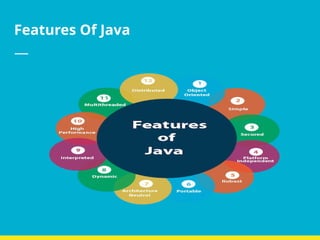
The document discusses the key characteristics of the Java programming language, describing it as simple, object-oriented, distributed, and secure, among other features. Java's design allows for portability across different computer architectures and is intended for networked environments, emphasizing robust security measures. The text highlights Java's multi-threading capabilities and dynamic nature, making it suitable for a variety of applications, particularly in web development.