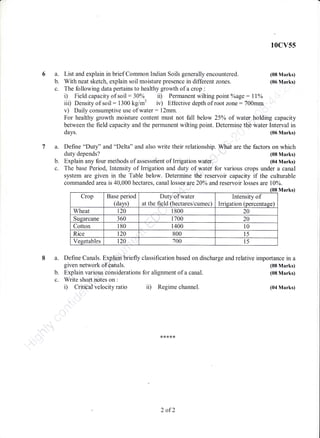
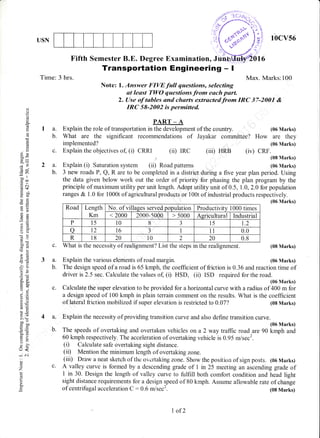
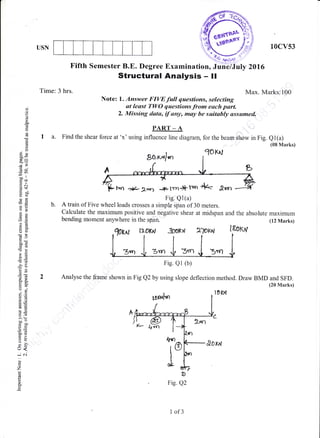
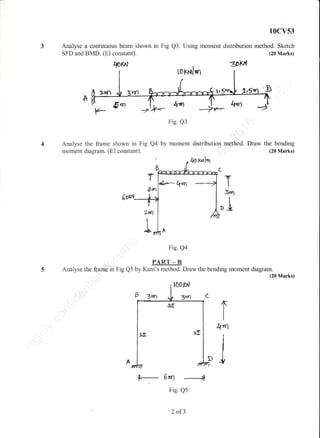
This document appears to be an exam paper containing multiple choice and long answer questions related to management, entrepreneurship, small scale industries, project management, and structural design of reinforced concrete elements.
Some of the long answer questions ask students to:
- Define management and discuss levels of management
- Explain planning and types of plans with examples
- Discuss steps in selection procedures and sources of recruitment for organizations
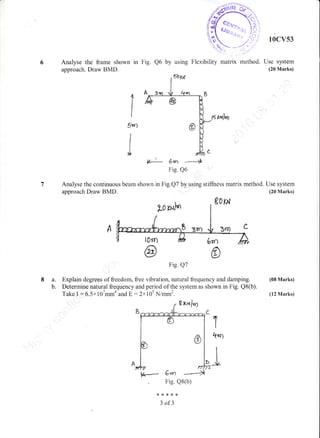
- Design structural elements like beams, slabs, columns, and footings.
The document contains questions from two parts - Part A and Part B. Questions range from design to theoretical concepts in management, entrepreneurship, and structural engineering.