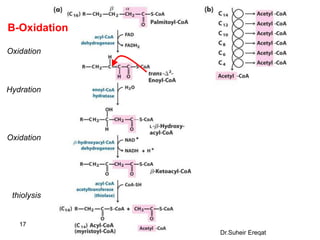
Fatty acid catabolism, or beta-oxidation, provides the greatest fraction of fuel for most organisms and organs. Fat sources include ingested fat, stores in adipose tissue, and fat synthesized in the liver from carbohydrates. Fat digestion produces lipoproteins called chylomicrons that transport triglycerides through the lymphatic system and bloodstream to tissues. Hormones trigger the mobilization of stored triglycerides, producing glycerol and fatty acids. Fatty acids undergo beta-oxidation in the mitochondria, producing acetyl-CoA which enters the citric acid cycle to generate ATP. Ketone bodies are produced when acetyl-CoA levels exceed the citric acid













![Two of the enzymes of oxidation are also regulated by metabolites that
signal energy sufficiency.
When the [NADH]/[NAD] ratio is high, acyl- CoA dehydrogenase is
inhibited
in addition, high concentrations of acetyl-CoA inhibit thiolase
Regulation of B-oxidation
[malonyl-CoA] ( the first intermediate in the cytosolic
biosynthesis of long-chain fatty acids from acetyl-CoA) inhibition of
CAT I to ensure that the oxidation of fatty acids is inhibited
whenever the liver is amply supplied with glucose as fuel and
is actively making triacylglycerols from excess glucose.
Dr.Suheir Ereqat](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/efsikzasrfyhsj7rhmhf-8-fatty-acid-oxidation-2021-240212153136-08feed30/85/8-Fatty_Acid_oxidation_2021-pdf-15-320.jpg)





