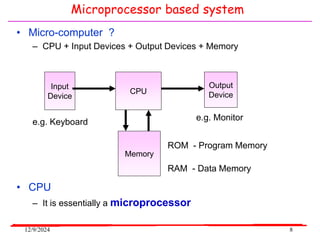
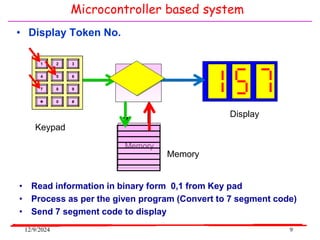
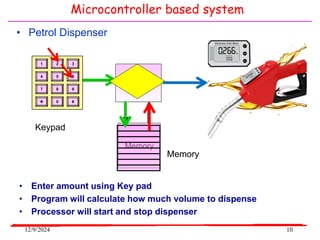
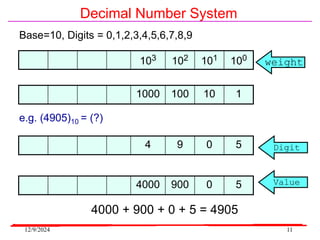
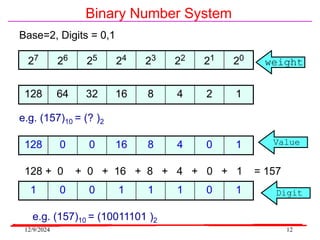
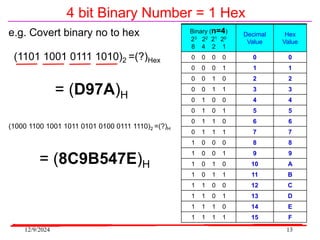
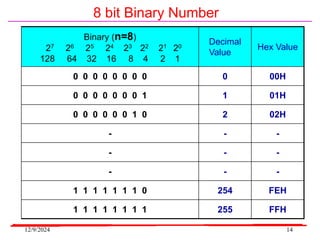
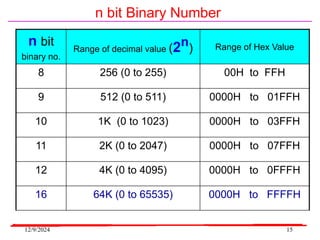
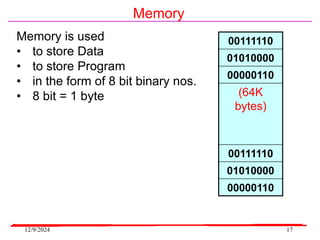
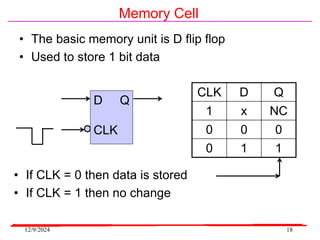
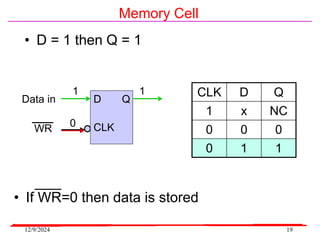
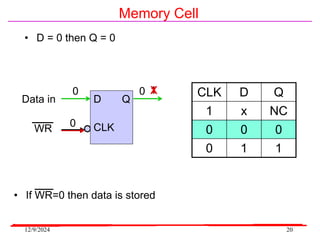
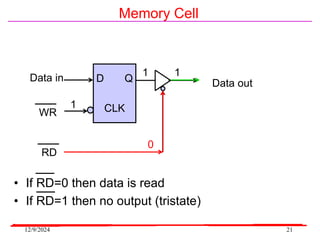
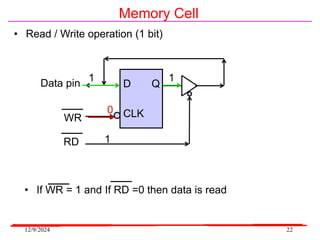
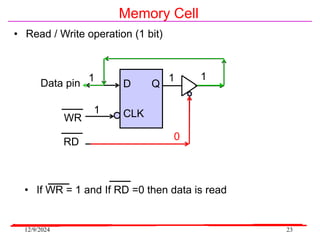
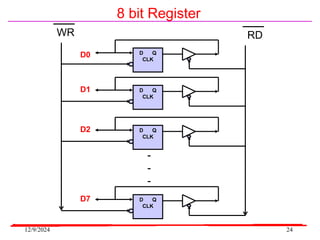
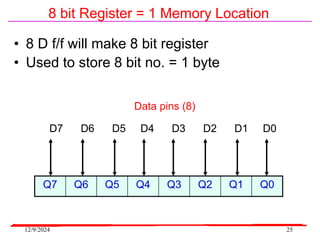
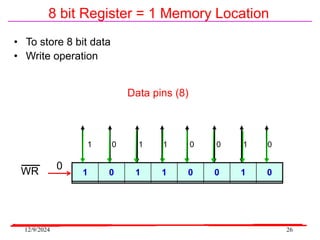
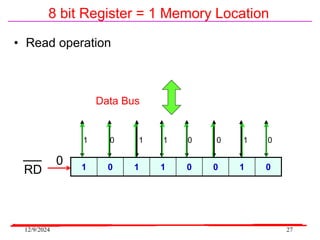
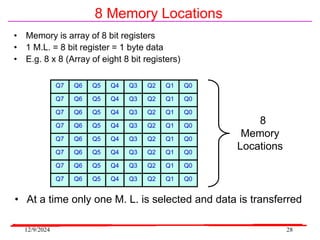
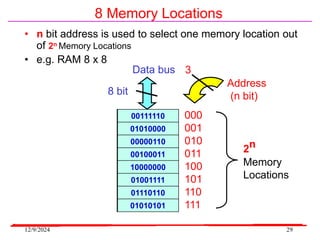
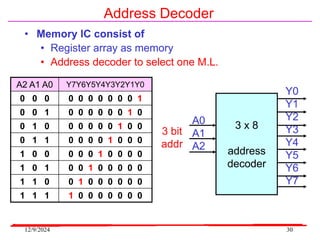
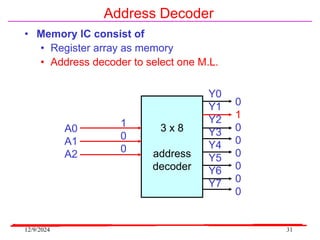
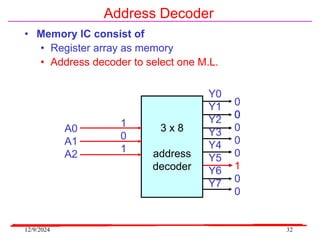
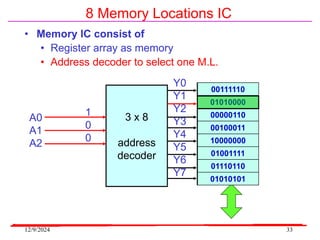
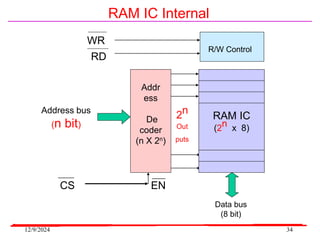
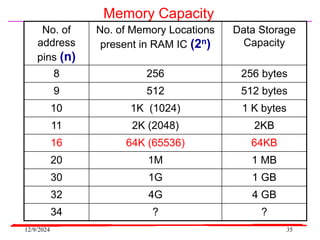
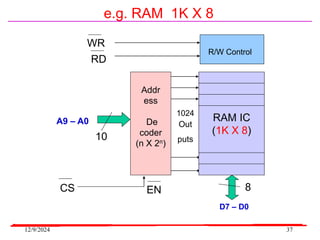
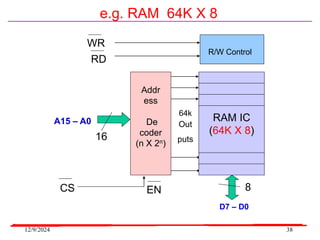
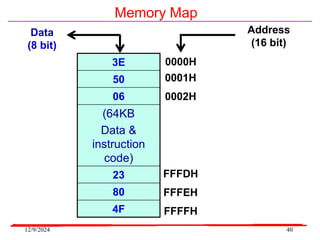
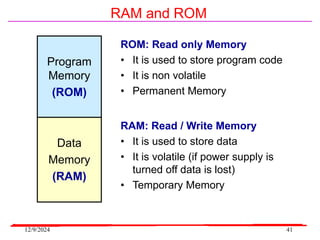
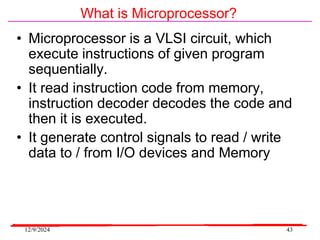
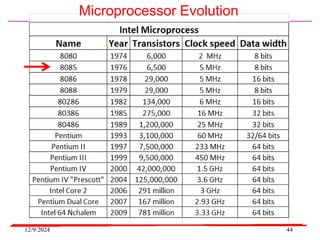
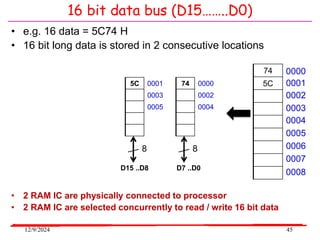
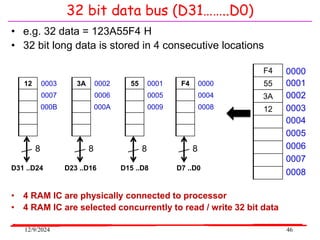
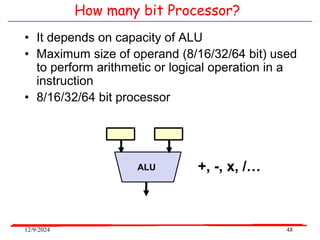
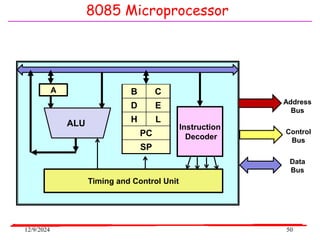
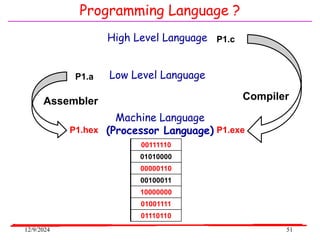
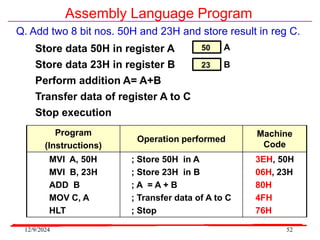
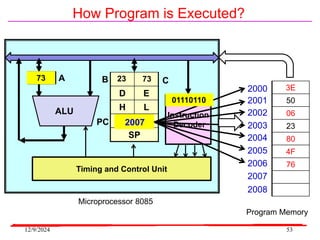
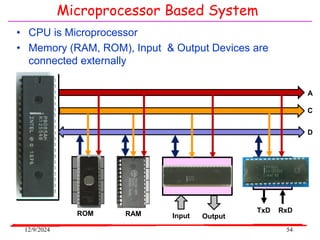
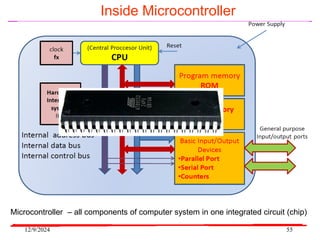
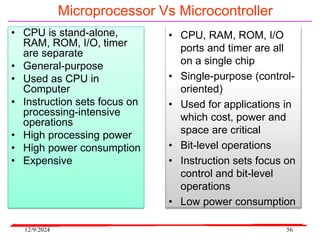
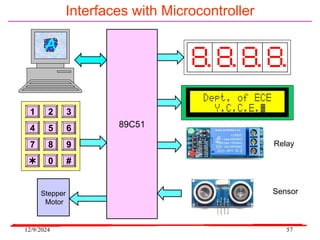
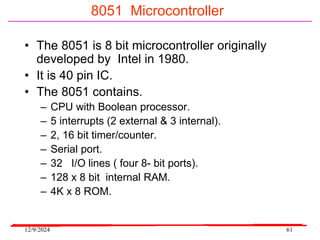
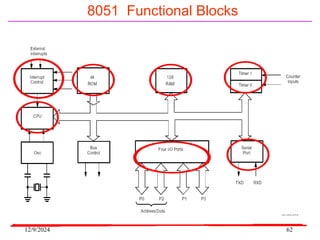
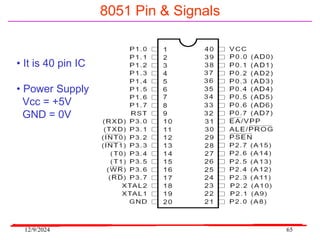
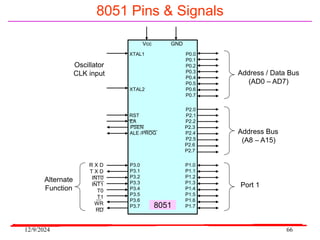
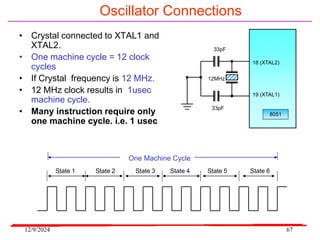
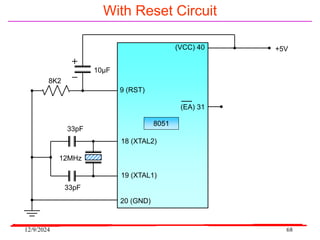
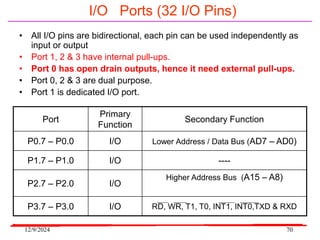
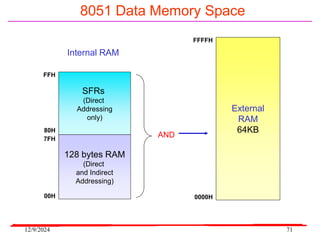
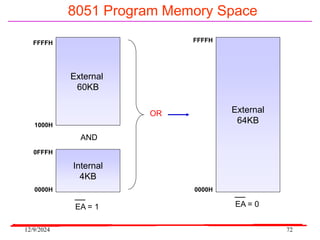
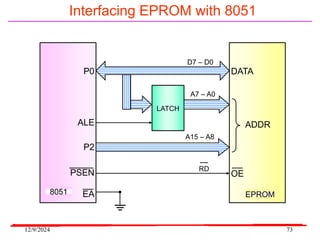
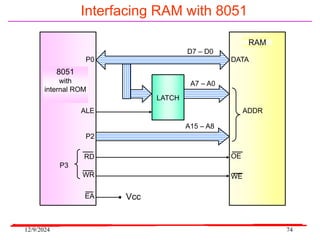
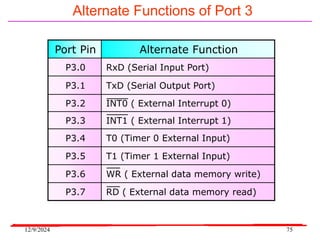
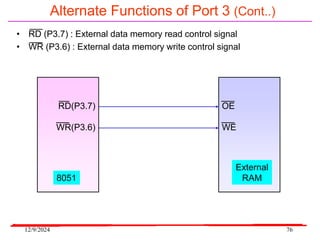
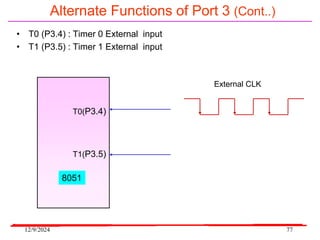
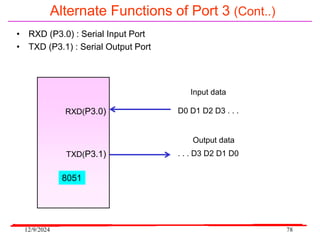
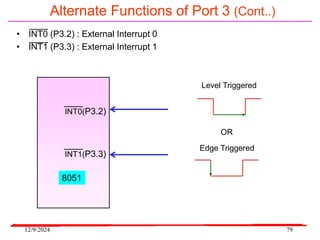
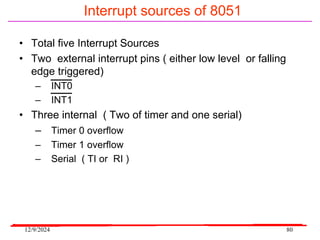
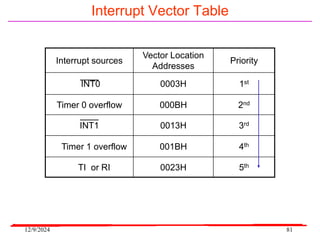
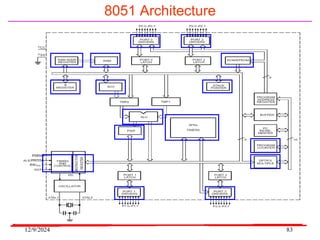
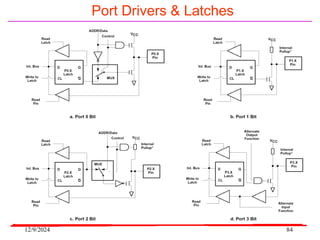
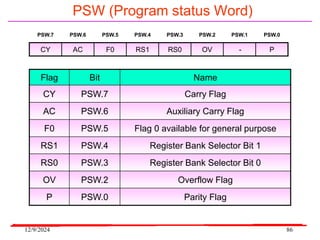
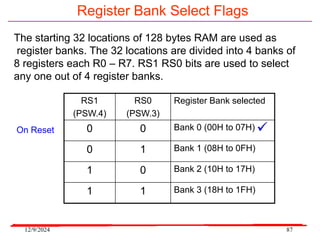
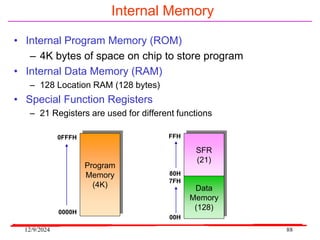
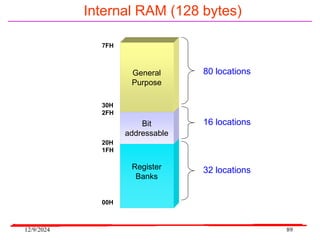
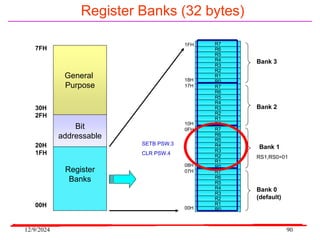
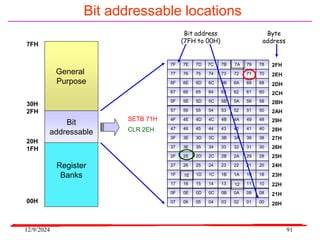
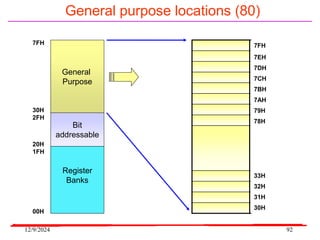
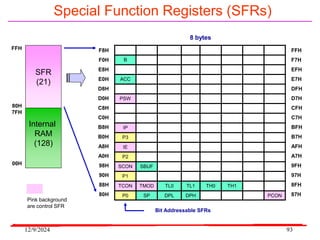
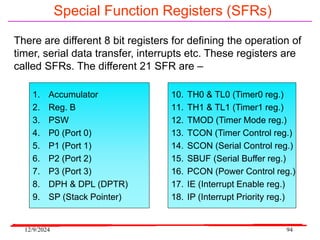
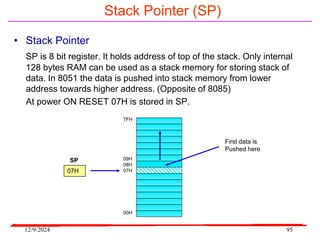
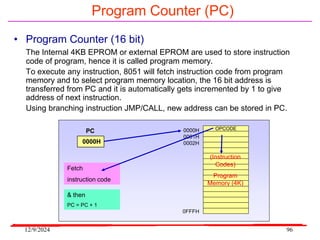
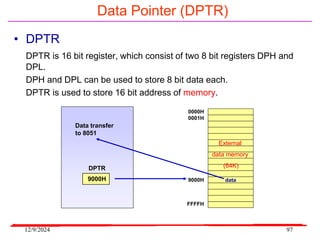
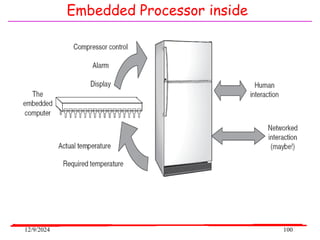
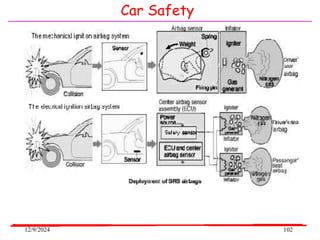
The document provides an overview of microcontrollers, specifically focusing on the 8051 microcontroller, its architecture, and applications in various devices such as mobile phones and automated systems. It covers topics including instruction sets, programming, memory types (RAM and ROM), and interfacing with components like LEDs and keypads. The document serves as a comprehensive guide for understanding the fundamental concepts related to microcontrollers and their functionalities.