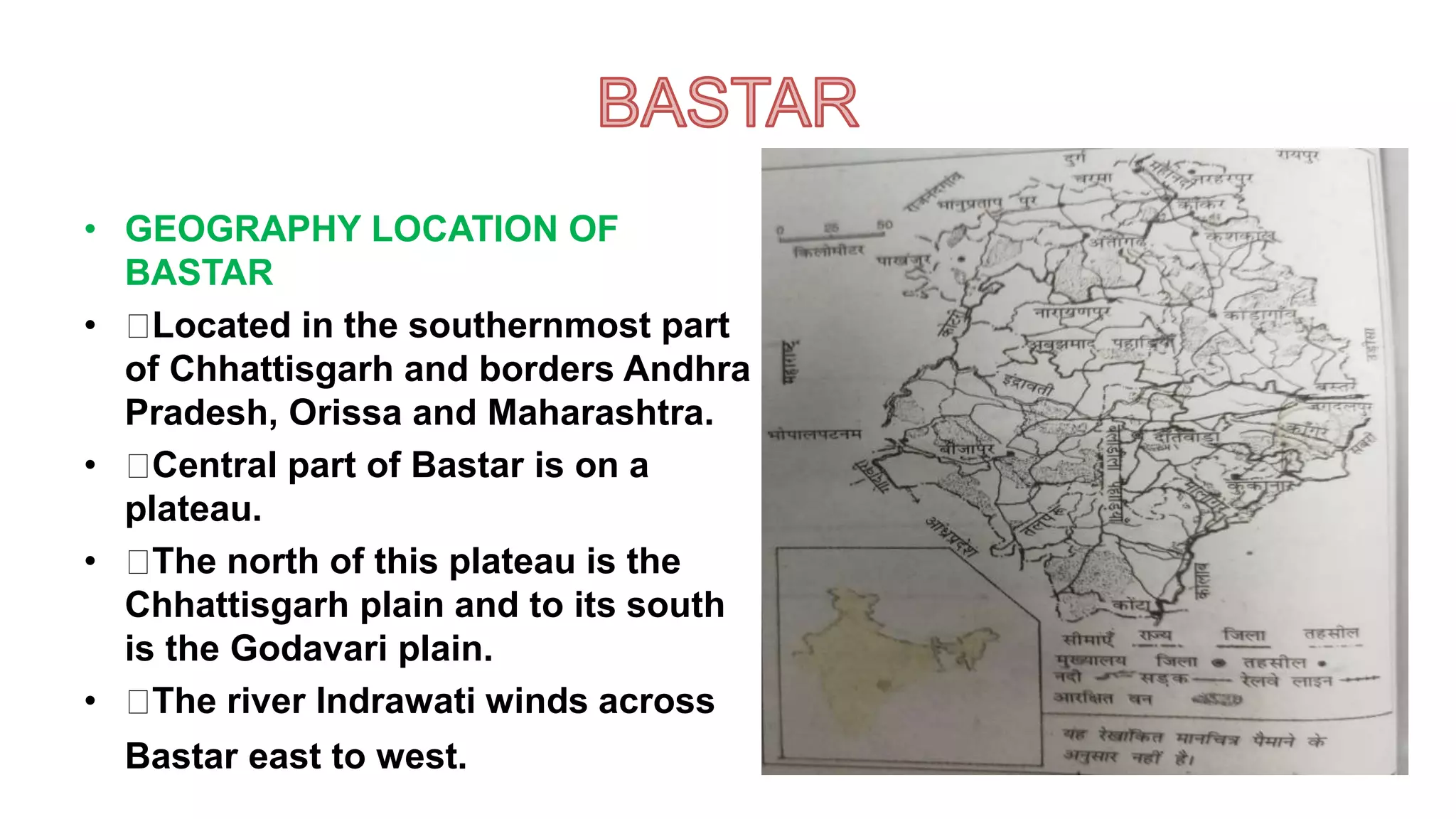
This document provides an overview of the history of deforestation under colonial rule in India and Indonesia. It discusses how the British and Dutch directly encouraged deforestation to produce commercial crops and meet demand for timber. This led to the systematic clearing of natural forests and displacement of local communities. It also describes the development of scientific forestry and protests by communities affected by new forest laws and restrictions on access.