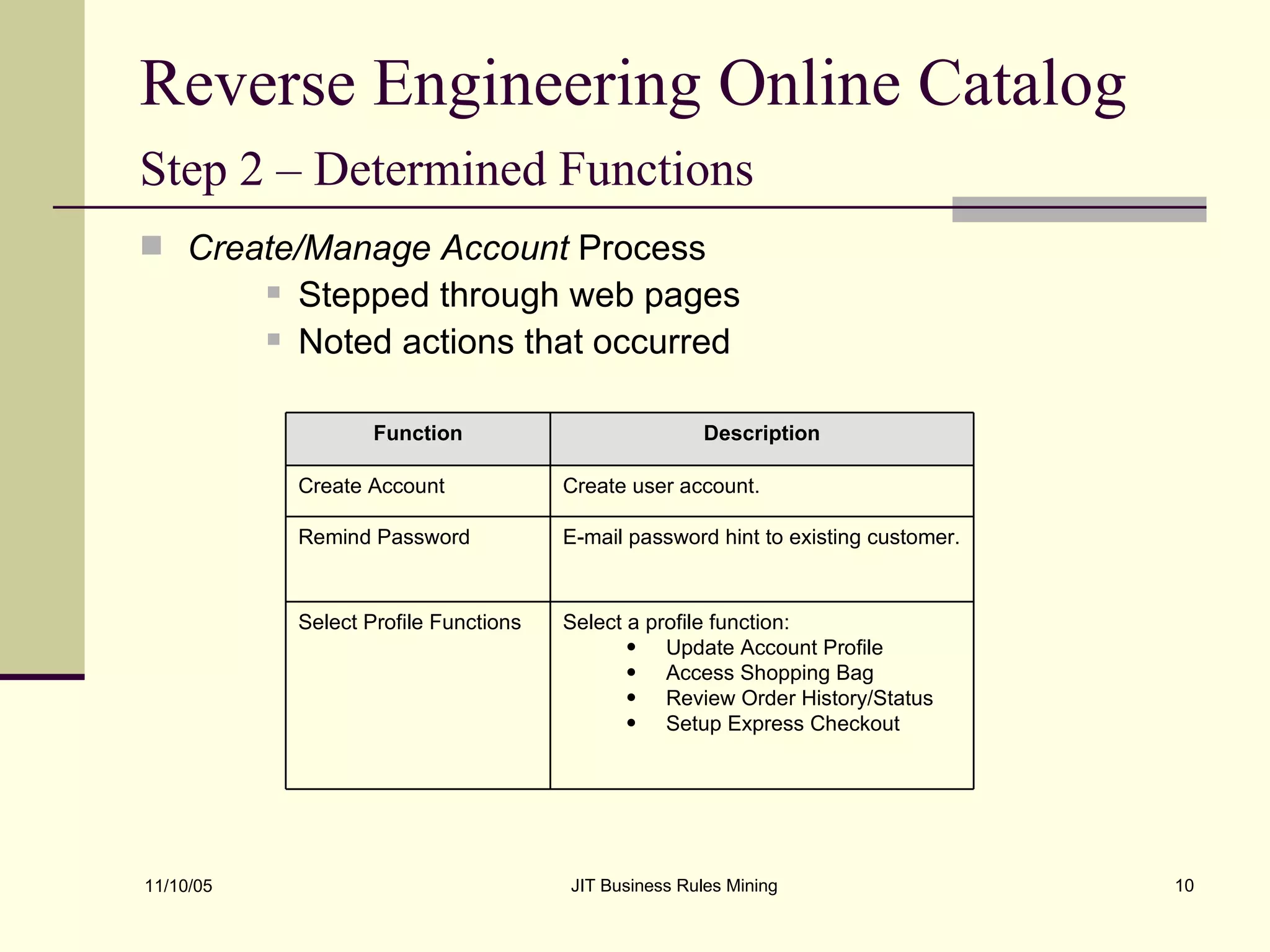
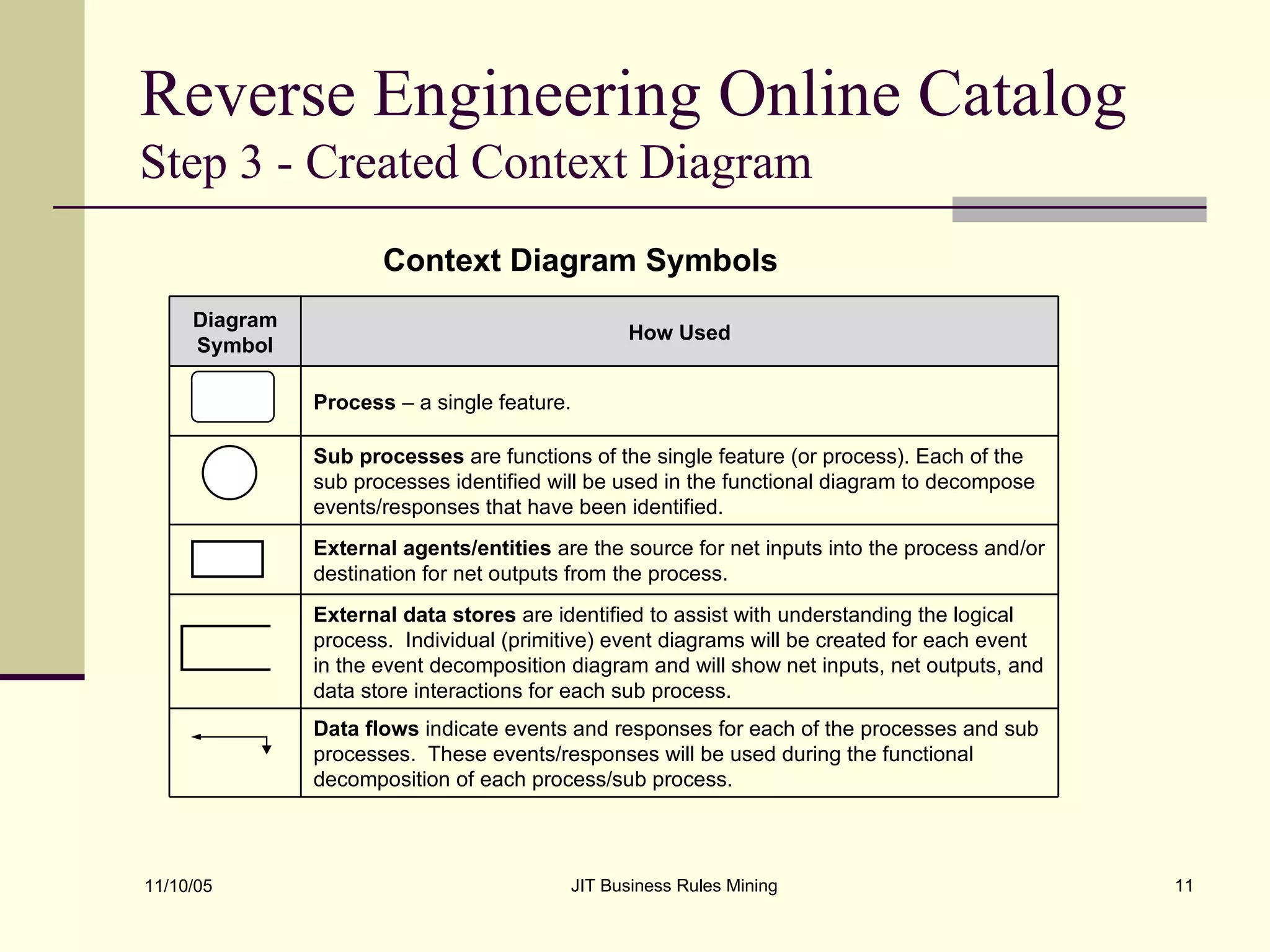
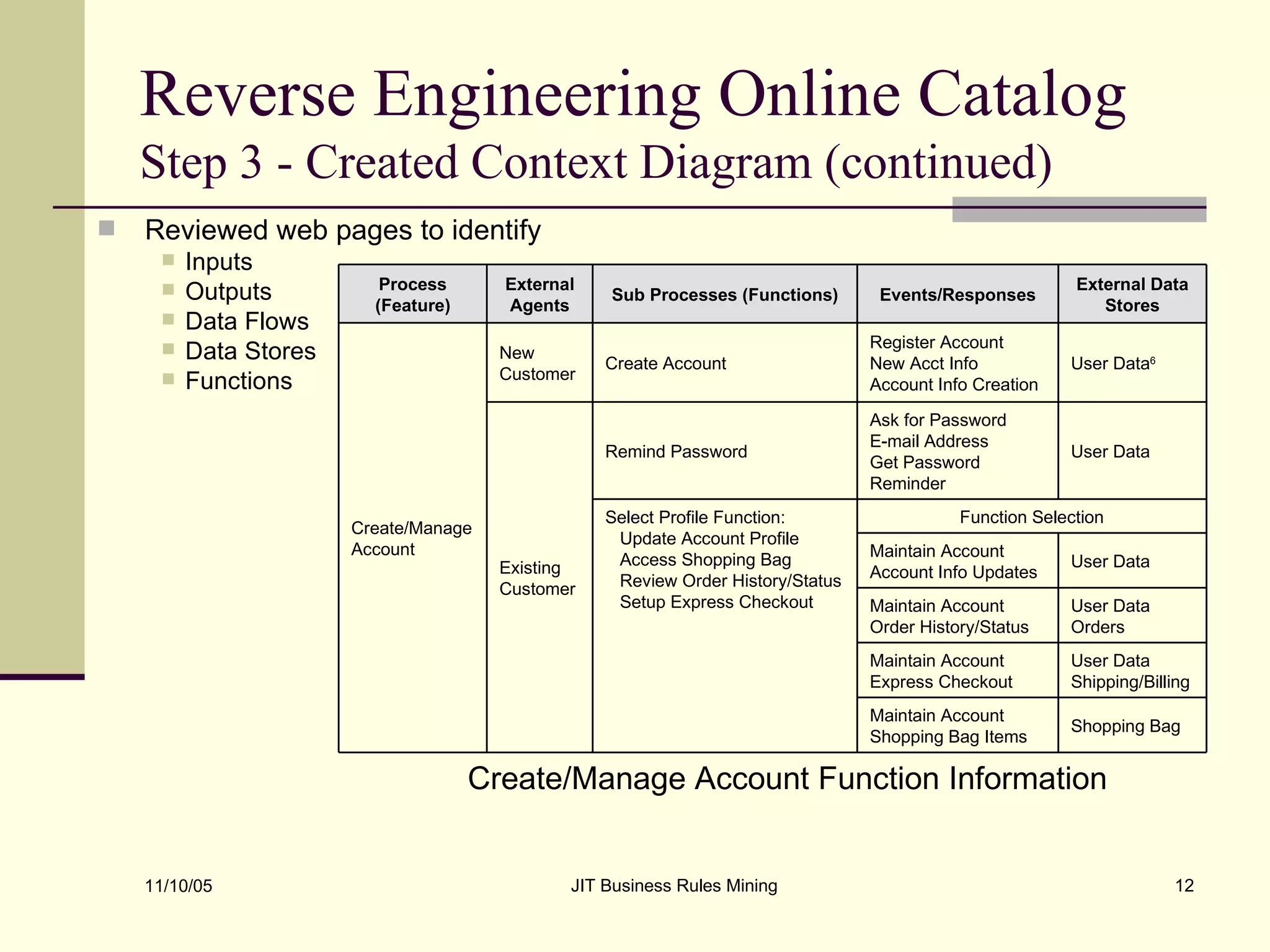
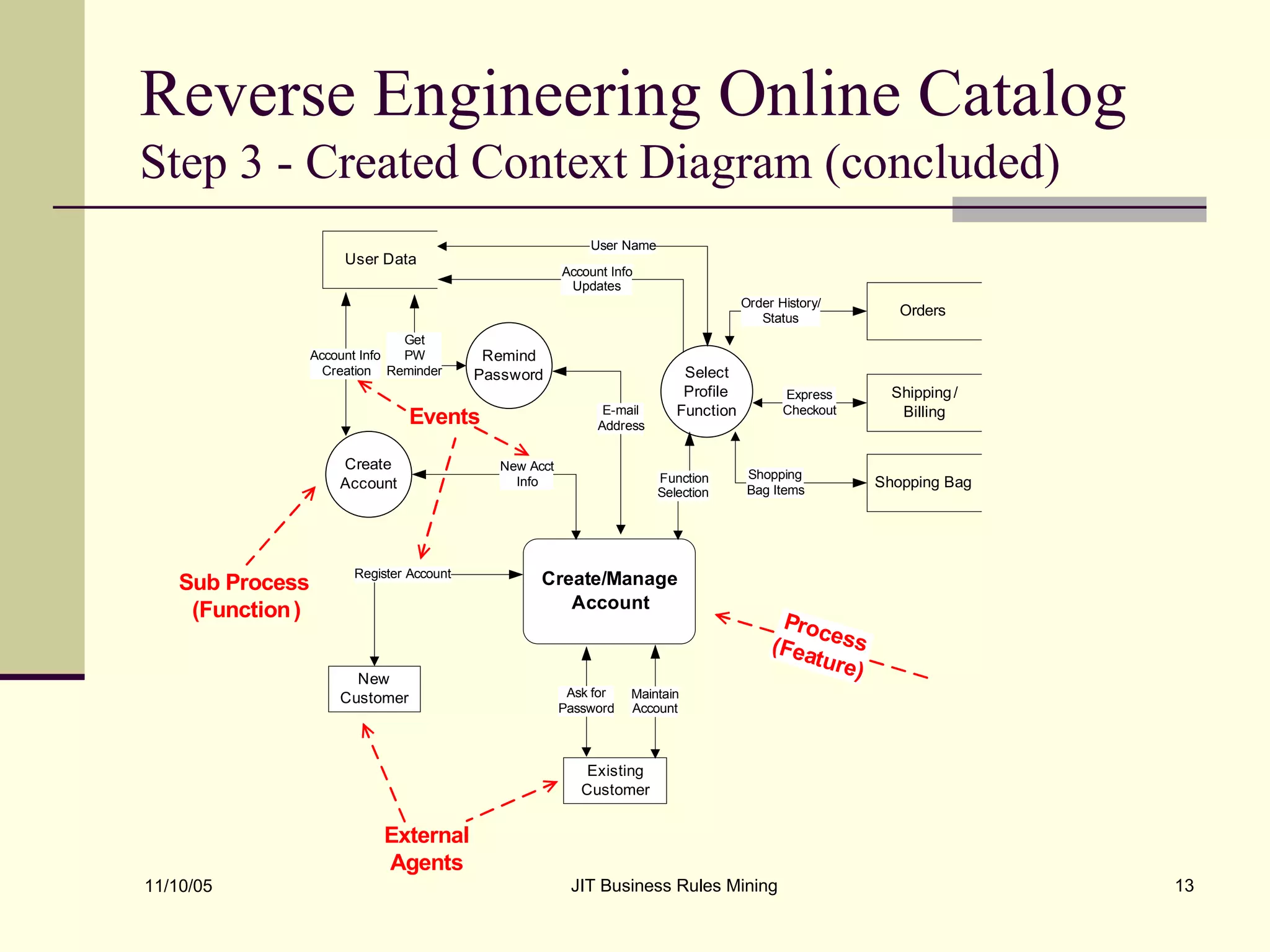
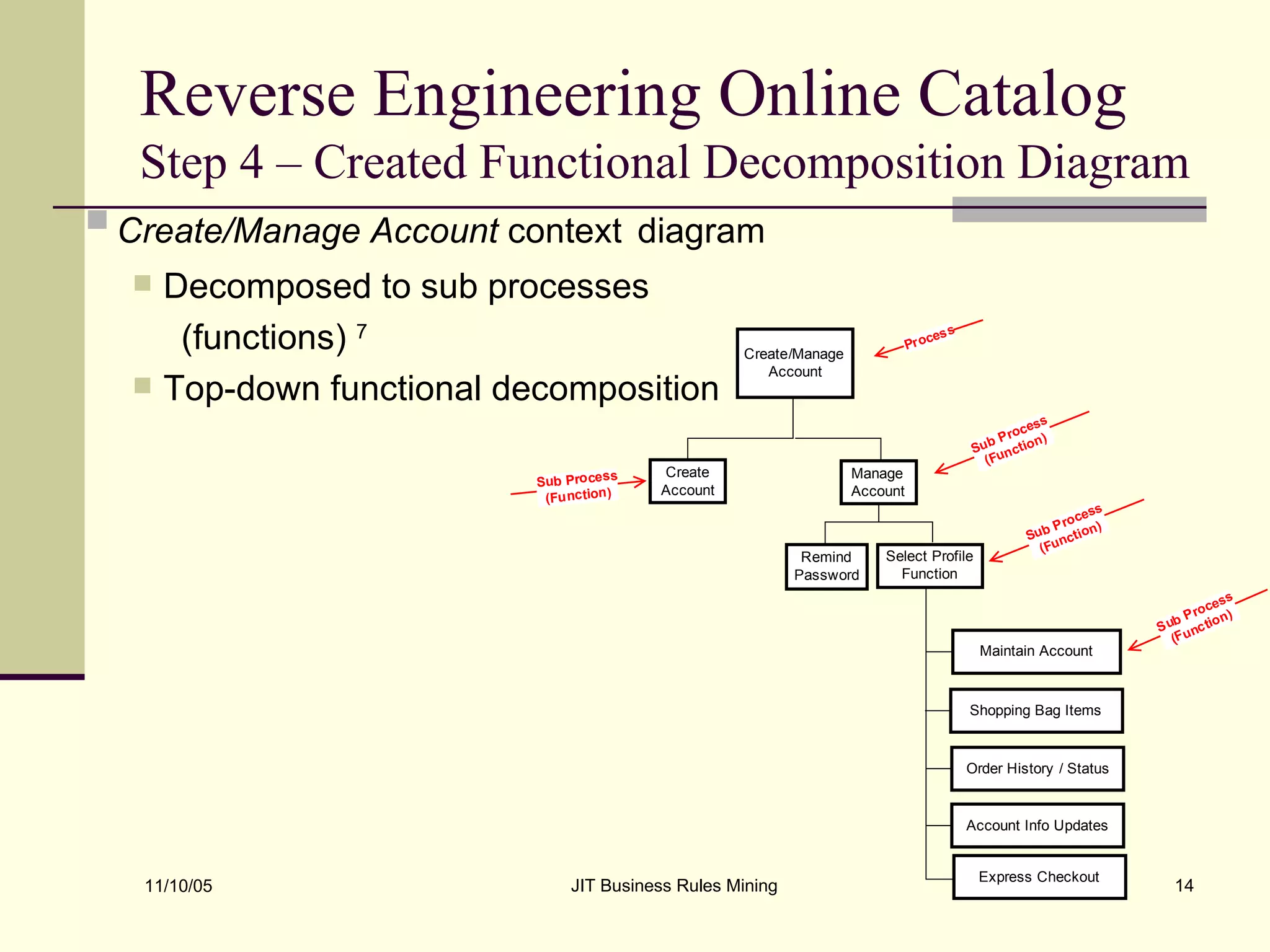
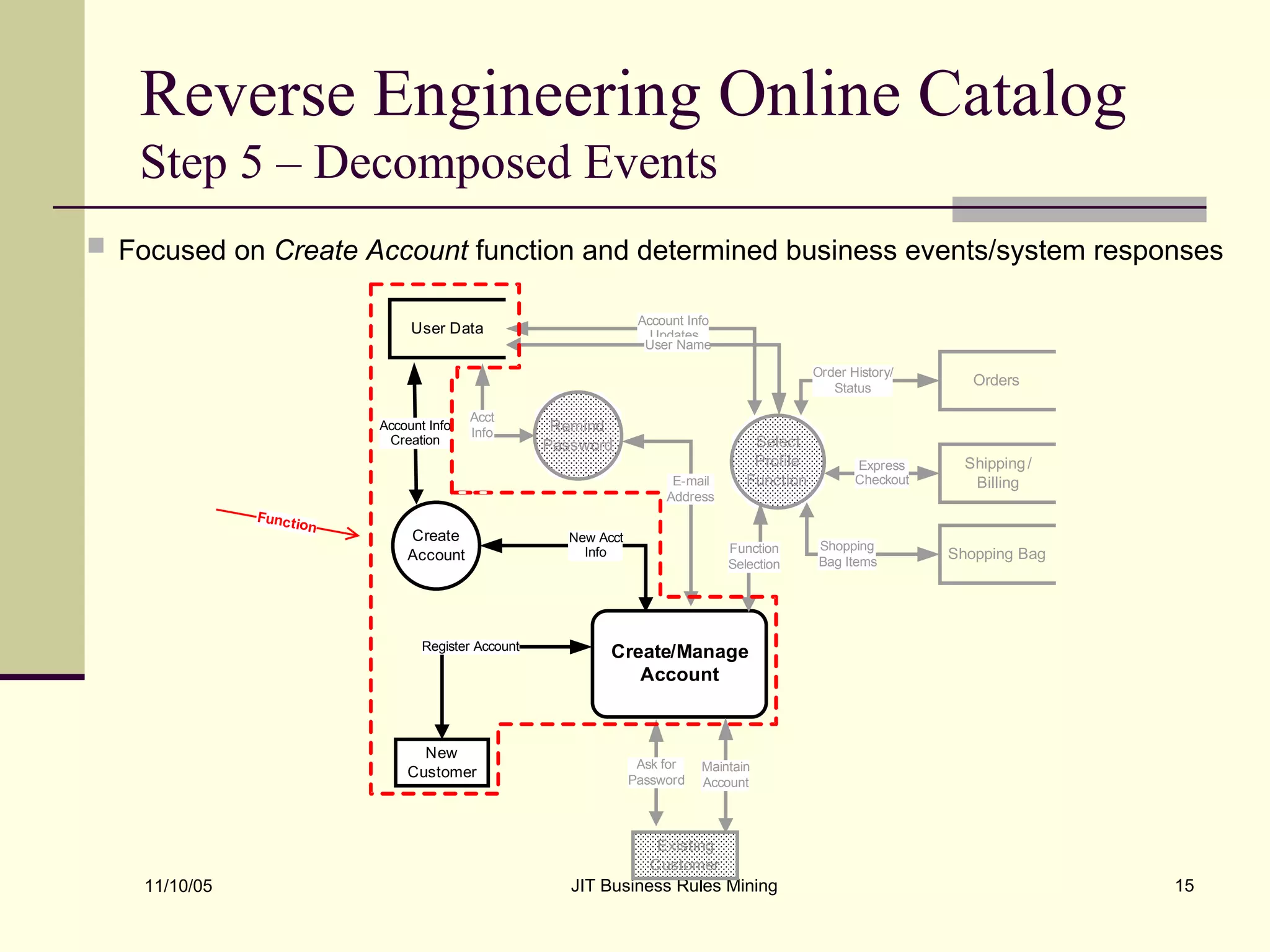
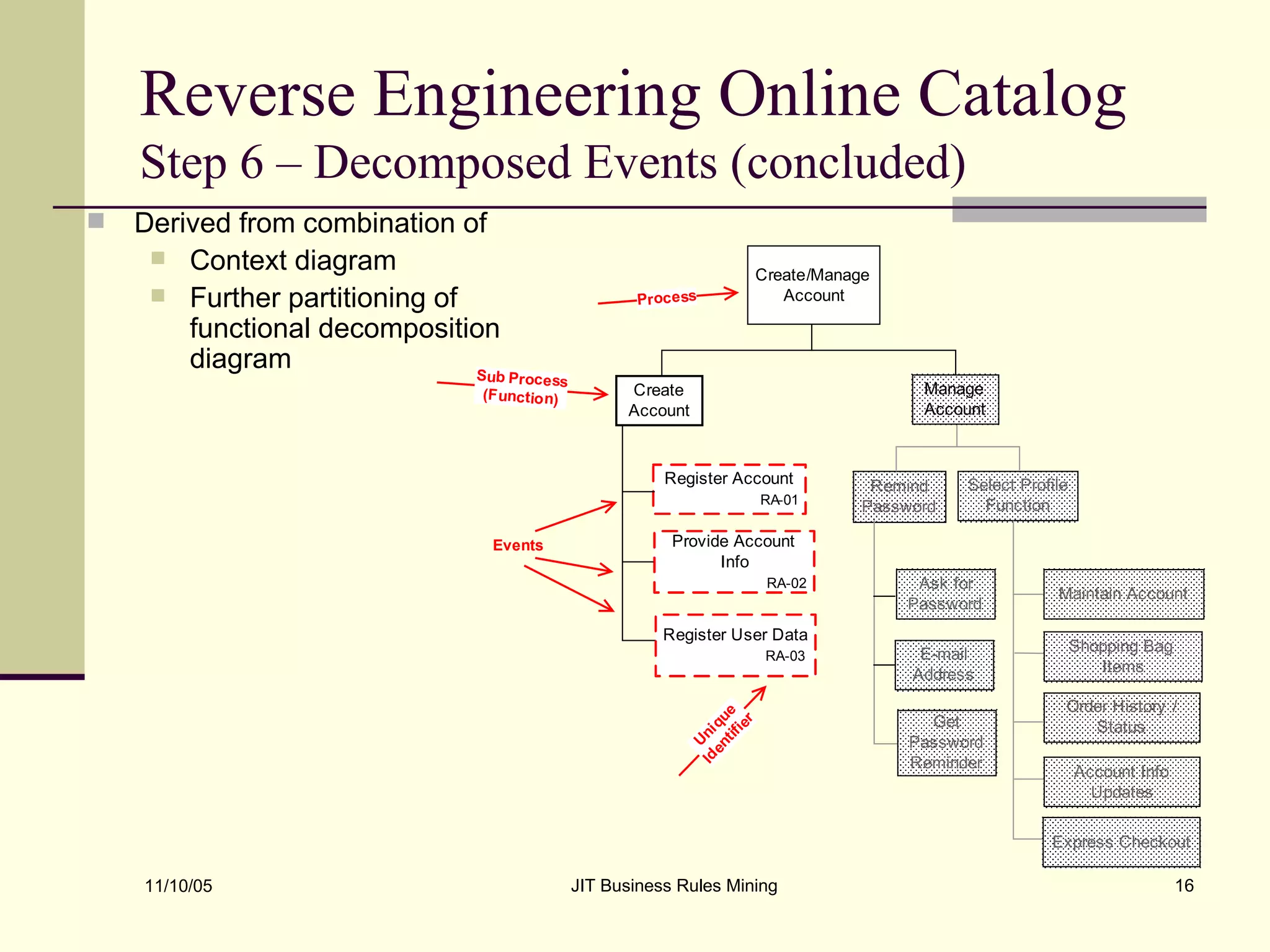
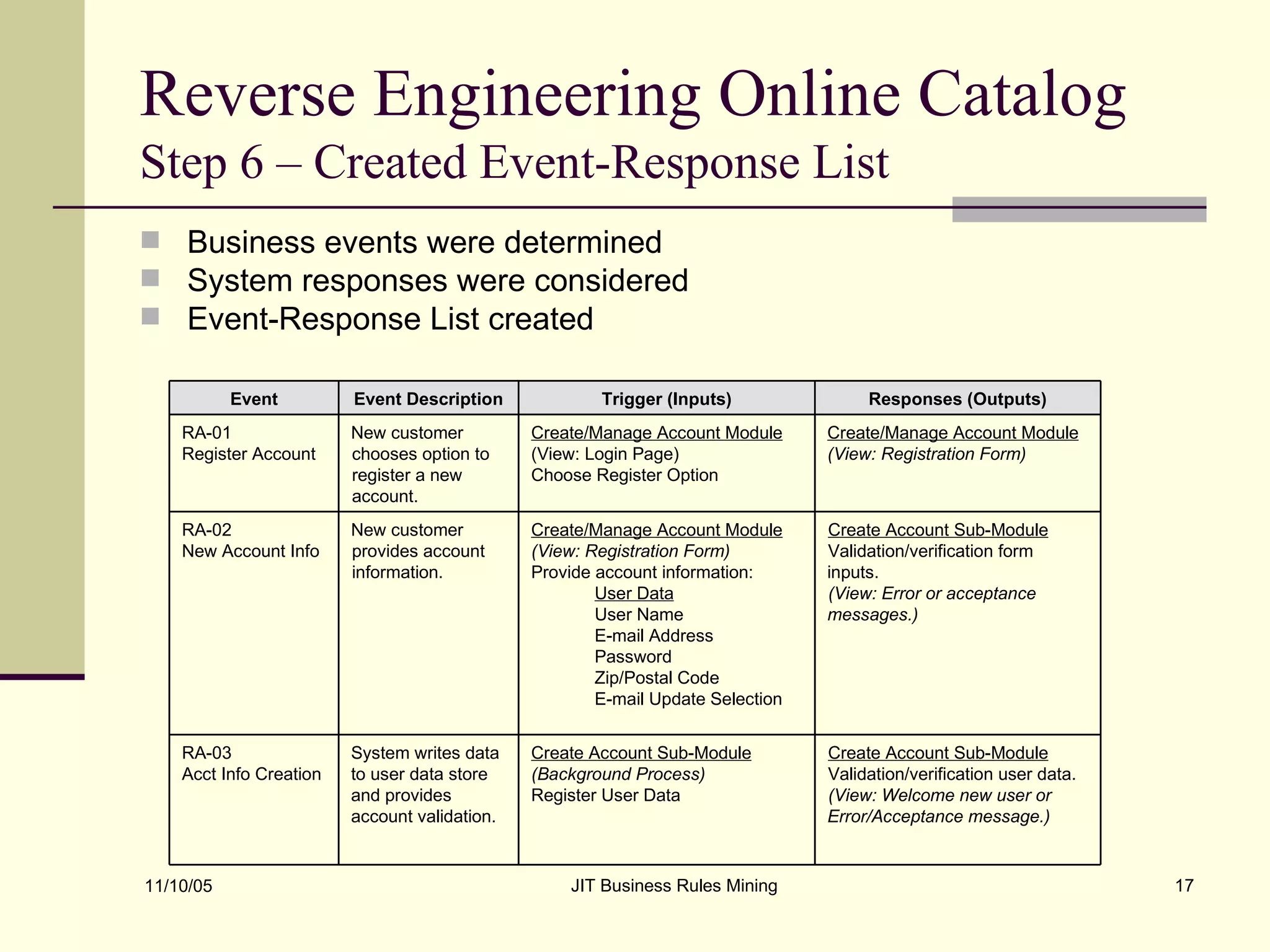
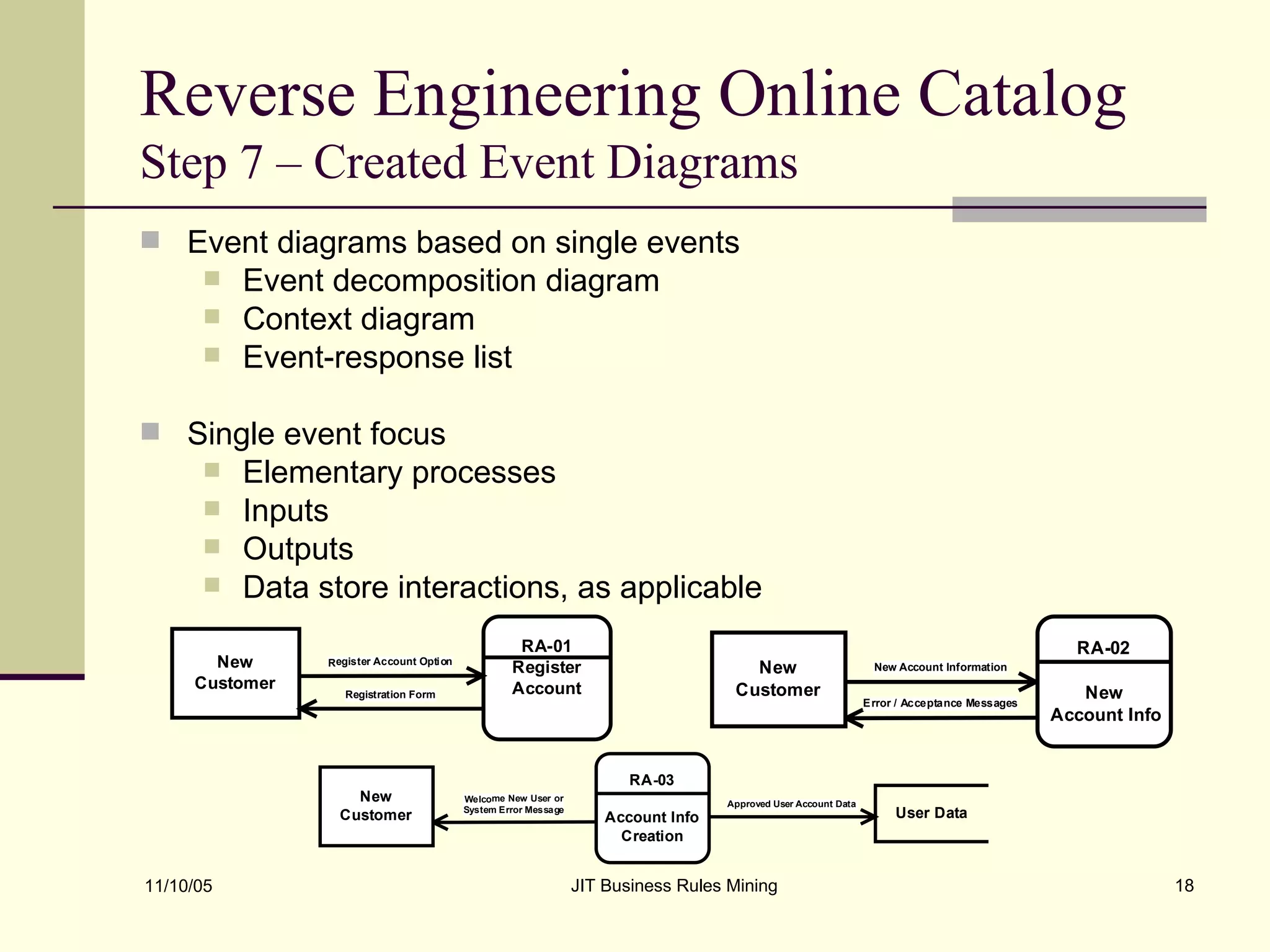
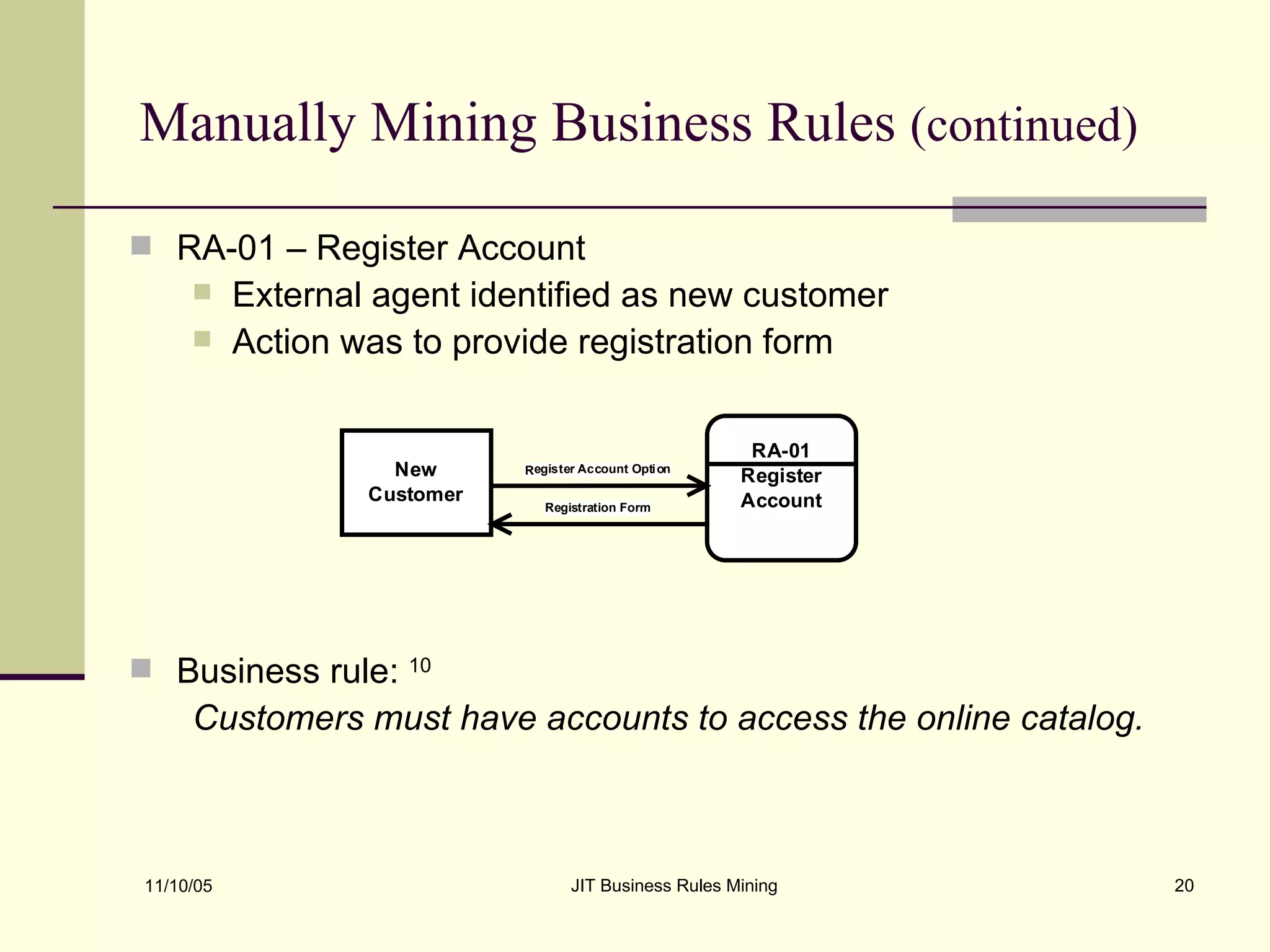
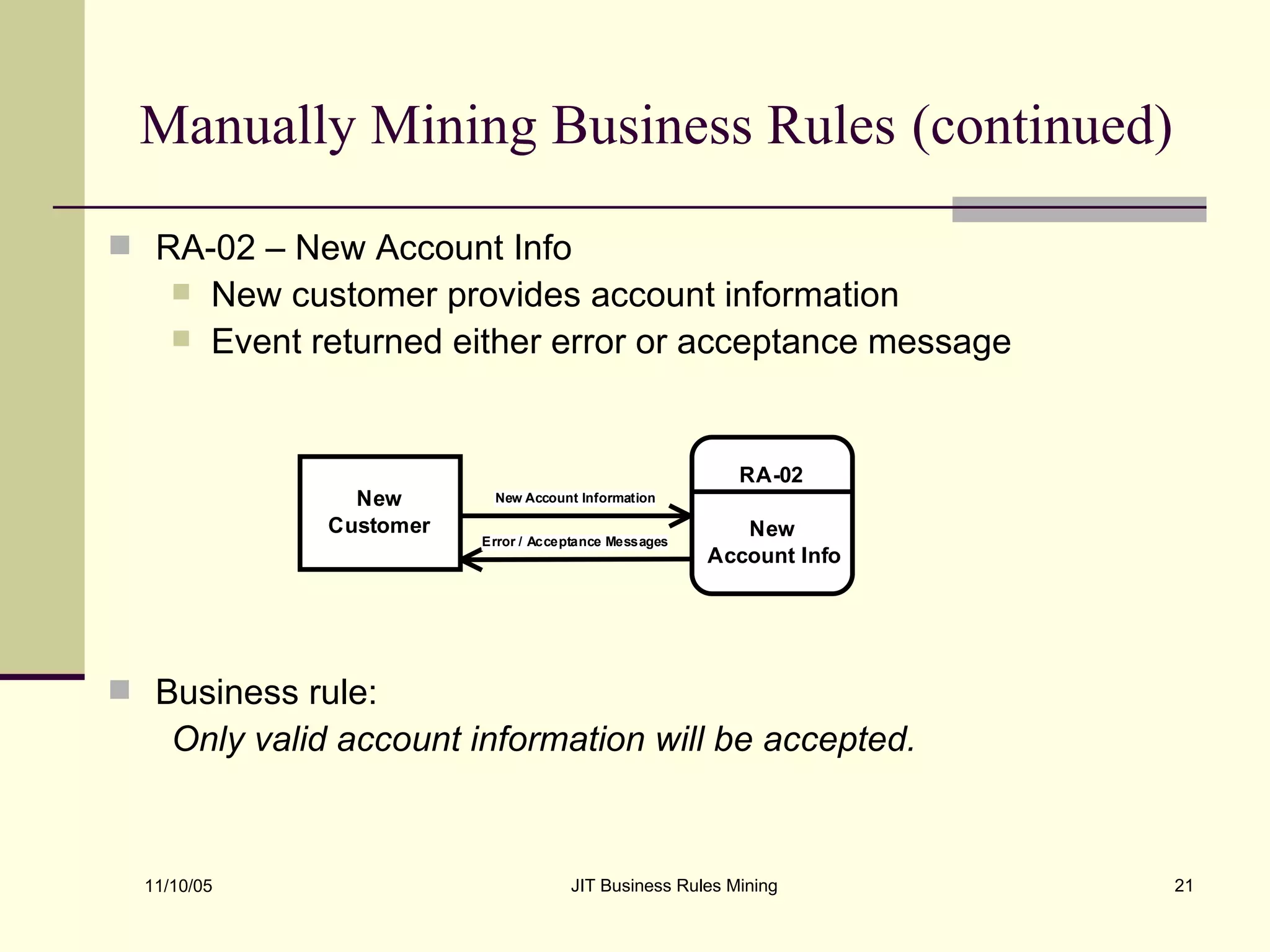
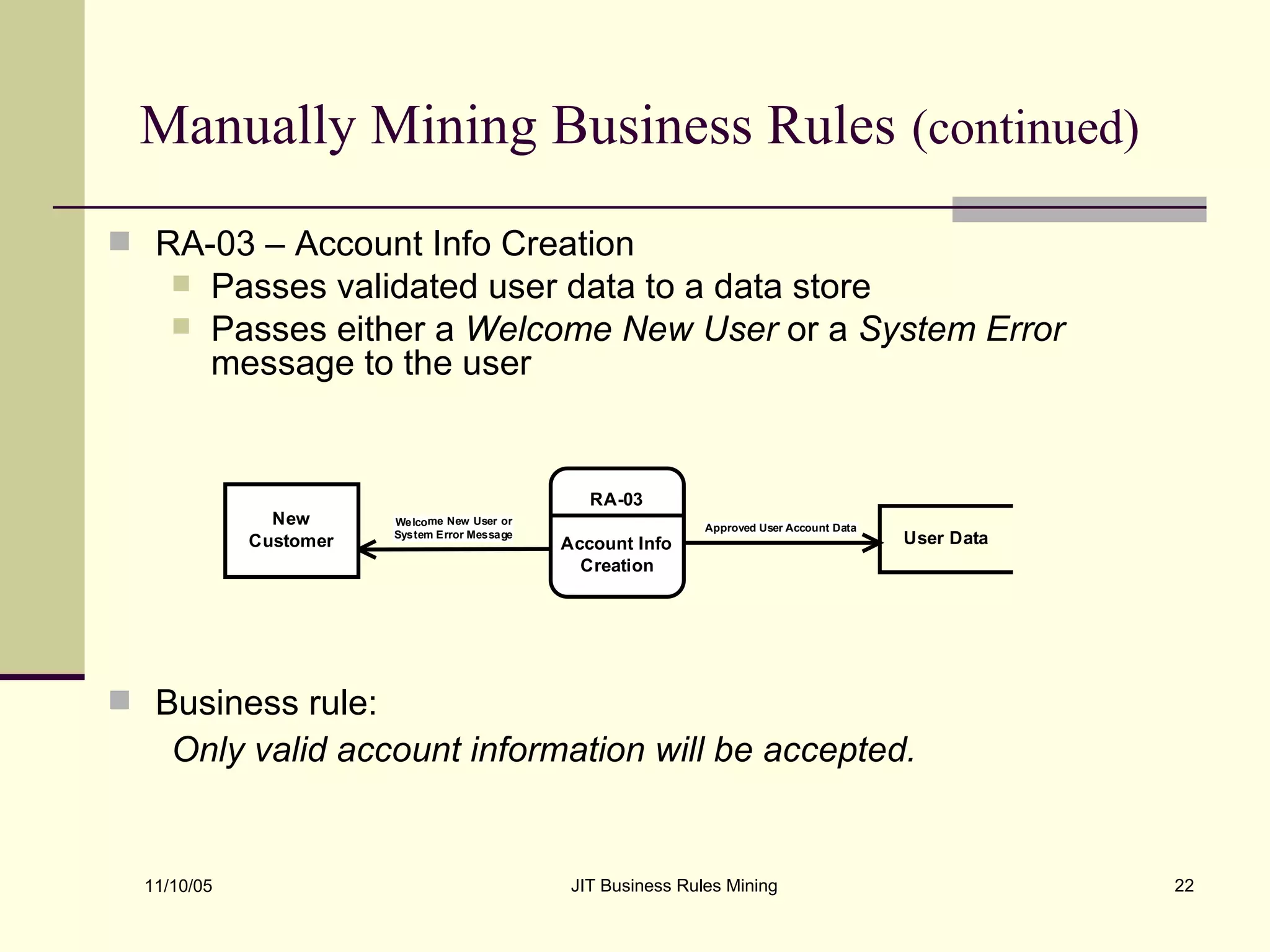
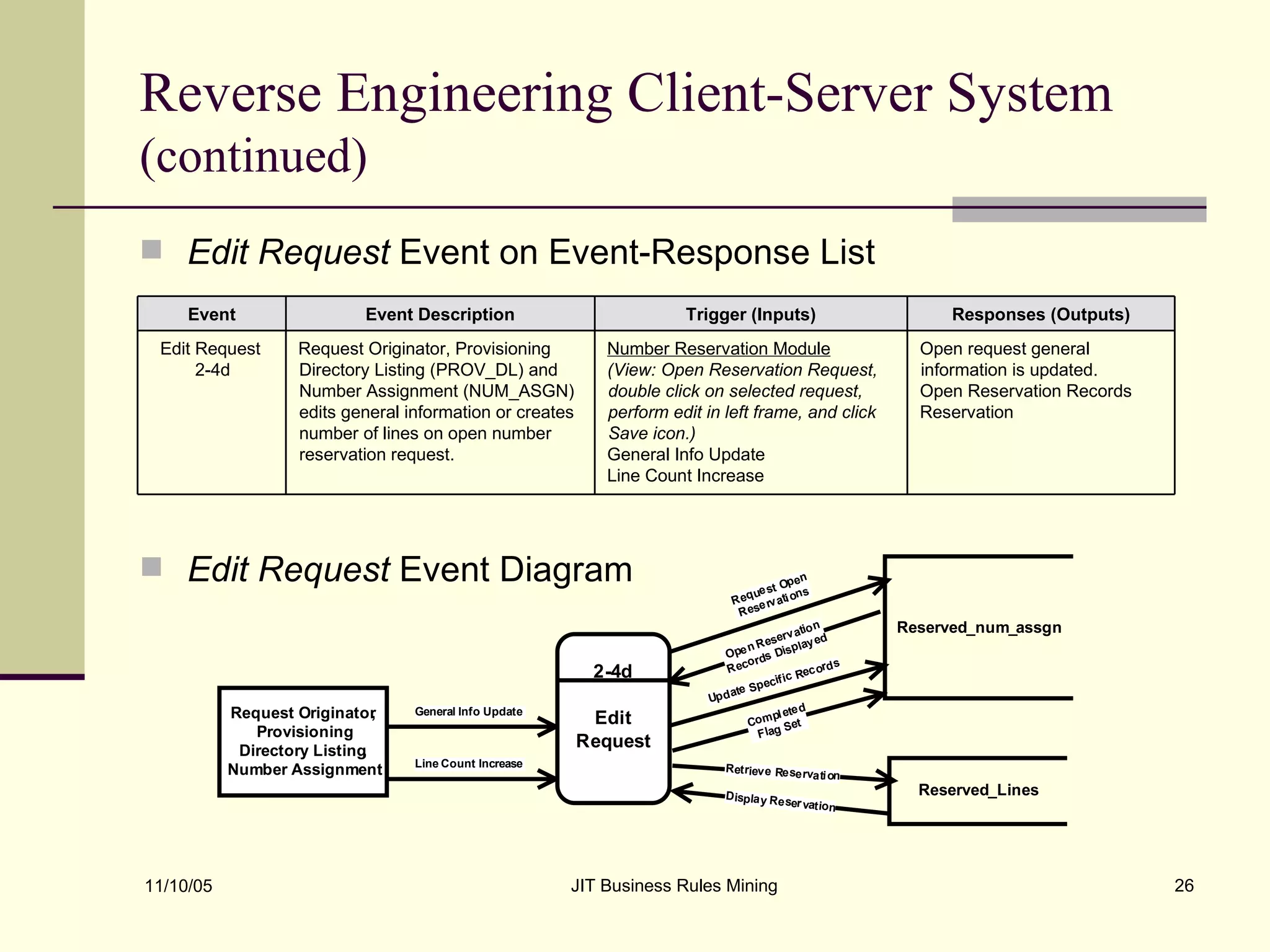
The document discusses Just-in-Time (JIT) business rules mining, emphasizing methods for extracting existing business rules in situations where documentation is lacking. It details a step-by-step process for reverse engineering applications, creating logical process models, event-response lists, and diagrams to derive and verify business rules. The approach includes practical examples of analyzing e-commerce systems and SQL stored procedures to facilitate better understanding and maintenance of software applications.