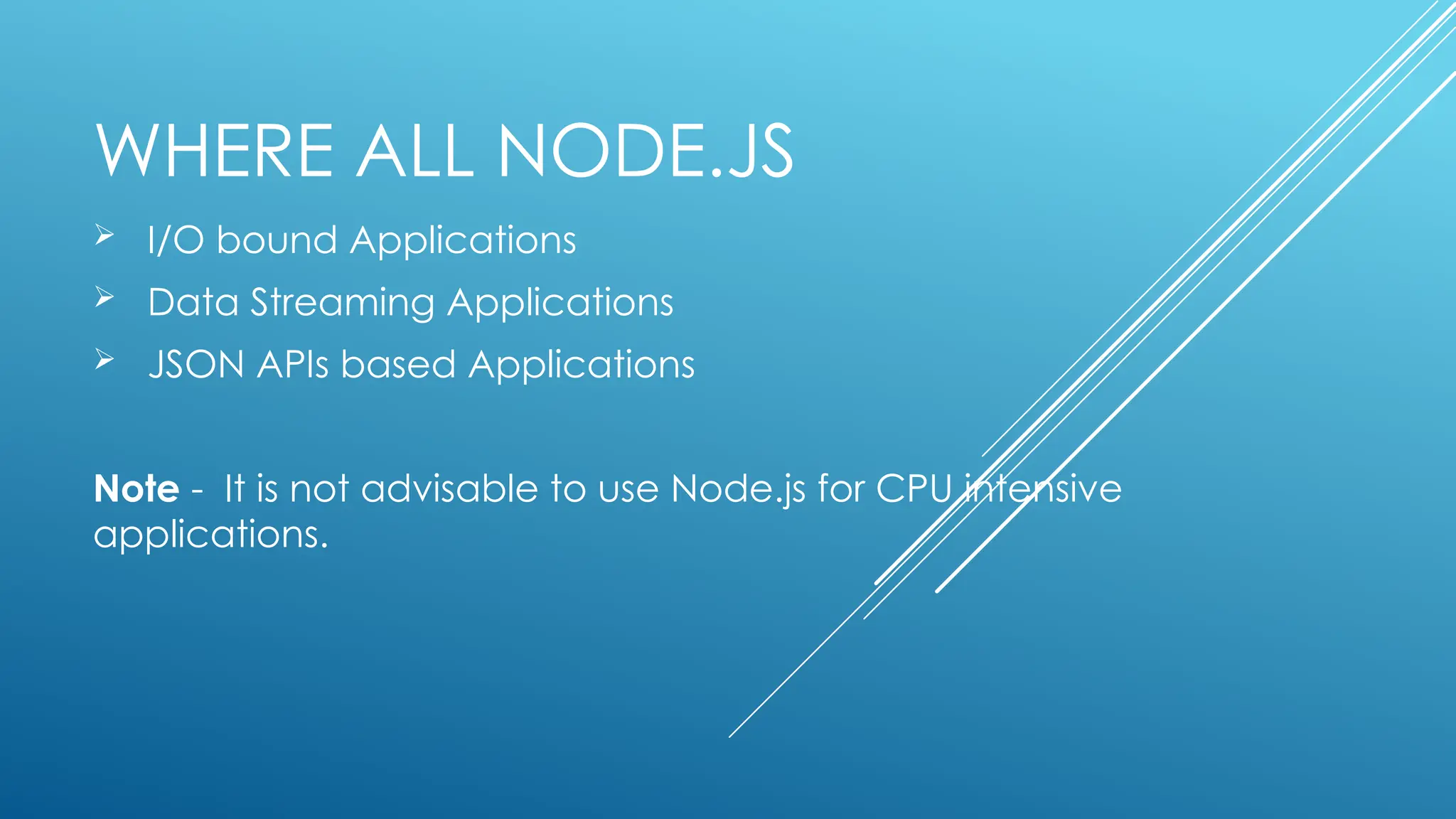
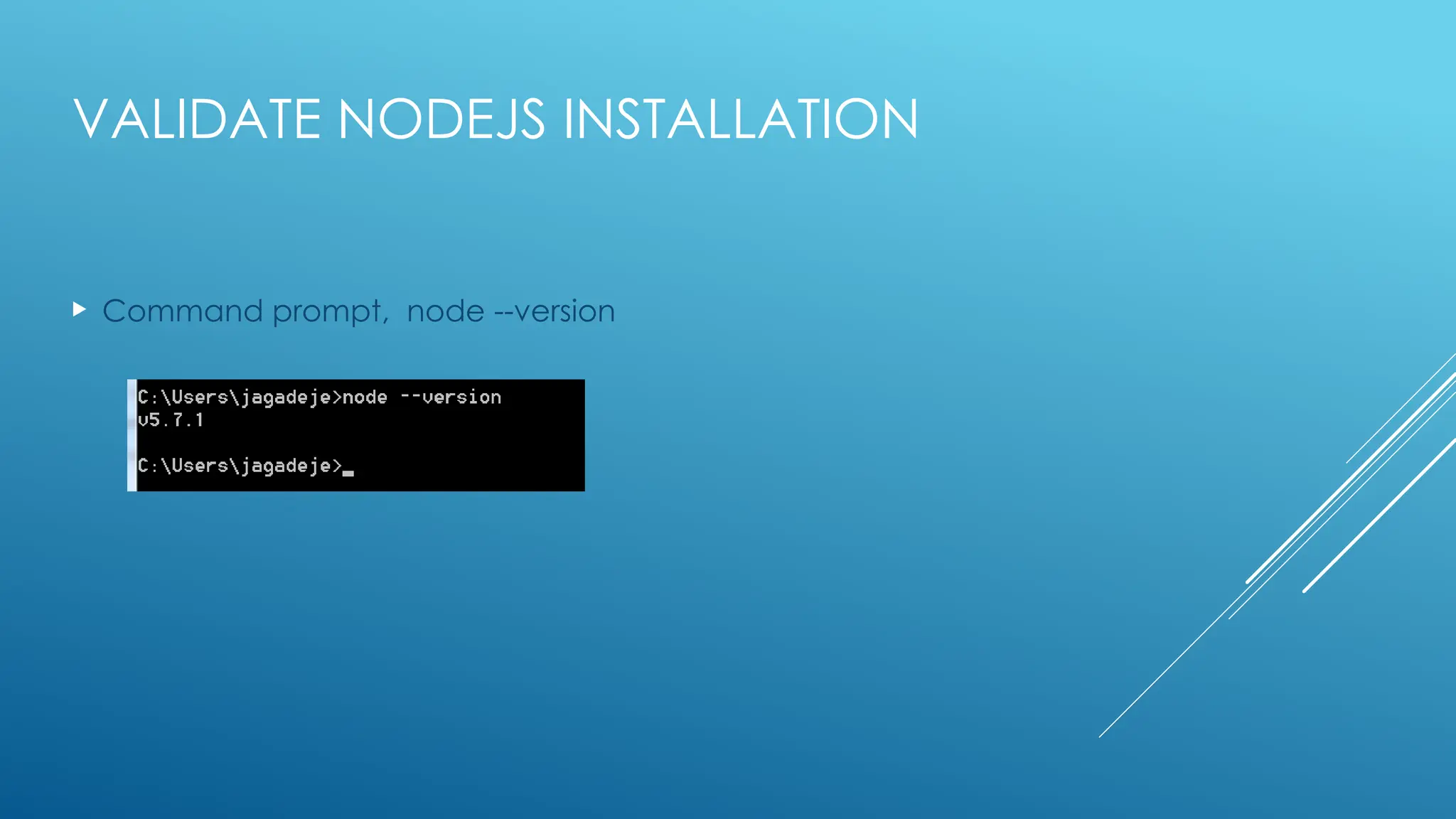
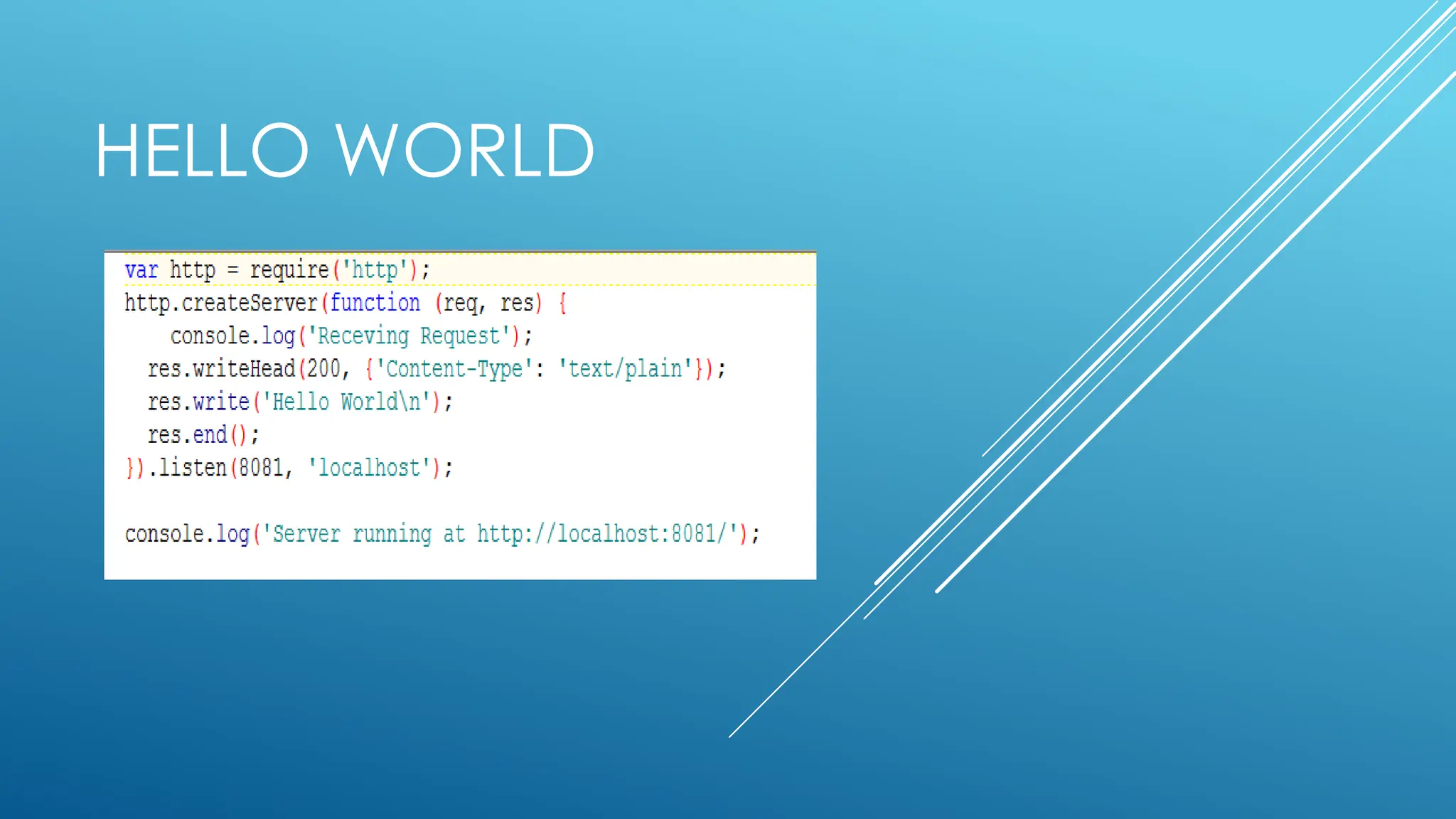
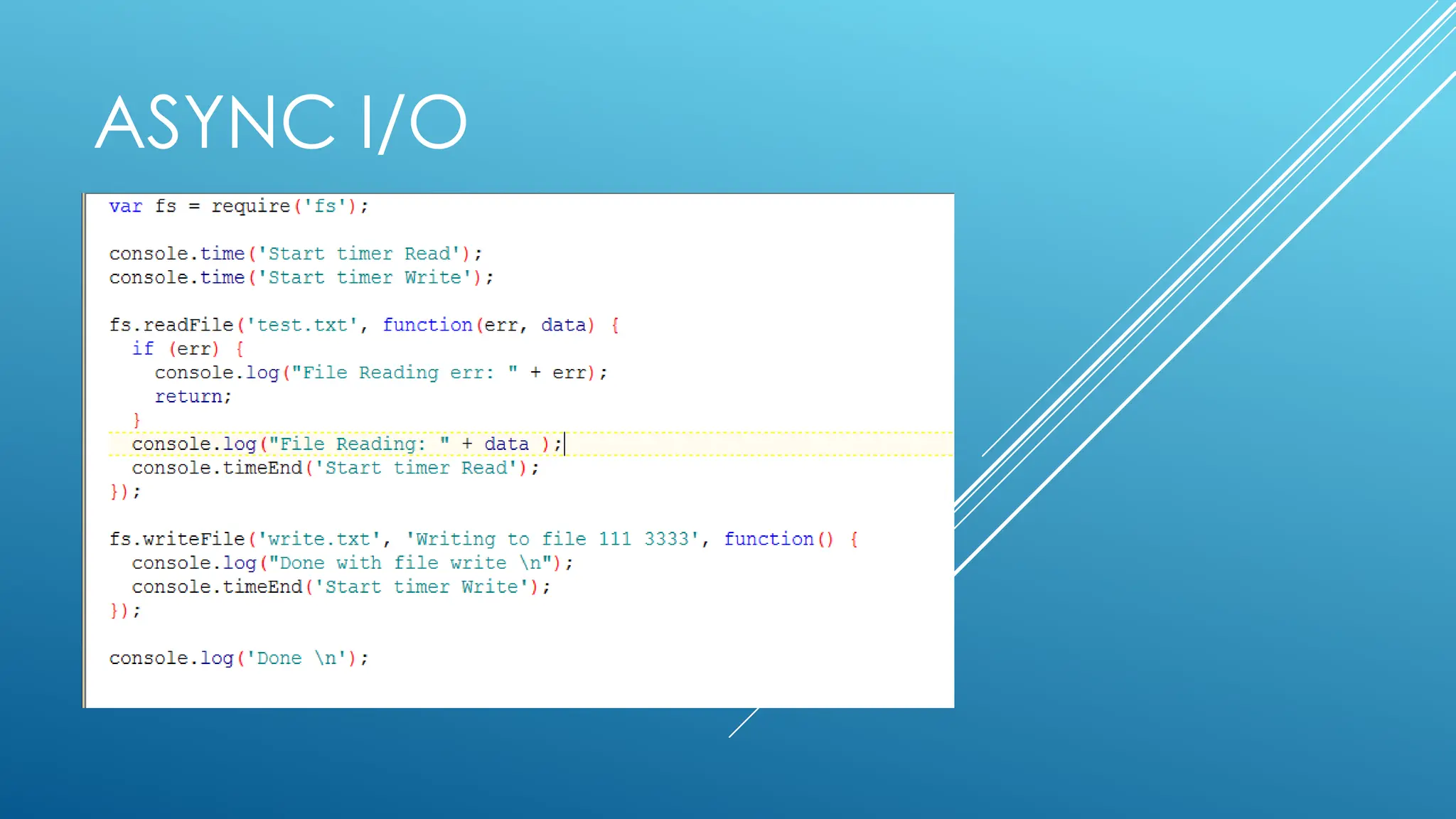
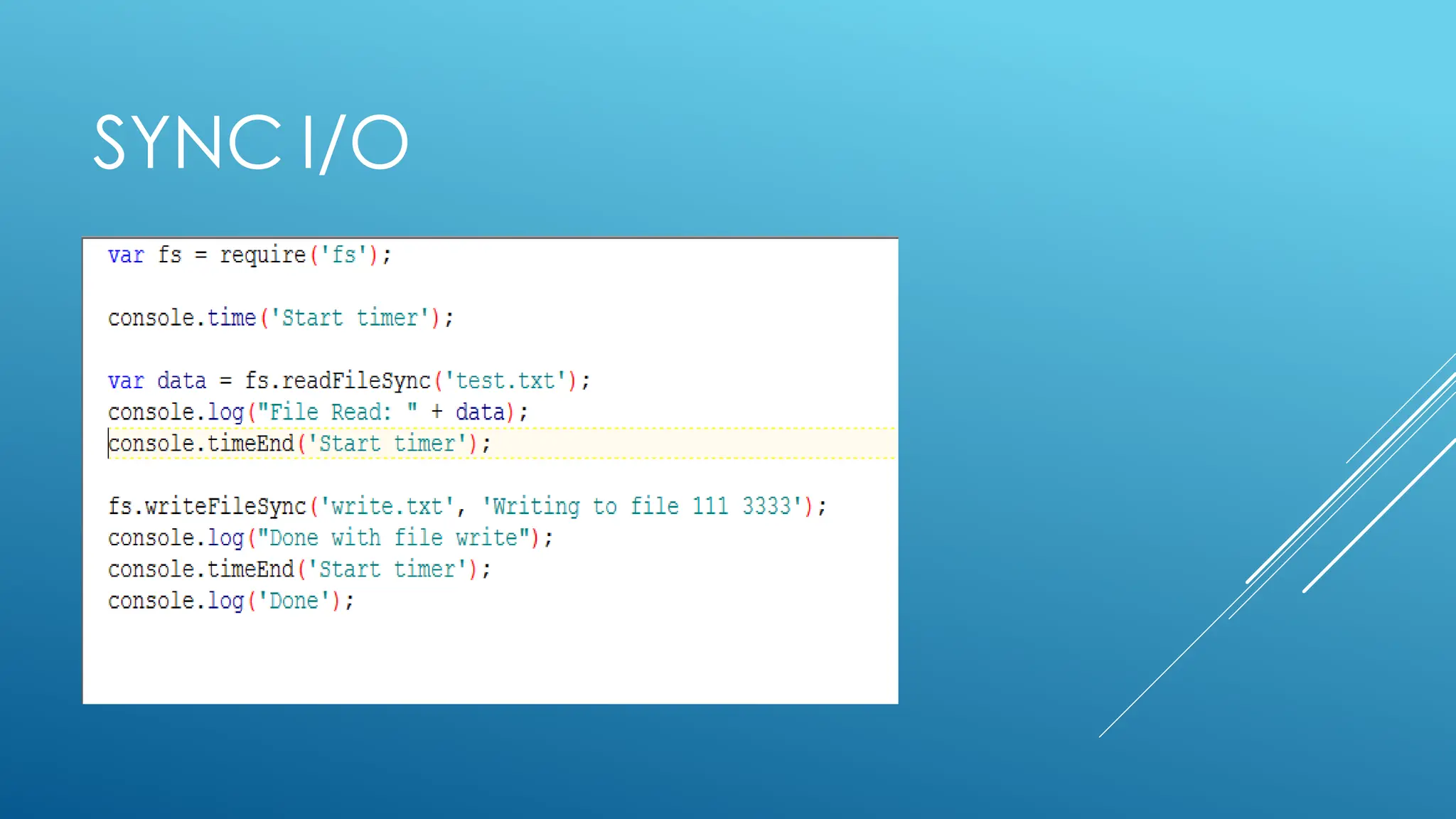
The document provides an introduction to Node.js, its installation process, and basic usage examples. It highlights Node.js as a lightweight, event-driven JavaScript runtime ideal for I/O bound applications and JSON APIs but not suited for CPU-intensive tasks. Additionally, it explains how to manage packages with npm and demonstrates module import/export functionalities.