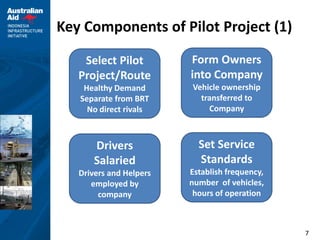
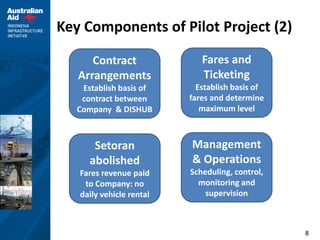
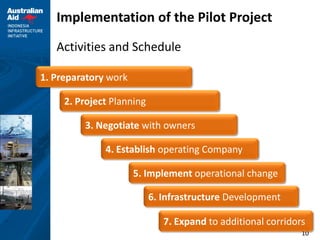
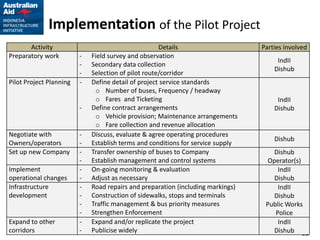
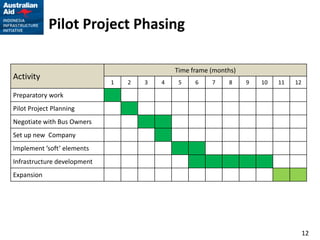
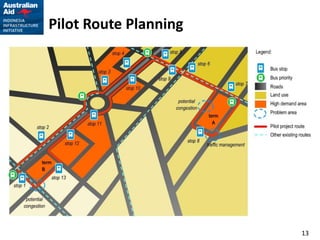
This document outlines plans for a pilot project to improve non-BRT bus services in a certain corridor. The objectives are to complement BRT, reduce private car usage, improve operational efficiency, and provide better passenger service. The recommended approach is to keep services in the private sector but reform operations through a pilot project. The pilot project would implement reforms in four key areas - institutional arrangements, operations, finances, and physical infrastructure. It would establish service standards, contract arrangements, fares and ticketing for a selected pilot route not served by BRT. The implementation strategy and activities over a 12-month period are also described.