This document summarizes discriminative models and linear discriminant functions for classification problems in machine learning. It discusses:
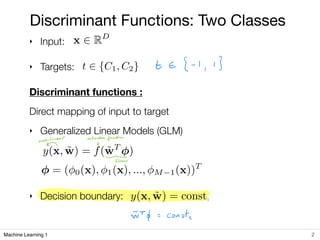
1) Discriminant functions that directly map inputs to targets using a linear model to determine decision boundaries between classes.
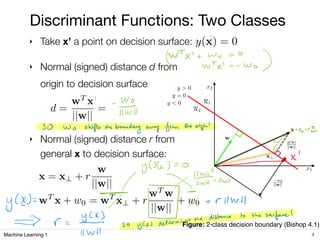
2) For two-class classification, the linear discriminant function determines a decision boundary that separates the space into two regions based on the sign of the function output.
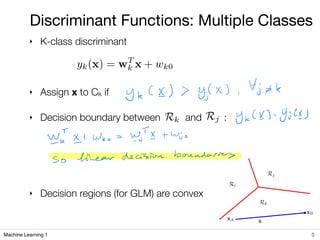
3) For multi-class classification, data points are assigned to the class whose discriminant function outputs the highest value, and decision boundaries are determined by where two discriminant function outputs are equal.