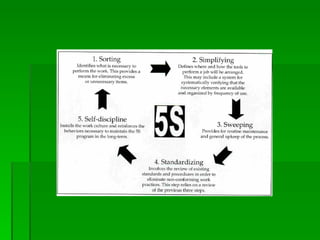
This document discusses 5S, a Japanese methodology for organizing and standardizing the workplace. It consists of five steps: sort, set in order, shine, standardize, and sustain. The document outlines each of the 5S steps and how to implement 5S through clear objectives, communication, training, and regular updates. It explains that 5S improves efficiency, reduces waste, enhances safety, and promotes continuous improvement and a competitive advantage for organizations.