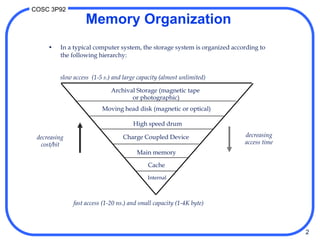
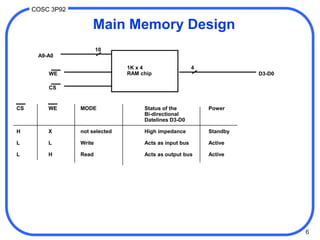
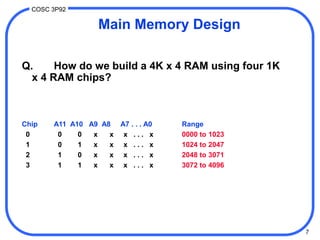
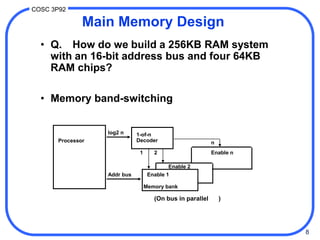
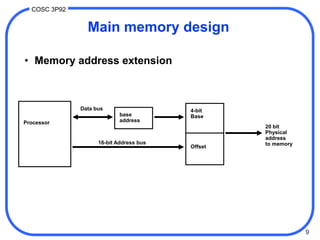
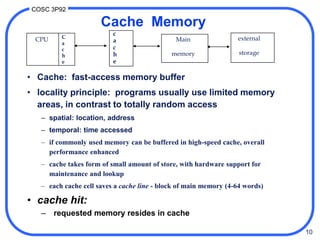
1. Computer memory is organized in a hierarchy from fast but small cache memory to slower but larger archival storage. Cache memory uses the locality principle to improve performance by keeping frequently used data close to the CPU.
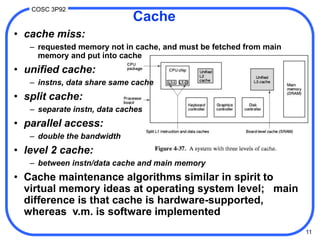
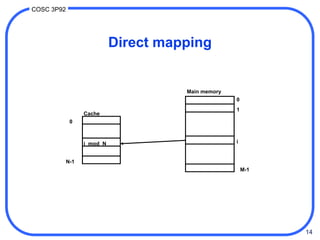
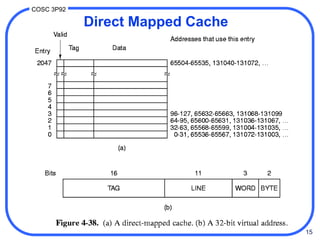
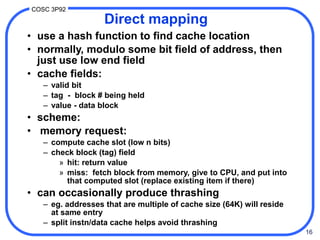
2. There are different techniques for mapping memory addresses to cache locations including direct mapping, set associative mapping, and fully associative mapping. Direct mapping uses the low-order address bits to determine the cache slot while set associative mapping distributes blocks across multiple slots in a set.
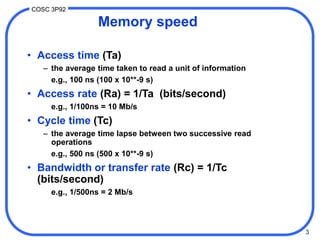
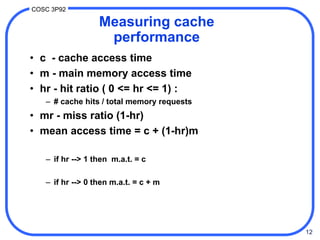
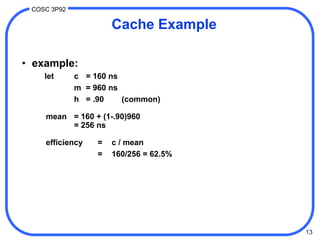
3. Cache performance is measured by hit ratio, miss ratio, and mean access time. With a high hit ratio, the mean access time approaches the fast cache access time. Cache maintenance policies like write-back and

![19
COSC 3P92
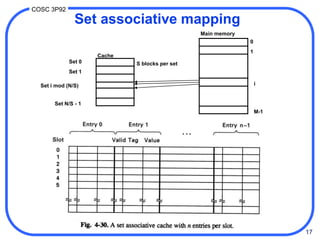
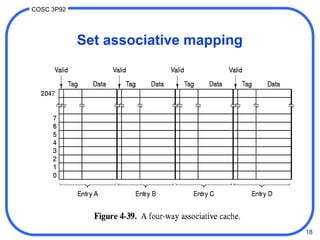
Set associative mapping
• [4.39]
• use same hash function as direct mapping, except
that each cache slot holds multiple data blocks
– usually max. 4 blocks (“4-way”)
• searching blocks in a slot done associatively:
simultaneous pattern matching
• more flexible than direct: multiple blocks in set
• use smaller tag than associative, therefore
cheaper to implement associative matching
• commonly used in larger systems (VAX 11-780)
• which line should be replaced when slot full?
– eg. LRU (least recently used)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7memcache-230507141907-ba60b9ba/85/7_mem_cache-ppt-19-320.jpg)



