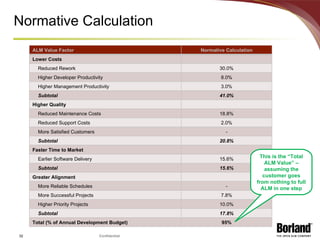
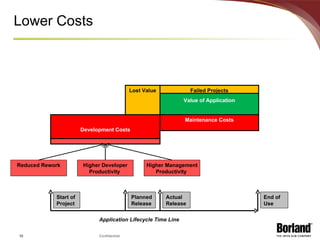
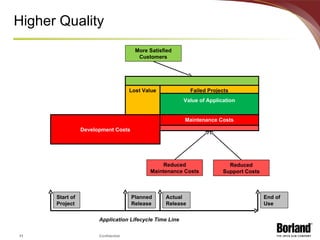
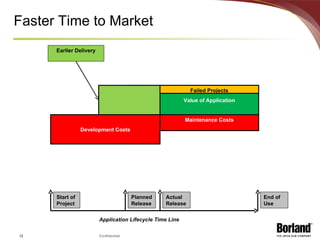
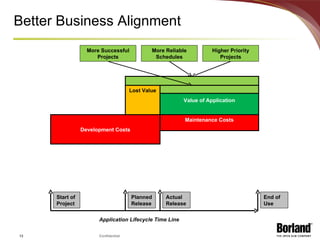
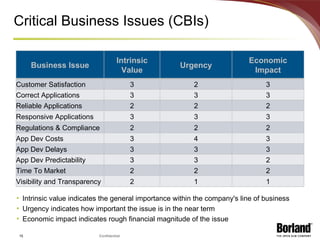
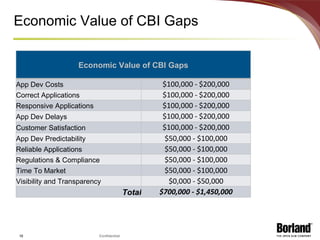
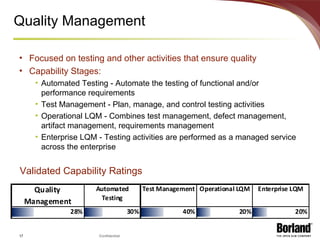
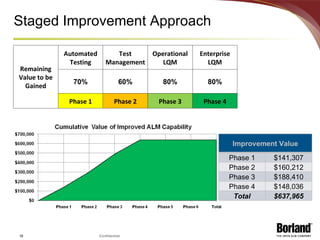
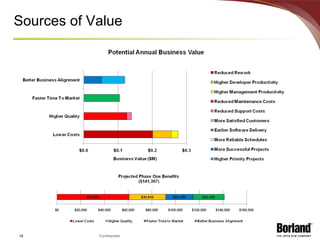
The document discusses profiling the economic value of improving lifecycle quality management (LQM) in a financial organization. It provides an example LQM profile for a sample company that analyzes the company's critical business issues, assesses the potential economic value of improving LQM capabilities, and outlines a staged approach to improvement. The total potential value of improving LQM capabilities across four phases is estimated to be $637,965.








![Thank You David A. Reo Consulting Services Manager Spain, Portugal & Italy C/ Ribera del Loira, 46 28042 – MADRID (Spain) t +34 915 030 632 m +34 659 756 165 f +34 946 773 729 [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9-borland-090314103950-phpapp02/85/9-Borland-Solo-Pruebas-2009-25-320.jpg)