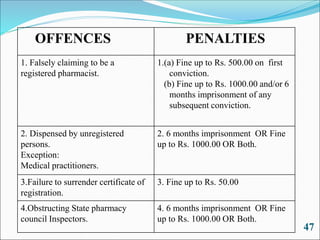
The Pharmacy Act of 1948 was enacted to regulate the profession of pharmacy in India by establishing the Pharmacy Council of India and State Pharmacy Councils. The objectives of the Act were to raise the standards of pharmacy education and practice. It provides for the registration of pharmacists, defines minimum qualifications, and establishes regulations regarding pharmacy education. The Act also outlines offenses and penalties for violations to protect public health.